German torpedo boat Greif
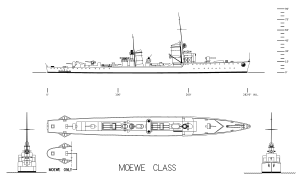 Right elevation and plan of the Type 23
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | Greif |
| Namesake | Griffin |
| Builder | Reichsmarinewerft Wilhelmshaven |
| Yard number | 104 |
| Laid down | 5 October 1925 |
| Launched | 15 July 1926 |
| Commissioned | 15 July 1927 |
| Fate | Sunk, 23 May 1944 |
| General characteristics (as built) | |
| Class and type | Type 23 torpedo boat |
| Displacement | |
| Length | 87.7 m (287 ft 9 in) (o/a) |
| Beam | 8.25 m (27 ft 1 in) |
| Draft | 3.65 m (12 ft) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | 2 × shafts; 2 × geared steam turbine sets |
| Speed | 32–34 knots (59–63 km/h; 37–39 mph) |
| Range | 1,800 nmi (3,300 km; 2,100 mi) at 17 knots (31 km/h; 20 mph) |
| Complement | 120 |
| Armament |
|
Greif was the third of six Type 23 torpedo boats built for the German Navy (initially called the Reichsmarine and then renamed as the Kriegsmarine in 1935). The boat made multiple non-intervention patrols during the Spanish Civil War in the late 1930s. During World War II, she played a minor role in the Norwegian Campaign of 1940 by transporting troops that captured Arendal. Greif spent the next couple of years escorting minelayers as they laid minefields and laying minefields herself. She also spent the latter half of 1941 escorting convoys through the Skagerrak. The boat had a lengthy refit that lasted all of 1942 and then spent March–April 1943 escorting ships in Norwegian waters before returning to France. While deployed there Greif laid numerous minefields and escorted U-boats through the Bay of Biscay. The boat was sunk by Allied aircraft in May 1944.
Design and armament[edit]
Derived from the World War I-era large torpedo boat SMS H145,[Note 1] the Type 23 torpedo boat was slightly larger, but had a similar armament and speed.[1] The Type 23s had an overall length of 87.7 meters (287 ft 9 in) and was 85.7 meters (281 ft 2 in) long at the waterline.[2] The ships had a beam of 8.25 meters (27 ft 1 in), and a mean draft of 3.65 meters (12 ft). They displaced 923 long tons (938 t) at standard load and 1,290 long tons (1,310 t) at deep load.[3] Greif was fitted with a pair of Vulcan geared steam turbine sets, each driving one propeller, that were designed to produce 23,000 shaft horsepower (17,000 kW) using steam from three water-tube boilers which would propel the ship at 33 knots (61 km/h; 38 mph).[4] The torpedo boats carried enough fuel oil to give them an intended range of 3,600 nautical miles (6,700 km; 4,100 mi) at 17 knots (31 km/h; 20 mph),[1] but it proved to be only 1,800 nmi (3,300 km; 2,100 mi) at that speed in service. Their crew consisted of 4 officers and 116 sailors.[3]
As built, the Type 23s mounted three 10.5 cm (4.1 in) SK L/45[Note 2] guns, one forward and two aft of the superstructure; the aft superfiring gun was on an open mount while the others were protected by gun shields.[6] They carried six rotating 500-millimeter (19.7 in) torpedo tubes in two triple mounts amidships and could also carry up to 30 mines.[2] After 1931, the torpedo tubes were replaced by 533-millimeter (21 in) tubes and a pair of 2-centimeter (0.8 in) C/30[Note 3] anti-aircraft guns were added.[1][3] At least some of the ships were fitted with depth charges, but details are lacking.[8] During the war a quadruple 2 cm mount was added just forward of No. 2 gun, three 2 cm guns were positioned around the aft funnel and another pair were mounted on the bridge wings, all in single mounts. Around 1944 a FuMB 4 Sumatra radar detector was installed as was radar.[9]
Construction and career[edit]
Named after the griffin, the boat was laid down at the Reichsmarinewerft Wilhelmshaven (Navy Yard) on 5 October 1925[4] as yard number 104,[10] launched on 15 July 1926 and commissioned on 15 July 1927.[4] By the end of 1936 Greif was assigned to the 4th Torpedo Boat Flotilla and the boat made several deployments to Spain during the Spanish Civil War. Around June 1938, she was transferred to the newly formed 5th Torpedo Boat Flotilla.[11]
Second World War[edit]
Greif was used in the North Sea mining operations that began on 3 September 1939. Together with three destroyers and her sisters Albatros and Falke, Greif was tasked with anti-shipping patrols in the Kattegat and Skaggerak from 3 to 5 October that captured four ships.[12] During the Invasion of Norway in April 1940, the boat was assigned to Group 4 under Kapitän zur See (Captain) Friedrich Rieve on the light cruiser Karlsruhe. Unlike the rest of the group, she was tasked to capture the undefended port of Arendal to capture a telegraph cable to England. Greif was loaded with 90 soldiers from the 163rd Infantry Division and carried the flotilla commander to oversee the operation. After its successful conclusion, she was ordered to rejoin the main force at Kristiansand. The group departed Wesermünde on the morning of 8 April and arrived off Kristiansand and Arendal the following morning, delayed by heavy fog.[13]
The torpedo boat entered Arendal harbor around 08:30 and offloaded her troops peacefully, not noticing the 2.-class torpedo boat HNoMS Jo which was anchored with her bow towards the land. The boat's captain, Løytnant (Lieutenant) Thore Holthe, was out of contact with his superiors and lacked orders to attack any intruders and did nothing to attract attention because he would have to cast off and turn around in order to fire his torpedoes. Greif did not notice the Norwegian boat and left shortly after 09:00 arriving at Kristiansand around 11:40.[14]
Rieve was under orders to return to Kiel, Germany, as soon as possible, so Karlsruhe sailed at 18:00, escorted by Greif, her sister Seeadler, and the torpedo boat Luchs. At 18:58, one torpedo from the British submarine Truant struck the cruiser amidships, knocking out all power, steering and the pumps. Luchs evaded the other nine torpedoes and followed them to their origin and began depth charging the submarine for the next several hours, joined by the other two torpedo boats. Truant was damaged, but survived their attacks. Rieve ordered his crew aboard the torpedo boats and sent Seeadler and Luchs ahead while he remained with Greif to finish off Karlsruhe with a pair of torpedoes. After the heavy cruiser Lützow had been crippled by a British submarine off the Danish coast on 11 April, Seeadler, Greif and Luchs, among other ships, arrived the following morning to render assistance.[15]
On 18 April, Greif and her sisters Möwe, Seeadler, and the torpedo boat Wolf escorted minelayers as they laid anti-submarine minefields in the Kattegat. From 21 to 23 June, Greif was one of the escorts for the badly damaged battleship Scharnhorst from Norway to Kiel. The 5th Flotilla, consisting of Greif, her sisters Falke, Kondor, and the torpedo boats Iltis, Jaguar, T2, and T3 escorted minelayers as they laid a minefield in the southwestern North Sea on 14–15 August. The flotilla escorted other minelaying missions in the same area on 31 August – 2 September and 6–7 September. Reinforced by Wolf, the flotilla made an unsuccessful sortie off the Isle of Wight on 8–9 October. They made a second, more successful, sortie on 11–12 October, sinking two Free French submarine chasers and two British trawlers. The 5th Flotilla was transferred to St. Nazaire later that month and its ships laid a minefield off Dover on 3–4 December and another one in the Channel on 21–22 December.[16]
1941–1944[edit]
Greif was refitted in Rotterdam, Netherlands, from April to May 1941. She was transferred afterwards to the Skagerrak where she was on convoy escort duties. The boat was again refitted from December 1941 to December 1942 and spent the next several months working up. On 11 March 1943, Greif and Jaguar were among the escorts for the battleships Tirpitz and Scharnhorst as they moved from Trondheim, Norway, to Bogen Bay, and continued onward to Altafjord with Lützow and the light cruiser Nürnberg from 22 to 24 March. Greif, Jaguar, and the destroyer Z4 Richard Beitzen screened Nürnberg from Harstad to Trondheim and then to Kiel between 27 April and 3 May. On 3–7 May, Greif, Möwe, and Jaguar escorted minelayers in the North Sea as they laid new minefields. From 4 to 6 June, Greif, Möwe, Kondor, Falke and the torpedo boat T22 laid two minefields in the English Channel. Later that month the ships returned to the Bay of Biscay to help escort U-boats through the Bay and continue to do so into early August. Greif, Kondor and the torpedo boats T19, T26, and T27 laid a minefield in the English Channel on 29–30 September.[17]
The 4th and 5th Torpedo Boat Flotillas, consisting Greif, Möwe, Kondor, Jaguar, T27 and the torpedo boat T29 laid minefields of 180 mines, off Le Havre and Fécamp, France, on 21 and 22 March 1944. On 17–19 April, the 5th Torpedo Boat Flotilla, including Greif, Möwe and Kondor sailed from Brest, France, to Cherbourg as distant cover for a convoy. A few days later, the flotilla laid a minefield on the night of 21/22 April. The following night the torpedo boats engaged British motor torpedo boats near Cape Barfleur and sank one of them. On the nights of 26/27 and 27/28 April, they laid 108 mines each night near Cherbourg. On 30 April and 1 May, the flotilla laid 260 mines in three minefields. Three weeks later, the flotilla was ordered to transfer from Cherbourg to Le Havre and departed on the night of 23/24 May. Greif, Möwe, Falke, Kondor and Jaguar were attacked by Allied aircraft early the next day and Greif was struck by two bombs that set her forward boiler room on fire and caused her to take on water forward. With both boiler rooms subsequently flooded, she was unmaneuverable and accidentally collided with Falke. The latter was only slightly damaged, but Greif's bow was badly bent which caused problems for Möwe when she began to tow her sister. Around 06:00 Greif lost all power and sank at 06:32.[18]
Notes[edit]
- ^ "SMS" stands for "Seiner Majestät Schiff" (German: His Majesty's Ship).
- ^ In Imperial German Navy gun nomenclature, "SK" (Schnelladekanone) denotes that the gun is quick firing, while the L/45 denotes the length of the gun. In this case, the L/45 gun is 45 caliber, meaning that the gun is 45 times as long as it is in diameter.[5]
- ^ In Kriegsmarine gun nomenclature, SK stands for Schiffskanone (ship's gun), C/30 stands for Constructionjahr (Construction year) 1930.[7]
Citations[edit]
- ^ a b c Gröner, p. 191
- ^ a b Sieche, p. 237
- ^ a b c Whitley 1991, p. 202
- ^ a b c Whitley 2000, p. 57
- ^ Friedman, pp. 130–131
- ^ Whitley 1991, p. 45
- ^ Campbell, p. 219
- ^ Haarr, p. 377
- ^ Whitley 1991, pp. 47, 202; Whitley 2000, pp. 57–58
- ^ Gröner, p. 192
- ^ Whitley 1991, pp. 77–79
- ^ Rohwer, pp. 2, 6
- ^ Haar, pp. 81, 201, 213
- ^ Haar, pp. 213, 215–217
- ^ Haar, pp. 377–379, 382
- ^ Haarr, pp. 352, 359; Rohwer, pp. 29, 36, 38–39, 43, 45, 51–52; Whitley 1991, p. 109
- ^ Rohwer, pp. 198, 233, 236, 247, 249, 254, 256, 279; Whitley 1991, pp. 164–165, 208
- ^ Rohwer, pp. 312, 317–318, 324; Whitley 1991, p. 158
Bibliography[edit]
- Campbell, John (1985). Naval Weapons of World War II. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-0-87021-459-2.
- Friedman, Norman (2011). Naval Weapons of World War One: Guns, Torpedoes, Mines and ASW Weapons of All Nations; An Illustrated Directory. Barnsley, UK: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-100-7.
- Gröner, Erich (1990). German Warships 1815–1945. Vol. 1: Major Surface Warships. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-790-9.
- Haarr, Geirr H. (2009). The German Invasion of Norway, April 1940. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-310-9.
- Rohwer, Jürgen (2005). Chronology of the War at Sea 1939–1945: The Naval History of World War Two (Third Revised ed.). Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-59114-119-2.
- Sieche, Erwin (1980). "Germany". In Chesneau, Roger (ed.). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1922–1946. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-85177-146-7.
- Whitley, M. J. (2000). Destroyers of World War Two: An International Encyclopedia. London: Cassell & Co. ISBN 1-85409-521-8.
- Whitley, M. J. (1991). German Destroyers of World War Two. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-55750-302-8.
