User:Mkper9/sandbox
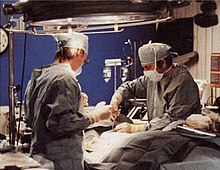
Cryonics (from Greek: κρύος kryos meaning 'cold') is the cooling to very low temperature (usually at −196 °C or −320.8 °F or 77.1 K) and storage of human remains, with the speculative hope that resurrection may be possible in the future.[1][2] Cryonics is regarded with skepticism within the mainstream scientific community. It is widely viewed as a pseudoscience,[3] and its practice has been characterized as quackery,[4][5] but it has also been defended in some mainstream, academic publications.[6][7][8][9]
Cryonics procedures can begin only after the "patients" are clinically and legally dead. Cryonics procedures may begin within minutes of death,[10] and use cryoprotectants to prevent ice formation during cryopreservation.[6] It is, however, not currently possible for reanimation to occur after vitrification, as this causes damage to the brain including its neural circuits.[11] The first cryonic preservation was that of James Bedford whose body was frozen in 1967.[12] As of 2020, about 400 whole-body or brain cryopreservations had occurred, and about 3,100 living people had made arrangements for the procedure.[13]
Critics argue that economic reality means it is improbable that any cryonics corporation could continue in business long enough to take advantage of the claimed long-term benefits offered.[14] Early attempts of cryonic preservations were performed in the 1960s and early 1970s which ended in failure. The major companies then involved went out of business, and their stored human remains were thawed and disposed of, though since then the track record has been better, with most cryopreservations continuing.[15][16]
Conceptual basis[edit]
Cryonicists argue that as long as brain structure remains intact, there is no fundamental barrier, given our current understanding of physical law, to recovering its information content. Cryonics proponents go further than the mainstream consensus in saying that the brain does not have to be continuously active to survive or retain memory. Cryonics controversially states that a human survives even within an inactive brain that has been badly damaged, provided that original encoding of memory and personality can, in theory, be adequately inferred and reconstituted from what structure remains.[7][17]
Cryonics uses temperatures below −130 °C, called cryopreservation, in an attempt to preserve enough brain information to permit the future revival of the cryopreserved person. Cryopreservation may be accomplished by freezing, freezing with cryoprotectant to reduce ice damage, or by vitrification to avoid ice damage. Even using the best methods, cryopreservation of whole bodies or brains is very damaging and irreversible with current technology.
Cryonics advocates hold that in the future the use of some kind of presently-nonexistent nanotechnology may be able to help bring the (apparently) dead back to life and treat the diseases which killed them.[18] Mind uploading has also been proposed.[19]
Cryonics in practice[edit]
Cryonics can be expensive. As of 2018[update], the cost of the procedure, including long-term storage requiring interest income, ranged from US$28,000 to $200,000.[20]
When used at high concentrations, cryoprotectants can stop ice formation completely. Cooling and solidification without ice crystal formation is called vitrification.[21] The first cryoprotectant solutions able to vitrify at very slow cooling rates while still being compatible with whole organ survival were developed in the late 1990s by cryobiologists Gregory Fahy and Brian Wowk for the purpose of banking transplantable organs.[22][23][24] This has allowed animal brains to be vitrified, warmed back up, and examined for ice damage using light and electron microscopy. No ice crystal damage was found;[25] cellular damage was due to dehydration and toxicity of the cryoprotectant solutions.
Costs can include payment for medical personnel to be on call for death, vitrification, transportation in dry ice to a preservation facility, and payment into a trust fund intended to cover indefinite storage in liquid nitrogen and future revival costs.[26][27] With costs ranging up to $200,000, life insurance is a common method of financing.[20][26] KrioRus, which stores bodies communally in large dewars, charges $12,000 to $36,000 for the procedure.[28] Some customers opt to have only their head or brain cryopreserved ("neuropreservation"), rather than their whole body.
As of 2020, about 400 whole-body or brain cryopreservations had occurred, and about 3,100 living people had made arrangements for the procedure.[13] As of 2016, four facilities exist in the world to retain cryopreserved bodies: three in the U.S. and one in Russia.[2][29]
Considering the lifecycle of corporations, it may be unlikely that any cryonics company could continue to exist for sufficient time to take advantage even of the supposed benefits offered: historically, even the most robust corporations have only a one-in-a-thousand chance of surviving even one hundred years.[14] Many cryonics companies have failed; as of 2018[update], all but one of the pre-1973 cryonics cases had been defrosted and disposed of.[15] Since the early years, however, the track record of cases has been better. A 2014 reference states that "[cryopreservation] failures once were tragically much the rule but now are quite rare."[16]
Obstacles to success[edit]
Preservation damage[edit]
Cryopreservation has long been used by medical laboratories to maintain animal cells, human embryos, and even some organized tissues, for periods as long as three decades.[30] Recovering large animals and organs from a frozen state is however not considered possible at the current level of scientific knowledge [31][22][32] Large vitrified organs tend to develop fractures during cooling,[33] a problem worsened by the large tissue masses and very low temperatures of cryonics.[34] Without cryoprotectants, cell shrinkage and high salt concentrations during freezing usually prevent frozen cells from functioning again after thawing. Ice crystals can also disrupt connections between cells that are necessary for organs to function.[35]
In 2016, Robert L. McIntyre and Gregory Fahy at the cryobiology research company 21st Century Medicine, Inc. won the Small Animal Brain Preservation Prize of the Brain Preservation Foundation by demonstrating to the satisfaction of neuroscientist judges that a particular implementation of fixation and vitrification called aldehyde-stabilized cryopreservation[36] could preserve a rabbit brain in "near perfect" condition at −135 °C, with the cell membranes, synapses, and intracellular structures intact in electron micrographs.[37][38] Brain Preservation Foundation President, Ken Hayworth, said, "This result directly answers a main skeptical and scientific criticism against cryonics—that it does not provably preserve the delicate synaptic circuitry of the brain."[39] However, the price paid for perfect preservation, as seen by microscopy, was tying up all protein molecules with chemical crosslinks, eliminating biological viability.[38]
Some cryonics organizations use vitrification without a chemical fixation step,[40] sacrificing some structural preservation quality for less damage at the molecular level. Some scientists, like João Pedro Magalhães, have questioned whether using a deadly chemical for fixation eliminates the possibility of biological revival, making chemical fixation unsuitable for cryonics.[41]
Outside of cryonics firms and cryonics-linked interest groups, many scientists show strong skepticism toward cryonics methods. Cryobiologist Dayong Gao states that "we simply don't know if (subjects have) been damaged to the point where they've 'died' during vitrification because the subjects are now inside liquid nitrogen canisters." Biochemist Ken Storey argues (based on experience with organ transplants), that "even if you only wanted to preserve the brain, it has dozens of different areas, which would need to be cryopreserved using different protocols."[42]
Revival[edit]
Revival would require repairing damage from lack of oxygen, cryoprotectant toxicity, thermal stress (fracturing) and freezing in tissues that do not successfully vitrify, finally followed by reversing the cause of death. In many cases, extensive tissue regeneration would be necessary.[43] This revival technology remains speculative and does not currently exist.[1] An imaginative, book-length study by Robert Freitas explores ways it might happen, using physics-based, mathematical arguments, and also considering mind uploading.[44]
Legal issues[edit]
Historically, a person had little control regarding how their body was treated after death as religion held jurisdiction over the ultimate fate of their body.[45] However, secular courts began to exercise jurisdiction over the body and use discretion in carrying out of the wishes of the deceased person.[45] Most countries legally treat preserved individuals as deceased persons because of laws that forbid vitrifying someone who is medically alive.[46] In France, cryonics is not considered a legal mode of body disposal;[47] only burial, cremation, and formal donation to science are allowed. However, bodies may legally be shipped to other countries for cryonic freezing.[48] As of 2015, the Canadian province of British Columbia prohibits the sale of arrangements for body preservation based on cryonics.[49] In Russia, cryonics falls outside both the medical industry and the funeral services industry, making it easier in Russia than in the U.S. to get hospitals and morgues to release cryonics candidates.[28]
In London in 2016, the English High Court ruled in favor of a mother's right to seek cryopreservation of her terminally ill 14-year-old daughter, as the girl wanted, contrary to the father's wishes. The decision was made on the basis that the case represented a conventional dispute over the disposal of the girl's body, although the judge urged ministers to seek "proper regulation" for the future of cryonic preservation following concerns raised by the hospital about the competence and professionalism of the team that conducted the preservation procedures.[50] In Alcor Life Extension Foundation v. Richardson, the Iowa Court of Appeals ordered for the disinterment of Richardson, who was buried against his wishes for cryopreservation.[45][51]
A detailed legal examination by Jochen Taupitz concludes that cryonic storage is legal in Germany for an indefinite period of time.[52]
Ethics[edit]
In 2009, writing in Bioethics, David Shaw examines the ethical status of cryonics. The arguments against it include changing the concept of death, the expense of preservation and revival, lack of scientific advancement to permit revival, temptation to use premature euthanasia, and failure due to catastrophe. Arguments in favor of cryonics include the potential benefit to society, the prospect of immortality, and the benefits associated with avoiding death. Shaw explores the expense and the potential payoff, and applies an adapted version of Pascal's Wager to the question.[53]
In 2016, Charles Tandy wrote in favor of cryonics, arguing that honoring someone's last wishes is seen as a benevolent duty in American and many other cultures.[54]
History[edit]
Cryopreservation was applied to human cells beginning in 1954 with frozen sperm, which was thawed and used to inseminate three women.[55] The freezing of humans was first scientifically proposed, independently, in two book-length studies in 1962, Evan Cooper's Immortality: Physically, Scientifically, Now and Robert Ettinger's The Prospect of Immortality.[56][57] In April 1966, the first human body was frozen and placed in liquid nitrogen—though it had been embalmed and stored at just above freezing for two months. The middle-aged woman from Los Angeles, tentatively identified as Sarah Frances Gilbert (birthname), was soon thawed out and buried by relatives.[58][16]
The first body to be cryopreserved with the hope of future revival was that of James Bedford, claimed by Alcor's Mike Darwin to have occurred within around two hours of his death from cardiorespiratory arrest (secondary to metastasized kidney cancer) on January 12, 1967.[59] Bedford's cryopreservation is the only one before 1974 that still continues today.[16] In 1976, Ettinger founded the Cryonics Institute; he was cryopreserved in 2011.[57] Robert Nelson, "a former TV repairman with no scientific background" who led the Cryonics Society of California, was sued in 1981 for allowing nine bodies to thaw and decompose in the 1970s; in his defense, he claimed that the Cryonics Society had run out of money.[16] This led to the lowered reputation of cryonics in the U.S.[28]
In 2018, a Y-Combinator startup called Nectome was recognized for developing a method of preserving brains with chemicals rather than by freezing. The method is fatal, performed as euthanasia under general anesthesia, but the hope is that future technology would allow the brain to be physically scanned into a computer simulation, neuron by neuron.[60]
Demographics[edit]
According to The New York Times, cryonicists are predominantly non-religious white males, outnumbering women by about three to one.[61] According to The Guardian, as of 2008, while most cryonicists used to be young, male, and "geeky", recent demographics have shifted slightly towards whole families.[46]
In 2015, Du Hong, a 61-year-old female writer of children's literature, became the first known Chinese national to have her head cryopreserved.[62]
Reception[edit]
Cryonics is widely regarded as a fringe pseudoscience.[3] The Society for Cryobiology rejected members who practiced cryonics,[3] and issued a public statement saying that cryonics is "not science", and that it is a "personal choice" how people want to have their dead bodies disposed of.[63] Some mainstream, academic publications, however, have defended the practice as at least a rational gamble for an extended life in the future.[6][7][8][9]
Russian company KrioRus is the first non-US vendor of cryonics services. Yevgeny Alexandrov, chair of the Russian Academy of Sciences commission against pseudoscience, said there was "no scientific basis" for cryonics, and that the company's offering was based on "unfounded speculation".[64]
Scientists have expressed skepticism about cryonics in media sources,[28] and the Norwegian philosopher Ole Martin Moen has written that the topic receives a "minuscule" amount of attention from academia, though himself defending the practice in an academic publication.[7]
While some neuroscientists contend that all the subtleties of a human mind are contained in its anatomical structure,[65] few neuroscientists will comment directly upon the topic of cryonics due to its speculative nature. Individuals who intend to be frozen are often "looked at as a bunch of kooks".[66] Cryobiologist Kenneth B. Storey said in 2004 that cryonics is impossible and will never be possible, as cryonics proponents are proposing to "over-turn the laws of physics, chemistry, and molecular science".[67] Neurobiologist Michael Hendricks has said that "Reanimation or simulation is an abjectly false hope that is beyond the promise of technology and is certainly impossible with the frozen, dead tissue offered by the 'cryonics' industry".[28] However, in 2014 Natasha Vita-More of Alcor Research Center, together with Daniel Barranco from the Department of Cryobiology of the Spanish University of Seville, for the first time, proved that the use of cryonic technologies does not destroy the long-term memory of the simplest multi-cellular organisms.[68] More recently (2023), a group at the University of Minnesota successfully rewarmed and implanted rat kidneys after up to 100 days of cryogenic storage at −150°C, using a special technique to achieve a very uniform rewarming.[69]
William T. Jarvis has written that "Cryonics might be a suitable subject for scientific research, but marketing an unproven method to the public is quackery".[4][5] Ole Martin Moen, however, offers a thoughtful rebuttal: "Cryonics is costly. It is also unproven, for it relies on the development of technologies that are not yet available and thus cannot be clinically tested. Neither its cost nor the fact that it is unproven, however, constitutes a knockdown argument, for though the chances that cryonics will work might be low, the potential value that it might help realise is very big, and the alternatives—burial and cremation—offer no potential value at all."[7]
According to cryonicist Aschwin de Wolf and others, cryonics can often produce intense hostility from spouses who are not cryonicists. James Hughes, the executive director of the pro-life-extension Institute for Ethics and Emerging Technologies, chooses not to personally sign up for cryonics, calling it a worthy experiment but stating laconically that "I value my relationship with my wife."[61]
Cryobiologist Dayong Gao, in 2013, said that "People can always have hope that things will change in the future, but there is no scientific foundation supporting cryonics at this time."[42] However, the following year Vita-More and Barranco obtained results showing survival of memories after cryopreservation, as noted.[28]
While it is universally agreed that "personal identity" is uninterrupted when brain activity temporarily ceases during incidents of accidental drowning (where people have been restored to normal functioning after being completely submerged in cold water for up to 66 minutes), one argument against cryonics is that a centuries-long absence from life might interrupt the conception of personal identity, such that the revived person would "not be themself".[7]
Maastricht University bioethicist David Shaw raises the argument that there would be no point in being revived in the far future if one's friends and families are dead, leaving them all alone; he notes, however, that family and friends can also be frozen, that there is "nothing to prevent the thawed-out freezee from making new friends", and that a lonely existence may be preferable to no existence at all for the revived.[53]
In fiction[edit]
Suspended animation is a popular subject in science fiction and fantasy settings. It is often the means by which a character is transported into the future.
A survey in Germany found that about half of the respondents were familiar with cryonics, and about half of those familiar with cryonics had learned of the subject from films or television.[70]
In popular culture[edit]
The town of Nederland, Colorado, hosts an annual Frozen Dead Guy Days festival to commemorate a substandard attempt at cryopreservation.[71]
Notable people[edit]
Notable cryopreservations include those of baseball players Ted Williams and son John Henry Williams (in 2002 and 2004, respectively),[72] engineer and doctor L. Stephen Coles (in 2014),[73] economist and entrepreneur Phil Salin, and software engineer Hal Finney (in 2014).[74]
People known to have arranged for cryopreservation upon death include PayPal founders Luke Nosek[75] and Peter Thiel,[76] Oxford transhumanists Nick Bostrom and Anders Sandberg, and transhumanist philosopher David Pearce.[77] Larry King previously arranged for cryonics, but according to Inside Edition, later changed his mind.[78][79]
Some are mistakenly believed to have undergone cryopreservation – for instance, the urban legend suggesting Walt Disney was cryopreserved is false; he was cremated and interred at Forest Lawn Memorial Park Cemetery.[80][a] Robert A. Heinlein, who wrote enthusiastically of the concept in The Door into Summer (serialized in 1956), was cremated and had his ashes distributed over the Pacific Ocean. Timothy Leary was a long-time cryonics advocate and signed up with a major cryonics provider, but he changed his mind shortly before his death and was not cryopreserved.[82]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ Robert Nelson told the Los Angeles Times that he thought Walt Disney wanted to be cryopreserved as Walt Disney Studios had called him to ask detailed questions about his organisation, the Cryonics Society of California. However, Nelson clarified that "They had him cremated. I personally have seen his ashes."[81]
Citations[edit]
- ^ a b McKie, Robin (13 July 2002). "Cold facts about cryonics". The Observer. Archived from the original on 8 July 2017. Retrieved 1 December 2013.
Cryonics, which began in the Sixties, is the freezing – usually in liquid nitrogen – of human beings who have been legally declared dead. The aim of this process is to keep such individuals in a state of refrigerated limbo so that it may become possible in the future to resuscitate them, cure them of the condition that killed them, and then restore them to functioning life in an era when medical science has triumphed over the activities of the Grim Reaper.
- ^ a b "Dying is the last thing anyone wants to do – so keep cool and carry on". The Guardian. 10 October 2015. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ a b c Steinbeck RL (29 September 2002). "Mainstream science is frosty over keeping the dead on ice". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- ^ a b Butler K (1992). A Consumer's Guide to "Alternative" Medicine. Prometheus Books. p. 173.
- ^ a b * Zimmer, Carl; Hamilton, David (October 2007). "Could He Live to 2150?". Best Life.
Quack watch: The following controversial treatments are all being touted as antiaging miracle cures.
- Harold Schechter (2 June 2009). The Whole Death Catalog: A Lively Guide to the Bitter End. Random House Publishing Group. p. 206. ISBN 978-0-345-51251-2. Archived from the original on 23 November 2019. Retrieved 1 July 2019.
- Pein, Corey (8 March 2016). "Everybody Freeze!". The Baffler. Archived from the original on 28 April 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- Chiasson, Dan (December 2014). "Heads Will Roll". Harper's Magazine. ISSN 0017-789X. Archived from the original on 24 June 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2019.; Miller, Laura (24 June 2012). ""The Mansion of Happiness": Matters of life and death". Salon. Archived from the original on 24 June 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- Almond, Steve (28 February 2014). "Sparks of Life". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 24 June 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- Carroll, Robert Todd (2003). The Skeptics Dictionary: A Collection of Strange Beliefs, Amusing Deceptions, and Dangerous Delusions. Wiley. ISBN 0471272426.
A business based on little more than hope for developments that can be imagined by science is quackery. There is little reason to believe that the promises of cryonics will ever be fulfilled.
- ^ a b c Best BP (April 2008). "Scientific justification of cryonics practice" (PDF). Rejuvenation Research. 11 (2): 493–503. doi:10.1089/rej.2008.0661. PMC 4733321. PMID 18321197. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 July 2018. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f Moen, OM (August 2015). "The case for cryonics". Journal of Medical Ethics. 41 (18): 493–503. doi:10.1136/medethics-2015-102715. PMID 25717141. S2CID 31744039.
- ^ a b Swan, Melanie (17 December 2019). "Worldwide cryonics attitudes about the body, cryopreservation, and revival: personal identity malleability and a theory of cryonic life extension". Sophia. 58: 699–735. doi:10.1007/s11841-019-0727-4.
- ^ a b Ekpo, M. D.; Boafo, G. F.; Gambo, S. S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Tan, S. (9 June 2022). "Cryopreservation of animals and cryonics: current technical progress, difficulties and possible research directions". Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 9. doi:10.3389/fvets.2022.877163.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Hendry, Robert; Crippen, David (2014). "Brain Failure and Brain Death". ACS Surgery: Principles and Practice critical care. Decker Intellectual Properties Inc. pp. 1–10. Archived from the original on 23 January 2021. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
A physician will pronounce a patient using the usual cardiorespiratory criteria, whereupon the patient is legally dead. Following this pronouncement, the rules pertaining to procedures that can be performed change radically because the individual is no longer a living patient but a corpse. In the initial cryopreservation protocol, the subject is intubated and mechanically ventilated, and a highly efficient mechanical cardiopulmonary resuscitation device reestablishes circulation.
- ^ Devlin, Hannah (18 November 2016). "The cryonics dilemma: will deep-frozen bodies be fit for new life?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 24 January 2019. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ^ "Death To Dust: What Happens To Dead Bodies? 2nd Edition, Chapter 7: Souls On Ice". Archived from the original on 27 March 2019. Retrieved 21 March 2016.
- ^ a b Gillett, C R; Brame, T; Kendziorra, E (7 January 2021). "Comprehensive survey of United States internet users' sentiments toward cryopreseration". PLoS One. 16 (1). PMID 33411839.
- ^ a b Stodolsky DS (2016). "The growth and decline of cryonics". Cogent Social Sciences. 2 (1): 1167576. doi:10.1080/23311886.2016.1167576.
- ^ a b "The law on cryonics". Human Tissue Authority. 26 September 2018. Archived from the original on 30 September 2019. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
- ^ a b c d e Perry, R. Michael (October 2014). "Suspension Failures – Lessons from the Early Years". ALCOR: Life Extension Foundation. Archived from the original on 16 April 2020. Retrieved 29 August 2018. Cite error: The named reference "alcor" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Doyle, DJ (2012). "Cryonic Life Extension: Scientific Possibility or Stupid Pipe Dream?". Ethics in Biology, Engineering and Medicine. 3 (1–3): 9–28. doi:10.1615/EthicsBiologyEngMed.2013006985.
- ^ Crippen, DW; Whetstine, L (2007). "Ethics review: Dark angels – the problem of death in intensive care". Critical Care. 11 (1): 202. doi:10.1186/cc5138. PMC 2151911. PMID 17254317.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Frozen in time: Oregon firm preserves bodies, brains in hopes that science catches up". Portland Tribune. 18 February 2016. Archived from the original on 11 July 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ a b "Things to consider when making your decision on cryonics". Human Tissue Authority. 26 September 2018. Archived from the original on 30 September 2019. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
- ^ Fahy GM, MacFarlane DR, Angell CA, Meryman HT (August 1984). "Vitrification as an approach to cryopreservation". Cryobiology. 21 (4): 407–26. doi:10.1016/0011-2240(84)90079-8. PMID 6467964.
- ^ a b Fahy GM, Wowk B, Pagotan R, et al. (July 2009). "Physical and biological aspects of renal vitrification". Organogenesis. 5 (3): 167–75. doi:10.4161/org.5.3.9974. PMC 2781097. PMID 20046680.
- ^ Fahy GM, Wowk B, Wu J, et al. (April 2004). "Cryopreservation of organs by vitrification: perspectives and recent advances". Cryobiology. 48 (2): 157–78. doi:10.1016/j.cryobiol.2004.02.002. PMID 15094092.
- ^ Fahy, G; Wowk, B; Wu, J; Phan, J; Rasch, C; Chang, A; Zendejas, E (2005). "Corrigendum to "Cryopreservation of organs by vitrification: perspectives and recent advances" [Cryobiology 48 (2004) 157–178]". Cryobiology. 50 (3): 344. doi:10.1016/j.cryobiol.2005.03.002.
- ^ Lemler J, Harris SB, Platt C, Huffman TM (June 2004). "The arrest of biological time as a bridge to engineered negligible senescence". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1019 (1): 559–63. Bibcode:2004NYASA1019..559L. doi:10.1196/annals.1297.104. PMID 15247086. S2CID 27635898.
- ^ a b "Cryonics: the chilling facts". The Independent. 26 July 2011. Archived from the original on 14 June 2018. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ "A Dying Young Woman's Hope in Cryonics and a Future". The New York Times. 12 September 2015. Archived from the original on 2 August 2018. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f "Inside the weird world of cryonics". Financial Times. 18 December 2015. Archived from the original on 8 September 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ "'The ultimate lottery ticket:' Inside one of four cryonics facilities in the world". KOIN (CBS Portland). 18 February 2016. Archived from the original on 4 July 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ Crippen DW, Reis RJ, Risco R, Vita N (October 2015). "The Science Surrounding Cryonics". MIT Technology Review.
- ^ Smith Audrey U (1957). "Problems in the Resuscitation of Mammals from Body Temperatures Below 0 °C". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 147 (929): 533–44. Bibcode:1957RSPSB.147..533S. doi:10.1098/rspb.1957.0077. JSTOR 83173. PMID 13494469. S2CID 40568140.
- ^ Fahy GM, Wowk B, Wu J (2006). "Cryopreservation of complex systems: the missing link in the regenerative medicine supply chain" (PDF). Rejuvenation Research. 9 (2): 279–91. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.539.7419. doi:10.1089/rej.2006.9.279. PMID 16706656. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 October 2017. Retrieved 24 October 2017.
- ^ Fahy GM, Saur J, Williams RJ (October 1990). "Physical problems with the vitrification of large biological systems". Cryobiology. 27 (5): 492–510. doi:10.1016/0011-2240(90)90038-6. PMID 2249453.
- ^ Wowk B (2011). "Systems for Intermediate Temperature Storage for Fracture Reduction and Avoidance". Cryonics. Vol. 2011, no. 3. Alcor Life Extension Foundation. pp. 7–13. ISSN 1054-4305.
- ^ Fahy GM, Levy DI, Ali SE (June 1987). "Some Emerging Principles Underlying the Physical Properties, Biological Actions, and Utility of Vitrification Solutions". Cryobiology. 24 (3): 196–213. doi:10.1016/0011-2240(87)90023-X. PMID 3595164.
- ^ McIntyre RL, Fahy GM (December 2015). "Aldehyde-stabilized cryopreservation". Cryobiology. 71 (3): 448–458. doi:10.1016/j.cryobiol.2015.09.003. PMID 26408851.
- ^ Claire Maldarelli (9 February 2016). "Researchers Have Preserved an Entire Rabbit Brain". Popular Science. Archived from the original on 14 March 2016. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ^ a b Michael Shermer (1 February 2016). "Can Our Minds Live Forever?". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 22 March 2016. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ^ Anthony Cuthbertson (10 February 2016). "Rabbit Brain Returns Successfully from Cryopreservation". Newsweek. Archived from the original on 20 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ "Alcor Position Statement on Brain Preservation Prize". Alcor Life Extension Foundation. 12 February 2016. Archived from the original on 15 February 2016. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ^ "Mammal brain frozen and thawed out perfectly for first time". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 16 June 2016. Retrieved 6 June 2016.
- ^ a b "Frozen body: Can we return from the dead?". BBC News. 15 August 2013. Archived from the original on 12 March 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ Karow, Armand; Webb, Watts (1965). "Tissue Freezing: A theory for injury and survival". Cryobiology. 2 (3): 99–108. doi:10.1016/s0011-2240(65)80094-3. PMID 5860601.
- ^ Cryostasis Revival: The Recovery of Cryonics Patients through Nanomedicine.Robert Freitas. Cryonics 2022 #2 (pages 15–23)
- ^ a b c Dukeminier, Jesse; Sitkoff, Robert (2013). Wills, Trusts, and Estates. Wolters Kluwer Law & Business in New York. p. 507. ISBN 978-1-4548-2457-2.
- ^ a b "Patients who are frozen in time". TheGuardian.com. 14 February 2008. Archived from the original on 12 May 2019. Retrieved 12 October 2020.
- ^ "Conseil d'État du 06/01/2006, n° 260307 : Cryogénisation - interdiction". Archived from the original on 7 January 2014. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ^ Chrisafis, Angelique (16 March 2006). "Freezer failure ends couple's hopes of life after death". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 8 January 2014. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ Proctor, Jason (16 July 2015). "Immortality sought through B.C. Supreme Court lawsuit". CBC News. Archived from the original on 21 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ "Terminally ill teen won historic ruling to preserve body". BBC News. 18 November 2016. Archived from the original on 18 November 2016. Retrieved 18 November 2016.
- ^ "Alcor Life Extension Foundation v. Richardson". 785 N.W.2d 717. 2010. Archived from the original on 7 January 2017. Retrieved 7 January 2017.
- ^ Taupitz, Jochen; Fuhr, Günther; Zwick, Anna; Salkic, Amina (2013). Unterbrochenes Leben?. St. Ingbert, Germany: Fraunhofer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-8396-0593-6. Archived from the original on 27 December 2018. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ^ a b Shaw, David. "Cryoethics: seeking life after death." Bioethics 23.9 (2009): 515–521. APA
- ^ Tandy, Charles (8 February 2017). "An Open Letter to Physicians in Death-with-Dignity States (The Case of a Terminally Ill Cryonicist)". SSRN 2913107.
- ^ "Fatherhood After Death Has Now Been Proved Possible". Cedar Rapids Gazette. 9 April 1954.
- ^ Ev Cooper,Cryonics, March 1983, accessed 13 June 2013
- ^ a b Devlin, Hannah (18 November 2016). "The cryonics dilemma: will deep-frozen bodies be fit for new life?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 23 September 2018. Retrieved 22 September 2018.
- ^ A Year of Jubilees: Some Important Cryonics Anniversaries. R. Michael Perry. Cryonics 2017 #3 (pages 34–35)
- ^ "Dear Dr. Bedford (and those who will care for you after I do)". Cryonics. July 1991. Archived from the original on 16 March 2020. Retrieved 23 August 2009.
- ^ "A startup is pitching a mind-uploading service that is "100 percent fatal"". Technology Review. 13 March 2018. Archived from the original on 23 January 2021. Retrieved 22 March 2018.
- ^ a b Howley, Kerry (7 July 2010). "Until Cryonics Do Us Part". The New York Times Magazine. Archived from the original on 16 May 2016. Retrieved 2 February 2016.
- ^ Stephen Chen (18 September 2015). "Cheating death? Elderly writer is the first known Chinese to embrace cryogenics, her head now frozen by lab in Arizona | South China Morning Post". Scmp.com. Archived from the original on 20 September 2015. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ^ "Present SfC Position statement" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 18 July 2019.
- ^ Luhn, Alex (11 November 2017). "'Insurance' against death: Russian cryonics firm plans Swiss lab for people in pursuit of eternal life". Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 28 July 2019. Retrieved 28 July 2019.
- ^ Jerry Adler (May 2015). "The Quest to Upload Your Mind into the Digital Space". Smithsonian Magazine. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ "Brain Freeze: Can putting faith in cryonics deliver life after death?". Toronto Sun. 6 October 2015. Archived from the original on 12 March 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ Miller K (2004). "Cryonics redux: is vitrification a viable alternative to immortality as a popsicle?". Skeptic. 11 (1): 24.
- ^ Vita-More, Natasha; Barranco, Daniel (2015). "Persistence of Long-Term Memory in Vitrified and Revived Caenorhabditis elegans". Rejuvenation Research. 18 (5): 458–463. doi:10.1089/rej.2014.1636. ISSN 1549-1684. PMC 4620520. PMID 25867710.
- ^ https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38824-8
- ^ Kaiser S, Gross D, Lohmeier J, Rosentreter M, Raschke J (2014). "Attitudes and acceptance toward the technology of cryonics in Germany". International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care. 5 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1017/S0266462313000718. PMID 24499638. S2CID 41185307.
- ^ McPheeters, Sam (May 2010). "Home Cryonics in the Smirk Age". The Corpse. ViceLand.com. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ^ "Leukemia claims son of Hall of Famer". ESPN.com. 7 March 2004. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- ^ Los Angeles Times (4 December 2014). "L. Stephen Coles dies at 73; studied extreme aging in humans". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 27 December 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ "Bitcoin's Earliest Adopter Is Cryonically Freezing His Body to See the Future – WIRED". WIRED. 29 August 2014. Archived from the original on 3 August 2018. Retrieved 6 March 2017.
- ^ Thiel, Peter (16 September 2014). Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the Future. Crown Business. p. 1 (chapter 14). ISBN 978-0-8041-3929-8.
- ^ Brown, Mick (19 September 2014). "Peter Thiel: the billionaire tech entrepreneur on a mission to cheat death". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 18 October 2014. Retrieved 16 October 2014.
- ^ Pearce, David. "Quora Answers 2015 - 2022 by David Pearce". The Hedonistic Imperative. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022.
- ^ "Was Larry King Cryogenically Frozen After his Death?". Inside Edition. 27 January 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ Leibovich M (26 August 2015). "Larry King Is Preparing for the Final Cancellation". New York Times. Archived from the original on 6 December 2019. Retrieved 14 February 2020.
- ^ Mikkelson, David (19 October 1995). "FACT CHECK: Was Walt Disney Frozen?". Snopes. Archived from the original on 23 January 2021. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ^ Conradt, Stacy (15 December 2013). "Disney on Ice: The Truth About Walt Disney and Cryogenics". Mental Floss. Archived from the original on 10 January 2019. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ^ The New York Times", "A Final Turn-On Lifts Timothy Leary Off" by Marlise Simons, April 22, 1997
Further reading[edit]
- "Mistakes Were Made". This American Life. Episode 354. 18 April 2008. The Public Radio Exchange (PRX). WBEZ Chicago. Transcript.
External links[edit]
Category:Cooling technology Category:Death customs Category:Fictional technology Category:Health fraud Category:Life extension Category:Pseudoscience Category:Scientific speculation

