User:Cop 663/English
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 90,000,000 worldwide (inc. census figures that permit claiming multiple ancestry) | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| 45.26 million (estimate)[1] | |
| 27,516,394 a[2] | |
| 6,570,015 b[3] | |
| 6,358,880 c[4] | |
| 44,202 - 281,895[5] | |
| Languages | |
| English | |
| Religion | |
| Traditionally Christianity, mostly Anglicanism, but also non-conformists (see History of the Church of England) and also Roman Catholics (see Catholic Emancipation). Agnostics, atheist as well as other religions. (see Religion in England). | |
a English American, b English Canadian, c English Australian | |
The English (from Old English: Englisc) are people from, or descended from residents of, England. This identity is often considered both a nationality and an ethnic group. The English identity as a people is of early medieval origin, when they were known in Old English as the Anglecynn. England is now a country of the United Kingdom, and the majority of English people in Britain are British Citizens.
Historically, the indigenous English population were descended from several genetically similar peoples: the earlier Britons (or Brythons), the Germanic tribes that settled in the area, including Angles, Saxons, Jutes, who founded what was to become England (from the Old English Engla-lond), and the later Norse Vikings and Normans. Following the Act of Union in 1707, in which the Kingdom of England became part of a new state called "Great Britain", English customs and identity became closely aligned with British customs and identity.
Today, many English people are descended from more recent immigrants from other European countries and the Commonwealth. Through their position at the centre of the British Empire, the English peoples are the source of the English language, the parliamentary system, common law systems in many countries and a variety of the globe's most popular sports.
Population[edit]
It is unclear how many British people today consider themselves English, as British censuses have traditionally not requested this information. In the 2001 UK census, respondents were invited to state their ethnicity, but while there were tick boxes for 'Irish' and for 'Scottish', there were none for 'English' or 'Welsh', who were subsumed into the general heading 'White British'.[6] Following complaints about this, the 2011 census will "allow respondents to record their English, Welsh, Scottish, Northern Irish, Irish or other identity."[7]
The CIA World Factbook claims that 83.6% of the UK population is in the "English" ethnic group. This figure was apparently arrived at by calculating the number of people in England who listed themselves as "white".[6]
History of English identity[edit]
Origins[edit]
The term "English" is not used to refer to the earliest inhabitants of the area that would become England: Palaeolithic hunter-gatherers, Celtic Britons, and Roman colonists,[8] (the same applies to the "Irish", "Welsh" and "Scots"). This is because up to and during the Roman occupation of Britain, the region now called England was not a distinct country; all the native inhabitants of Britain spoke Brythonic languages and were regarded as Britons (or Brythons) divided into many tribes. The word "English" refers to a heritage that began with the arrival of the Anglo-Saxons in the 5th century, who settled lands already inhabited by Romano-British tribes. That heritage then comes to include later arrivals, including Scandinavians, Normans, as well as those Romano-Britons who still lived in England.[8]
Traditional history[edit]

The first people to be called 'English' were the Anglo-Saxons, a group of closely related Germanic tribes that began migrating to eastern and southern Great Britain, from southern Denmark and northern Germany, in the 5th century AD, after the Romans had withdrawn from Britain. The Anglo-Saxons gave their name to England (Angle-land) and to the English.

The Anglo-Saxons arrived in a land that was already populated by people commonly referred to as the 'Romano-British'—the descendants of the native Brythonic-speaking population that lived in the area of Britain under Roman rule during the 1st-5th centuries AD. The multi-ethnic nature of the Roman Empire meant that small numbers of other peoples may have also been present in England before the Anglo-Saxons arrived. There is archaeological evidence, for example, of an early North African presence in a Roman garrison at Aballava, now Burgh-by-Sands, in Cumbria; a fourth-century inscription says that the Roman military unit Numerus Maurorum Aurelianorum ("unit of Aurelian Moors") from Muretania (Morocco) was stationed there.[9]
Traditionally, the Anglo-Saxons have been imagined as pushing away the Romano-British tribes into the mountainous areas of Britain. This notion of the Anglo-Saxon English has traditionally been important in defining English identity and distinguishing the English from their Celtic neighbours, such as the Scots, Welsh and Irish. Indeed, historian Catherine Hills describes this as the "national origin myth" of the English:
- The arrival of the Anglo-Saxons ... is still perceived as an important and interesting event because it is believed to have been a key factor in the identity of the present inhabitants of the British Isles, involving migration on such a scale as to permanently change the population of south-east Britain, and making the English a distinct and different people from the Celtic Irish, Welsh and Scots ....this is an example of a national origin myth ... and shows why there are seldom simple answers to questions about origins.[10]
The notion of a mass invasion by various Anglo-Saxon tribes that largely displaced the indigenous British population in southern and eastern Great Britain (modern day England with the exception of Cornwall) is supported by the writings of Gildas, the only contemporary historical account of the period, describing slaughter and starvation of native Britons by invading peoples (aduentus Saxonum).[11] Added to this is the fact that the English language contains no more than a handful of words borrowed from Brythonic sources (although the names of some towns, cities, rivers etc. do have Brythonic or pre-Brythonic origins, becoming more frequent towards the west of Britain).[12]
Questioning the tradition[edit]
The exact nature of the arrival of the Anglo-Saxons and their relationship with the Romano-British is a matter of debate, and the notion of the English as descending primarily from Anglo-Saxon invaders is considered by some historians and geneticists as simplistic or even incorrect.
Linguists note that the Brythonic languages such as Cornish, Cumbric, and Welsh, held on for several centuries in parts of England such as Cornwall, Devon, Cumbria, Northumberland, the West Midlands (particularly Herefordshire and Shropshire), Cheshire, Lancashire, and parts of Yorkshire (particularly West Yorkshire). [citation needed]
Since the 1960s, archaeologists and historians, and, more recently, geneticists,[13] have argued that they see only minimal evidence for mass displacement. Archaeologist Francis Pryor has stated that he "can't see any evidence for bona fide mass migrations after the Neolithic."[14] While the historian Malcolm Todd writes "It is much more likely that a large proportion of the British population remained in place and was progressively dominated by a Germanic aristocracy, in some cases marrying into it and leaving Celtic names in the, admittedly very dubious, early lists of Anglo-Saxon dynasties. But how we identify the surviving Britons in areas of predominantly Anglo-Saxon settlement, either archaeologically or linguistically, is still one of the deepest problems of early English history."[15]
Recent genetic and sociological studies have attempted to discern whether the present day English can be distinguished from their neighbours. These have stimulated interest in the popular press, although their complex results are heavily simplified. In 2002, the BBC used the headline "English and Welsh are races apart" to report a genetic survey of test subjects from market towns in England and Wales,[16] while in September 2006, The Sunday Times reported that a survey of first names and surnames in the UK had identified Ripley in Derbyshire as "the 'most English' place in England with 88.58% of residents having an English ethnic background".[17] The Daily Mail printed an article with the headline "We're all Germans! (and we have been for 1,600 years)".[18] In all these cases, the conclusions of these studies have been exaggerated or misinterpreted, with the language of race being employed by the journalists.[19]
The genetic studies suggest that 'English' and 'Celtic' people in Britain are more similar to each other than to the peoples of Germanic-speaking continental Europe. In a survey of the genes of British and Irish men that compared them to Frisians (a Germanic people thought to be related to the Anglo-Saxons) "the Frisians were more 'Continental' than any of the British samples, although they were somewhat closer to the British ones than the North German/Denmark sample. For example, the part of mainland Britain that has the most Continental input is Central England, but even here the AMH+1 frequency, not below 44% (Southwell), is higher than the 35% observed in the Frisians. These results demonstrate that even with the choice of Frisians as a source for the Anglo-Saxons, there is a clear indication of a continuing indigenous component in the English paternal genetic makeup."[20]
Several recent books, including those of Stephen Oppenheimer and Brian Sykes, have argued that the recent genetic studies in fact do not show a clear dividing line between the English and their 'Celtic' neighbours, but that there is a gradual clinal change from west coast Britain to east coast Britain. They suggest that the majority of the ancestors of British peoples were the original palaeolithic settlers of Great Britain, and that the differences that exist between the east and west coasts of Great Britain though not large, are deep in prehistory, mostly originating in the upper palaeolithic and Mesolithic (15,000-7,000 years ago). Furthermore, Oppenheimer states that genetic testing has proven that "75% of British and Irish ancestors arrive[d] between 15,000 and 7,500 years ago".[21]
Oppenheimer also claims that Celtic split from Indo-European earlier than previously suspected, some 6000 years ago, while English split from Germanic before the Roman period. Oppenheimer believes that a Germanic language that became English was spoken by the tribes of what is now England long before the arrival of the Anglo-Saxons and also discounts the view that the people of the area were ever Celtic.[22][13]
The Danelaw, and the origins of the English nation[edit]
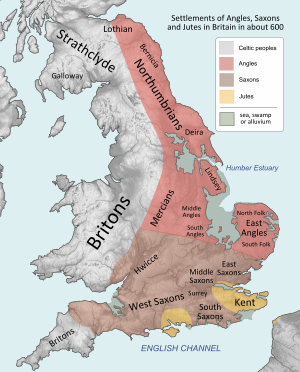
The English population was not politically unified until the 10th century. Before then, it consisted of a number of petty kingdoms which gradually coalesced into a Heptarchy of seven powerful states, the most powerful of which were Mercia and Wessex. The English nation state began to form when the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms united against Danish Viking invasions.
From about AD 800, waves of Danish Viking assaults on the coastlines of the British Isles were gradually followed by a succession of Danish settlers in England. At first, the Vikings were very much considered a separate people from the English. This separation was enshrined when Alfred the Great, King of Wessex, signed the Treaty of Alfred and Guthrum to establish the Danelaw, a division of England between English and Danish rule, with the Danes occupying northern and eastern England.[23]
The nation of England was formed in 937 by Athelstan of Wessex after the Battle of Brunanburh,[24][25] as Wessex grew from a relatively small kingdom in the South West to become the founder of the Kingdom of the English, incorporating all Anglo-Saxon kingdoms and the Danelaw.[26]
Over the following century and a half England was for the most part a politically unified entity, and remained permanently so after 959. Alfred's successors subsequently won military victories against the Danes, incorporating much of the Danelaw into the nascent kingdom of England. Danish invasions continued into the 11th century, and there were both English and Danish kings in the period following the unification of England (for example, Æthelred II (978–1013 and 1014–1016) was English but Cnut (1016–1035) was Danish).
Gradually, the Danes in England came to be seen as 'English'. They had a noticeable impact on the English language: many English words, such as dream, take, they and them are of Old Norse origin,[27] and place names that end in -thwaite and -by are Scandinavian in origin.[28]
Norman and Angevin rule[edit]

The Norman conquest of England during 1066 brought Anglo-Saxon and Danish rule of England to an end, as the new Norman elite almost universally replaced the Anglo-Saxon aristocracy and church leaders. After the conquest, the word "English" normally included all natives of England, whether they were of Anglo-Saxon, Scandinavian or Celtic ancestry, to distinguish them from the Norman invaders, who were regarded as "Norman" even if born in England, for a generation or two after the Conquest.[29] The Norman dynasty ruled England for 87 years until the death of King Stephen in 1154, when the succession passed to Henry II, House of Plantagenet (based in France), and England became part of the Angevin Empire until 1399.
Various contemporary sources suggest that within fifty years of the invasion most of the Normans outside the royal court had switched to English, with Anglo-Norman remaining the prestige language of government and law largely out of social inertia. For example, Orderic Vitalis, a historian born in 1075 and the son of a Norman knight, said that he learned French only as a second language. Anglo-Norman continued to be used by the Plantagenet kings until Edward I came to the throne.[30] Over time the English language became more important even in the court, and the Normans were gradually assimilated, until, by the 14th Century, both rulers and subjects regarded themselves as English and spoke the English language.[31]
Despite the assimilation of the Normans, the distinction between 'English' and 'French' survived in official documents long after it had fallen out of common use, in particular in the legal phrase Presentment of Englishry (a rule by which a hundred had to prove an unidentified murdered body found on their soil to be that of an Englishman, rather than a Norman, if they wanted to avoid a fine). This law was abolished in 1340.[32]
England and the United Kingdom[edit]
The Acts of Union[edit]
Since the 18th century, England has been one part of a wider political entity covering all or part of the British Isles, which today is called the United Kingdom. Wales was annexed by England by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542, which incorporated Wales into the English state.[33] A new British identity subsequently began to develop after James VI of Scotland became James I of England as well, and expressed the desire to be known as the king of "Great Britain".[34] In 1707, England formed a union with Scotland by passing an Act of Union in March 1707 that ratified the Treaty of Union. The Parliament of Scotland had previously passed its own Act of Union, so a new kingdom to be called Great Britain came into being on May 1, 1707. In 1801, another Act of Union combined the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland, creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. About two thirds of the Irish population (those who lived in 26 of the 32 counties of Ireland), left the United Kingdom in 1922, to form the Irish Free State. The remainder became the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Englishness and Britishness[edit]
Although England is no longer an independent nation state, but rather a constituent country within the United Kingdom, the English may still be regarded as a "nation" according to the Oxford English Dictionary's definition: a group united by factors that include "language, culture, history, or occupation of the same territory".[35] However, throughout the history of the UK, the English have been dominant in population and political weight. As a consequence, notions of 'Englishness' and 'Britishness' are often very similar. At the same time, after the 1707 Union, the English, along with the other peoples of the British Isles, have been encouraged to think of themselves as British rather than identifying themselves by the smaller constituent nations.[36]
One result is a common tendency for the words "English" and "British" to be used interchangeably. In his study of English identity, Krishan Kumar describes a common slip of the tongue in which people say "English, I mean British". He notes that this slip is normally made only by the English themselves and by foreigners: "Non-English members of the United Kingdom rarely say 'British' when they mean 'English'". Kumar suggests that although this blurring is a sign of England's dominant position with the UK, it is also "problematic for the English [...] when it comes to conceiving of their national identity. It tells of the difficulty that most English people have of distinguishing themselves, in a collective way, from the other inhabitants of the British Isles".[37]
In 1965, the historian A. J. P. Taylor wrote,
- "When the Oxford History of England was launched a generation ago, "England" was still an all-embracing word. It meant indiscriminately England and Wales; Great Britain; the United Kingdom; and even the British Empire. Foreigners used it as the name of a Great Power and indeed continue to do so. Bonar Law, a Scotch Canadian, was not ashamed to describe himself as "Prime Minister of England" [...] Now terms have become more rigorous. The use of "England" except for a geographic area brings protests, especially from the Scotch."[38]
However, although Taylor believed this blurring effect was dying out, in his 1999 book The Isles, Norman Davies lists numerous examples in history books of "British" still being used to mean "English" and vice versa.[39]
Modern migrations to England[edit]
History of immigration[edit]
Although England has not been successfully conquered since the Norman conquest nor extensively settled since, it has been the destination of varied numbers of migrants at different periods from the seventeenth century. While some members of these groups maintain a separate ethnic identity, others have assimilated and intermarried with the English. Since Oliver Cromwell's resettlement of the Jews in 1656, there have been waves of Jewish immigration from Russia in the nineteenth century and from Germany in the twentieth.[40] After the French king Louis XIV declared Protestantism illegal in 1685 with the Edict of Fontainebleau, an estimated 50,000 Protestant Huguenots fled to England.[41] Due to sustained and sometimes mass emigration from Ireland, current estimates indicate that around 6 million people in the UK have at least one grandparent born in Ireland.[42]
There has been a black presence in England since at least the 16th century due to the slave trade and an Indian presence since the mid 19th century because of the British Raj.[43] Black and Asian proportions have grown in England as immigration from the British Empire and the subsequent Commonwealth of Nations was encouraged due to labour shortages during post-war rebuilding.[44] In 2006, an estimated 591,000 migrants arrived to live in the UK for at least a year,[45] while 400,000 people emigrated from the UK for a year or more.[46][47] The largest group of arrivals was people from the Indian subcontinent.[48] While one result of this immigration has been incidents of racial tension, such as the Brixton and Bradford riots, there has also been considerable intermarriage; the 2001 census recorded that 1.31% of England's population call themselves "Mixed",[49] and The Sunday Times reported in 2007 that mixed race people are likely to be the largest ethnic minority in the UK by 2020.[50]
Ethnic minorities and English identity[edit]
Some recent migrants to England and their descendants have assumed a solely British identity, while others have developed dual or hyphenated identities.[51][52]. Use of the word "English" to describe Britons from ethnic minorities in England is complicated by most non-white people in England identifying as British rather than English. In their 2004 Annual Population Survey, the Office of National Statistics compared the ethnic identities of British people with their perceived national identity. They found that while 58% of white people described their nationality as "English", the vast majority of non-white people called themselves "British".[53]
Resurgence of English identity[edit]
The 1990s witnessed a revival in English self-consciousness.[54] This is linked to the expressions of national self-awareness of the other British nations of Wales and Scotland — which take their most solid form in the new devolved political arrangements within the United Kingdom — and the waning of a shared British national identity with the growing distance between the end of the British Empire and the present.[55][56][57]
As England lacks its own devolved parliament, its laws are created only in the UK parliament, giving rise to the "West Lothian question", a reference to the situation in which a law affecting only England can be voted for or against by a Scottish MP.[58] Consequently, groups such as the Campaign for an English Parliament are calling for the creation of a devolved English Parliament, claiming that there is now a discriminative democratic deficit against the English. A rise in English self-consciousness has resulted, with increased use of the English flag.[54] Writer Paul Johnson has suggested that like most dominant groups, the English have only demonstrated interest in their ethnic self-definition when they were feeling oppressed.[59]
Opinion polls show support for a devolved English parliament from about two thirds of the residents of England as well as support from both Welsh and Scottish nationalists.[60][61][62] Conversely, the English Democrats gained just 14,506 votes in the 2005 UK general election. However, in the 2009 mayoral elections Peter Davies of the English Democrats became mayor of Doncaster.[63]
While prescriptions of English national identity can involve beliefs in common descent, most political English nationalists do not consider Englishness to be dependent upon kinship[64]
English ancestry abroad[edit]
English diaspora[edit]
From the earliest times English people have left England to settle in other parts of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, but it is not possible to identify their numbers, as British censuses have historically not invited respondents to identify themselves as English.[65] However, the census does record place of birth, revealing that 8.08% of Scotland's population,[66] 3.66% of the population of Northern Ireland[67] and 20% of the Welsh population were born in England.[68] Similarly, the census of the Republic of Ireland does not collect information on ethnicity, but it does record that there are over 200,000 people living in Ireland who were born in England and Wales.[7]

English emigrant and ethnic descent communities are found across the world, and in some places, settled in significant numbers. Substantial populations descended from English colonists and immigrants exist in the United States, Canada, Australia, South Africa and New Zealand.
In the 2000 United States Census, 24,509,692 Americans described their ancestry as wholly or partly English. In addition, 1,035,133 recorded British ancestry.[69] In the 1980 United States Census 50 million Americans claimed English ancestry.[70]
In the 2006 Canadian Census, 'English' was the most common ethnic origin (ethnic origin refers to the ethnic or cultural group(s) to which the respondent's ancestors belong[71]) recorded by respondents; 6,570,015 people described themselves as wholly or partly English, 16% of the population.[72] On the other hand people identifying as Canadian but not English may have previously identified as English before the option of identifying as Canadian was available.[73]
In Australia, the 2006 Australian Census recorded 6,298,945 people who described their ancestry, but not ethnicity, as 'English'. 1,425,559 of these people recorded that both their parents were born overseas.
Significant numbers of people with at least some English ancestry also live in Scotland and Wales, as well as in Ireland, Chile, Argentina, New Zealand, and South Africa.
Since the 1980s there have been increasingly large numbers of English people, estimated at over 3 million, permanently or semi-permanently living in Spain and France, drawn there by the climate and cheaper house prices.[citation needed]
Culture[edit]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (September 2009) |
The culture of England is sometimes difficult to separate clearly from the culture of the United Kingdom,[74] so influential has English culture been on the cultures of the British Isles and, on the other hand, given the extent to which other cultures have influenced life in England.
Institutions and politics[edit]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (September 2009) |
See also[edit]
- British People
- List of English people
- Anglo-Scot
- Anglo-Irish
- Old English (Ireland)
- English American
- English Australian
- New Zealand European
- Anglosphere
- Anglo Argentines
- British Chilean
- English Canadian
- List of Anglo-Indians
- English Brazilian
- English language
- Old English language
- Cumbric language
- Culture of England
- Immigration to the United Kingdom (1922-present day)
- Population of England (historical estimates)
- German-Briton
- Anglo-Indian
- Anglo-Burmese
- Anglo-African
- English folklore
- 100% English (Channel 4 TV programme, 2006)
- Manx people
- Genetic history of Europe
- European ethnic groups
References[edit]
- ^ The CIA World Factbook reports that in the 2001 UK census 92.1% of the UK population were in the White ethnic group, and that 83.6% of this group are in the English ethnic group. The UK Office for National Statistics reports a total population in the UK census of 58,789,194. A quick calculation shows this is equivalent to 45,265,093 people in the English ethnic group; however, this number may not represent a self-defined ethnic group because the 2001 census did not in fact offer "English" as an option under the 'ethnicity' question (the CIA's figure was presumably arrived at by calculating the number of people in England who listed themselves as "white").
- ^ Census 2008 ACS Ancestry estimates
- ^ (Ethnic origin) The 2006 Canadian Census gives 1,367,125 respondents stating their ethnic origin as English as a single response, and 5,202,890 including multiple responses, giving a combined total of 6,570,015.
- ^ (Ancestry) The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports 6,358,880 people of English ancestry in the 2001 Census.[1].
- ^ (Ethnic origin) The 2006 New Zealand census reports 44,202 people (based on pre-assigned ethnic categories) stating they belong to the English ethnic group. The 1996 census used a different question to both the 1991 and the 2001 censuses, which had "a tendency for respondents to answer the 1996 question on the basis of ancestry (or descent) rather than 'ethnicity' (or cultural affiliation)" and reported 281,895 people with English origins; See also the figures for 'New Zealand European'.
- ^ Scotland's Census 2001: Supporting Information (PDF; see p. 43); see also Philip Johnston, "Tory MP leads English protest over census", Daily Telegraph 15 June, 2006.
- ^ 'Developing the Questionnaires', National Statistics Office.
- ^ a b
Simpson, John (1989-03-30). The Oxford English Dictionary: second edition. Oxford: Clarendon Press. pp. English. ISBN 0198611862.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ The archaeology of black Britain, Channel 4, accessed 21 December 2009.
- ^ Hills, Catherine (2003) "The Origins of the English" p. 18. Duckworth Debates in Archaeology. Duckworth. London. ISBN 0 7156 3191 8
- ^ Gildas, The Ruin of Britain &c. (1899). pp. 4-252. The Ruin of Britain
- ^ celtpn
- ^ a b Oppenheimer, S. (2006). The Origins of the British: A Genetic Detective Story: Constable and Robinson, London. ISBN 978-1-84529-158-7.
- ^ Britain BC: Life in Britain and Ireland before the Romans by Francis Pryor, p. 122. Harper Perennial. ISBN 0-00-712693-X.
- ^ Todd, Malcolm. "Anglo-Saxon Origins: The Reality of the Myth", in Cameron, Keith. The nation: myth or reality?. Intellect Books, 1994, accessed December 21, 2009.
- ^ "English and Welsh are Races Apart", BBC, 30 June 2002
- ^ "Found: Migrants with the Mostest", Robert Winnett and Holly Watt, The Sunday Times, 10 June 2006
- ^ Julie Wheldon. We're all Germans! (and we have been for 1,600 years), The Daily Mail, 19 July 2006
- ^ The BBC article claims a 50-100% "wipeout" of "indigenous British" by Anglo-Saxon "invaders", while the original article (Y Chromosome Evidence for Anglo-Saxon Mass Migration Michael E. Weale et al., in Molecular Biology and Evolution 19 [2002]) claims only a 50-100% "contribution" of "Anglo-Saxons" to the current Central English male population, with samples deriving only from central England; the conclusions of this study have been questioned in Cristian Capelli, et al., A Y Chromosome Census of the British Isles Current Biology, 13 (2003). The Times article reports Richard Webber's OriginsInfo database, which does not use the word 'ethnic' and acknowledges that its conclusions are unsafe for many groups; see "Investigating Customers Origins", OriginsInfo.
- ^ Capelli, C., N. Redhead, J. K. Abernethy, F. Gratrix, J. F. Wilson, T. Moen, T. Hervig, M. Richards, M. P.H. Stumpf, P. A. Underhill, P. Bradshaw, A. Shaha, M. G. Thomas, N. Bradman and D. B. Goldstein A Y Chromosome Census of the British Isles Current Biology, 13 (2003).
- ^ A United Kingdom? Maybe NY Times
- ^ http://www.omniglot.com/blog/?p=516
- ^ The Age of Athelstan by Paul Hill (2004), Tempus Publishing. ISBN 0-7524-2566-8
- ^ Athelstan (c.895–939): Historic Figures: BBC - History. Retrieved 30 October 2006.
- ^ The Battle of Brunanburh, 937AD by h2g2, BBC website. Retrieved 30 October 2006.
- ^ A. L. Rowse, The Story of Britain, Artus 1979 ISBN 0-297-83311-1
- ^ Online Etymology Dictionary by Douglas Harper (2001), List of sources used. Retrieved 10 July 2006.
- ^ The Adventure of English, Melvyn Bragg, 2003. Pg 22
- ^ OED, 2nd edition, s.v. 'English'.
- ^ England — Plantagenet Kings
- ^ BBC - The Resurgence of English 1200 - 1400
- ^ OED, s.v. 'Englishry'.
- ^ Liberation of Ireland: Ireland on the Net Website. Retrieved 23 June 2006.
- ^ A History of Britain: The British Wars 1603-1776 by Simon Schama, BBC Worldwide. ISBN 0-563-53747-7.
- ^ "Nation", sense 1. The Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edtn., 1989'.
- ^ The English, Jeremy Paxman 1998
- ^ Krishan Kumar, The Making of English National Identity (Cambridge UP, 2003), pp.1-2.
- ^ A.J.P. Taylor, English History, 1914-1945 (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1965), p. v.
- ^ Norman Davies, The Isles, [page reference needed]
- ^ EJP looks back on 350 years of history of Jews in the UK: European Jewish Press. Retrieved 21 July 2006.
- ^ Meredith on the Guillet-Thoreau Genealogy
- ^ More Britons applying for Irish passports by Owen Bowcott The Guardian, 13 September 2006. Retrieved 9 January 2006.
- ^ Black Presence, Asian and Black History in Britain, 1500-1850: UK government website. Retrieved 21 July 2006.
- ^ Postwar immigration The National Archives Accessed October 2006
- ^ "Half a million migrants pour into Britain in a year".
- ^ "Record numbers seek new lives abroad".
- ^ "Indians largest group among new immigrants to UK".
- ^ "1,500 migrants enter UK a day".
- ^ Resident population: by ethnic group, 2001: Regional Trends 38, National Statistics.
- ^ Jack Grimston, "Mixed-race Britons to become biggest minority", The Sunday Times, 21 January 2007.
- ^ "Ethnic minorities feel strong sense of identity with Britain, report reveals" Maxine Frith The Independent 8 January 2004. [2]; Hussain, Asifa and Millar, William Lockley (2006) Multicultural Nationalism Oxford University Press p149-150 [3]; CONDOR Susan; GIBSON Stephen; ABELL Jackie. (2006) "English identity and ethnic diversity in the context of UK constitutional change" Ethnicities 6:123-158 abstract; "Asian recruits boost England fan army" by Dennis Campbell, The Guardian 18 June 2006. [4]; "National Identity and Community in England" (2006) Institute of Governance Briefing No.7. [5]
- ^ Andrea Levy, "This is my England", The Guardian, February 19, 2000.
- ^ "78 per cent of Bangladeshis said they were British, while only 5 per cent said they were English, Scottish or Welsh", and the largest percentage of non-whites to identify as English were the people who described their ethnicity as "Mixed" (37%).'Identity', National Statistics, 21 Feb, 2006
- ^ a b Krishan Kumar, The Rise of English National Identity (Cambridge University Press, 1997), pp. 262-290.
- ^ Krishan Kumar. The Making of English National Identity, Cambridge University Press, 2003
- ^ English nationalism 'threat to UK', BBC, Sunday, 9 January 2000
- ^ The English question Handle with care, the Economist 1 November 2007
- ^ An English Parliament...
- ^ Quoted by Kumar, Making, p.266.
- ^ Poll shows support for English parliament The Guardian, 16 January 2007
- ^ Fresh call for English Parliament BBC 24 October 2006.
- ^ Welsh nod for English Parliament BBC 20 December 2006
- ^ http://www.doncaster.gov.uk/mayor/index.asp
- ^ 'Introduction', The Campaign for an English Parliament
- ^ Scotland's Census 2001: Supporting Information (PDF; see p. 43)
- ^ Scottish Census Results Online Browser, accessed November 16, 2007.
- ^ Key Statistics Report, p. 10.
- ^ Country of Birth: Proportion Born in Wales Falling, National Statistics, 8 January 2004.
- ^ US Census 2000 data, table PHC-T-43.
- ^ Shifting Identities - statistical data on ethnic identities in the US, American Demographics, December 1, 2001
- ^ Ethnic Origin Statistics Canada
- ^ Staff. Ethnic origins, 2006 counts, for Canada, provinces and territories - 20% sample data, Statistics Canada, 2006.
- ^ According to Canada's Ethnocultural Mosaic, 2006 Census, (p.7) "...the presence of the Canadian example has led to an increase in Canadian being reported and has had an impact on the counts of other groups, especially for French, English, Irish and Scottish. People who previously reported these origins in the census had the tendency to now report Canadian."
- ^ Krishnan Kumar - The Making of English Identity
Bibliography[edit]
- Expert Links: English Family History and Genealogy Great for tracking down historical inhabitants of England.
- Kate Fox (2004). Watching the English. Hodder & Stoughton. ISBN 0340818867.
- Krishan Kumar (2003). The Making of English National Identity. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521777364.
- Jeremy Paxman (1999). The English. Penguin Books Ltd. ISBN 0140267239.
- BBC Nations Articles on England and the English
- The British Isles Information on England
- Mercator's Atlas Map of England ("Anglia") circa 1564.
- Viking blood still flowing; BBC; 3 December 2001.
- UK 2001 Census showing 49,138,831 people from all ethnic groups living in England.
- Tory MP leads English protest over census; The Telegraph; 23 April 2001.
- On St. George's Day, What's Become Of England?; CNSNews.com; 23 April 2001.
- Watching the English – an anthropologist's look at the hidden rules of English behaviour.
- The True-Born Englishman, by Daniel Defoe.
- The Effect of 1066 on the English Language Geoff Boxell
- BBC "English and Welsh are races apart"
- New York Times, When English Eyes Are Smiling Article on the common English and Irish ethnicity
- Y Chromosome Evidence for Anglo-Saxon Mass Migration
- Origins of Britons - Brian Sykes