Quduqian
Kingdom of Quduqian | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3rd century–? | |||||||||||
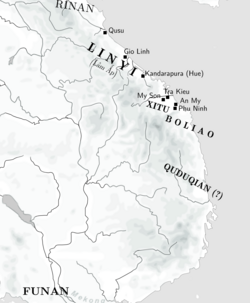 Quduqian in c. 300 AD | |||||||||||
| Common languages | Chamic languages, Bahnaric languages | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical Antiquity | ||||||||||
• Established | 3rd century | ||||||||||
• Disestablished | ? | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Vietnam | ||||||||||
Quduqian (Chinese: 屈都乾; pinyin: Qūdūqián) was the Chinese designation for an ancient kingdom, chiefdom, or a polity that perhaps located around Binh Dinh province, Central Vietnam, then became part of Champa Kingdoms.[1]
According to the Book of Jin, Quduqian situated 600 li or 186 miles/300 kilometers south of Boliao (波遼國,[2] Tam Kỳ). Quduqian sent an embassy to the Jin court in Luoyang in 286 AD.[3]
See also[edit]
- History of Champa
- Other early states in Central Vietnam
References[edit]
- ^ Schweyer 2010, pp. 105–106.
- ^ Taiping Yulan. Vol. 790.
《外國傳》曰:從波遼國南去,乘船可三千里,到屈都乾國地。有人民可二千餘家,皆曰朱吾縣民,叛居其中。
- ^ Miksic & Yian 2016, p. 186.
Sources[edit]
- Miksic, John Norman; Yian, Goh Geok (2016). Ancient Southeast Asia. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-41573-554-4.
- Schweyer, Anne-Valérie (2010). "The Birth of Champa". Crossing Borders in Southeast Asian Archaeology, Berlin: 102–117 – via HAL.
| History of Champa |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
