Portal:Stars/Selected article/15

Stellar nucleosynthesis is the collective term for the nucleosynthesis, or nuclear reactions, taking place in stars to build the nuclei of the elements heavier than hydrogen. Some small quantity of these reactions also occur on the stellar surface under various circumstances. For the creation of elements during the explosion of a star, the term supernova nucleosynthesis is used.
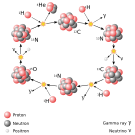
The processes involved began to be understood early in the 20th century, when it was first realized that the energy released from nuclear reactions accounted for the longevity of the Sun as a source of heat and light. The prime energy producer in the sun is the fusion of hydrogen to helium, which occurs at a minimum temperature of 3 million kelvin.
Hydrogen burning is an expression that astronomers sometimes use for the stellar process that results in the nuclear fusion of four protons to form a nucleus of helium-4. (This should not be confused with the combustion of hydrogen in an oxidizing atmosphere.) There are two predominant processes by which stellar hydrogen burning occurs.
