Hurdiidae
| Hurdiidae Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Stanleycaris (top left), Hurdia (top right), Aegirocassis (middle), Peytoia (bottom left), Cambroraster (bottom right) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | †Dinocaridida |
| Order: | †Radiodonta |
| Family: | †Hurdiidae Vinther et al., 2014 |
| Genera | |
|
See text | |
Hurdiidae (synonymous with the previously named Peytoiidae[1]) is an extinct cosmopolitan family of radiodonts, a group of stem-group arthropods, which lived during the Paleozoic Era. It is the most long-lived radiodont clade, lasting from the Cambrian period to the Devonian period.
Description[edit]

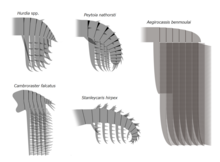

Hurdiidae is characterized by frontal appendages with distal region composed of 5 subequal blade-like endites, alongside the enlarged head carapaces and tetraradial mouthpart (oral cone).[2]
The frontal appendages of hurdiids have a distinctive morphology, with the appendage of most species bearing five equally-sized elongate blade-like ventral spines known as endites.[3] Subsequent podomeres were reduced in size and with only small endites or none. Each podomere bore only a single endite, unlike other radiodonts, in which the endites were paired.[3] In most species, the endites were curved medially, so that the appendages formed a basket-like structure.[2] Some hurdiids had greater numbers of endites, with Cordaticaris bearing seven endites of equal length.[4] Ursulinacaris is unique among hurdiids in bearing paired endites, which is likely a transitional form between the appendage of other radiodonts and that of hurdiids.[3]
Hurdiids exhibited a wide range of body size. The smallest known hurdiid specimen, of an unnamed species, is estimated to have had a body length of 6–15 millimetres (0.24–0.59 in), but it is not known whether this specimen was juvenile or adult.[5] Aegirocassis, the largest known hurdiid, was over 2 metres (6.6 ft) long, comparable in size to the largest known arthropods.[6]
Paleobiology[edit]
The majority of hurdiids appear to have been predators that fed by sifting sediment with their frontal appendages, but some members, like Aegirocassis, Pseudoangustidontus, and possibly Cambroraster were suspension feeders.[2][7][8]
Distribution[edit]
Hurdiids had a global distribution.[4] The earliest known hurdiid in the fossil record is Peytoia infercambriensis, which lived during the third age of the Cambrian in what is now the country of Poland.[9] The group increased in diversity during the Miaolingian epoch.[4] Post-Cambrian records of the group are rare, but the group lasted into the Devonian period, with the last known taxon being the Emsian Schinderhannes bartelsi from what is now Germany.[9][5]
Classification[edit]
Hurdiidae is classified within Radiodonta, a clade of stem-group arthropods. Hurdiidae is defined phylogenetically as the most inclusive clade containing Hurdia victoria but not Amplectobelua symbrachiata, Anomalocaris canadensis, or Tamisiocaris borealis.[10] Some authors have argued that Peytoiidae, which was named by Conway Morris and Robison, 1982, has priority over Hurdiidae, and that Hurdiidae has "yet to be properly established following ICZN standards".[1]
The phylogeny of hurdiids, accompanying the description of the hurdiids Aegirocassis benmoulae, Titanokorys gainesii, and the analyzation of Stanleycaris hirpex as follows:[6]
| Phylogenetic position of hurdiid radiodonts after Moysiuk & Caron 2022.[11] |
Species include
- Buccaspinea cooperi[12]
- Cambroraster falcatus[13]
- Cordaticaris striatus[13]
- Hurdia triangulata[13]
- Hurdia victoria[13]
- Hurdia hospes[14]
- Huangshandongia yichangensis [15]
- Liantuoia inflata[15]
- Pahvantia hastata[13]
- Peytoia nathorsti[13]
- Peytoia infercambriensis[3]
- Schinderhannes bartelsi[13]
- Stanleycaris hirpex[13]
- Titanokorys gainesii[13]
- Ursulinacaris grallae[3]
- Zhenghecaris shankouensis?[13]
- Aegirocassisinae
References[edit]
- ^ a b McCall, Christian R.A. (2023-12-13). "A large pelagic lobopodian from the Cambrian Pioche Shale of Nevada". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (5): 1009–1024. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.63. ISSN 0022-3360. S2CID 266292707.
- ^ a b c Moysiuk, J.; Caron, J.-B. (2019-08-14). "A new hurdiid radiodont from the Burgess Shale evinces the exploitation of Cambrian infaunal food sources". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 286 (1908): 20191079. doi:10.1098/rspb.2019.1079. PMC 6710600. PMID 31362637.
- ^ a b c d e Pates, Stephen; Daley, Allison C.; Butterfield, Nicholas J. (2019). "First report of paired ventral endites in a hurdiid radiodont". Zoological Letters. 5 (1): 18. doi:10.1186/s40851-019-0132-4. ISSN 2056-306X. PMC 6560863. PMID 31210962.
- ^ a b c Sun, Zhixin; Zeng, Han; Zhao, Fangchen (2020). "A new middle Cambrian radiodont from North China: Implications for morphological disparity and spatial distribution of hurdiids". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 558: 109947. Bibcode:2020PPP...55809947S. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109947. ISSN 0031-0182. S2CID 224868404.
- ^ a b Pates, Stephen; Botting, Joseph P.; McCobb, Lucy M. E.; Muir, Lucy A. (2020). "A miniature Ordovician hurdiid from Wales demonstrates the adaptability of Radiodonta". Royal Society Open Science. 7 (6): 200459. Bibcode:2020RSOS....700459P. doi:10.1098/rsos.200459. PMC 7353989. PMID 32742697.
- ^ a b Van Roy, Peter; Daley, Allison C.; Briggs, Derek E. G. (2015). "Anomalocaridid trunk limb homology revealed by a giant filter-feeder with paired flaps". Nature. 522 (7554): 77–80. Bibcode:2015Natur.522...77V. doi:10.1038/nature14256. PMID 25762145. S2CID 205242881.
- ^ De Vivo, Giacinto; Lautenschlager, Stephan; Vinther, Jakob (2021-07-28). "Three-dimensional modelling, disparity and ecology of the first Cambrian apex predators". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 288 (1955): 20211176. doi:10.1098/rspb.2021.1176. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 8292756. PMID 34284622.
- ^ a b Potin, G. J.-M.; Gueriau, P.; Daley, A. C. (2023). "Radiodont frontal appendages from the Fezouata Biota (Morocco) reveal high diversity and ecological adaptations to suspension-feeding during the Early Ordovician". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 11. 1214109. doi:10.3389/fevo.2023.1214109.
- ^ a b Daley, Allison C.; Legg, David A. (2015). "A morphological and taxonomic appraisal of the oldest anomalocaridid from the Lower Cambrian of Poland". Geological Magazine. 152 (5): 949–955. Bibcode:2015GeoM..152..949D. doi:10.1017/S0016756815000412. S2CID 130745134.
- ^ Vinther, Jakob; Stein, Martin; Longrich, Nicholas R.; Harper, David A. T. (2014). "A suspension-feeding anomalocarid from the Early Cambrian" (PDF). Nature. 507 (7493): 496–499. Bibcode:2014Natur.507..496V. doi:10.1038/nature13010. PMID 24670770. S2CID 205237459.
- ^ Moysiuk, Joseph; Caron, Jean-Bernard (2022-07-08). "A three-eyed radiodont with fossilized neuroanatomy informs the origin of the arthropod head and segmentation". Current Biology. 32 (15): 3302–3316.e2. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2022.06.027. ISSN 0960-9822. PMID 35809569. S2CID 250361698.
- ^ Pates S, Lerosey-Aubril R, Daley AC, Kier C, Bonino E, Ortega-Hernández J. 2021. The diverse radiodont fauna from the Marjum Formation of Utah, USA (Cambrian: Drumian) PeerJ 9:e10509 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.10509
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Caron, Jean-Bernard; Moysiuk, Joe (2021). "A giant nektobenthic radiodont from the Burgess Shale and the significance of hurdiid carapace diversity". R. Soc. Open Sci. 8 (210664): 210664. Bibcode:2021RSOS....810664C. doi:10.1098/rsos.210664. PMC 8424305. PMID 34527273.
- ^ Chlupač, Ivo; Kordule, Vratislav (2002). "Arthropods of Burgess Shale type from the Middle Cambrian of Bohemia (Czech Republic)". Bulletin of the Czech Geological Survey. 77 (3): 167–182.
- ^ a b Zhilin, Cui; Shicheng, Huo (1990). "鄂西下寒武统甲壳类化石新发现". Acta Palaeontologica Sinica.








