Cyanobacterin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
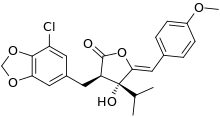
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3R,4R,5Z)-3-[(7-Chloro-2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-hydroxy-5-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methylidene]-4-(propan-2-yl)oxolan-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H23ClO6 | |
| Molar mass | 430.88 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cyanobacterin is a chemical compound produced by the cyanobacteria Scytonema hofmanni. It is a photosynthesis inhibitor with algaecidal and herbicidal effects.[1][2]
References[edit]
- ^ Gleason, FK; Case, DE (April 1986). "Activity of the natural algicide, cyanobacterin, on angiosperms". Plant Physiology. 80 (4): 834–7. doi:10.1104/pp.80.4.834. PMC 1075215. PMID 16664727.
- ^ Berry, John P. (June 2008). "Cyanobacterial Toxins as Allelochemicals with Potential Applications as Algaecides, Herbicides and Insecticides". Marine Drugs. 6 (2): 117–146. doi:10.3390/md6020117. PMC 2525484. PMID 18728763.
