Archimedes' heat ray
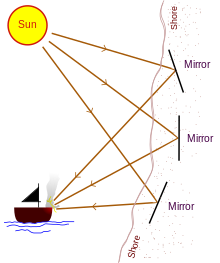
Archimedes' heat ray is a device that Archimedes is purported to have used to burn attacking Roman ships during the Siege of Syracuse (c. 213–212 BC). It does not appear in the surviving works of Archimedes and is described by historians writing many years after the siege.
Historical accounts of the heat ray[edit]
The 2nd century AD author Lucian wrote that during the Siege of Syracuse, Archimedes destroyed enemy ships with fire. Seven centuries later, Anthemius of Tralles mentions burning-glasses as Archimedes' weapon. The device was used to focus sunlight onto approaching ships, causing them to catch fire.[1]
Modern attempts to recreate the heat ray[edit]

The heat ray has been the subject of ongoing debate about its credibility since the Renaissance. René Descartes rejected it as false,[2] a test was conducted by Comte de Buffon (circa 1747), documented in the paper titled "Invention De Miroirs Ardens, Pour Brusler a Une Grande Distance", and an experiment by John Scott, documented in an 1867 paper.[3]
A test of the Archimedes heat ray was carried out in 1973 by the Greek scientist Ioannis Sakkas. The experiment took place at the Skaramagas naval base outside Athens. On this occasion, 70 mirrors were held up by Greek sailors, each with a copper coating and a size of around five by three feet (1.5 by 1 m). The mirrors were pointed at a plywood mock-up of a Roman warship at a distance of around 160 feet (50 m). When the mirrors were focused accurately, the ship burst into flames within a few seconds. The plywood ship had a coating of tar paint. Sakkas said after the experiment there was no doubt in his mind the great inventor could have used bronze mirrors to scuttle the Romans.[4][5]
In 2008, TV show Richard Hammond's Engineering Connections aired an episode, Deep Space Observer (S1E3), about the Keck Observatory, whose reflector glass is based on the Archimedes' Mirror. The episode demonstrated the use of a much smaller curved mirror to burn a wooden model.[6][7]
In 2004, the TV show MythBusters found mirrors implausible (s2e5 Ancient Death Ray). In 2005, a group of students from MIT carried out an experiment with 127 one-foot (30 cm) square mirror tiles, focused on a mock-up wooden ship at a range of around 100 feet (30 m). Flames broke out on a patch of the ship, but only after the sky had been cloudless and the ship had remained stationary for around ten minutes. It was concluded that the device was a feasible weapon under these conditions. The MIT group repeated the experiment for MythBusters (s4e3 Archimedes Death Ray), using a wooden fishing boat in San Francisco as the target. Again some charring occurred, along with a small amount of flame. When MythBusters broadcast the result of the San Francisco experiment in 2006, the claim was placed in the category of "busted" (or failed) because of the length of time and the ideal weather conditions required for combustion to occur. It was pointed out that since Syracuse faces the sea towards the east, the Roman fleet would have had to attack during the morning for optimal gathering of light by the mirrors. MythBusters also pointed out that conventional weaponry, such as flaming arrows or bolts from a catapult, would have been a far easier way of setting a ship on fire at short distances.[8] In December 2010, MythBusters again (s8e17 President's Challenge) looked at the heat ray. Several more experiments were carried out, including a large-scale test with 500 schoolchildren aiming mirrors at a mock-up of a Roman sailing ship 400 feet (120 m) away. In all of the experiments, the sail failed to reach the 210 °C (410 °F) required to catch fire, and the verdict was again "busted". The show concluded that a more likely effect of the mirrors would have been blinding, dazzling, or distracting the crew of the ship.[9]
See also[edit]
- Claw of Archimedes – Greek anti-ship weapon used in 213–212 BC
- Heliostat – Solar tracking device
- Sambuca (siege engine) – Ship-borne siege engine
- Solar furnace – Focal point for concentrated sunlight; contains working fluid to be heated
References[edit]
- ^ Hippias, 2 (cf. Galen, On temperaments 3.2, who mentions pyreia, "torches"); Anthemius of Tralles, On miraculous engines 153 [Westerman].
- ^ John Wesley. "A Compendium of Natural Philosophy (1810) Chapter XII, Burning Glasses". Online text at Wesley Center for Applied Theology. Archived from the original on 2007-10-12. Retrieved 2007-09-14.
- ^ skullsinthestars (2010-02-07). "Mythbusters were scooped — by 130 years! (Archimedes death ray)". Skulls in the Stars. Retrieved 2022-12-07.
- ^ "Archimedes and his Burning Mirrors, Reality or Fantasy?". www.mlahanas.de. Retrieved 2022-12-07.
- ^ "Archimedes' Weapon". Time Magazine. November 26, 1973. Archived from the original on 2011-02-04. Retrieved 2007-08-12.
- ^ Richard Hammond Engineering Connections S01E03 - Deep Space Observatory - Keck, Hawaii, retrieved 2022-12-07
- ^ Metcalfe, Nick (2010-12-23), Deep Space Observer, Engineering Connections, retrieved 2022-12-07
- ^ "Archimedes Death Ray: Testing with MythBusters". MIT. Archived from the original on 2013-05-28. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ "TV Review: MythBusters 8.27 – President's Challenge". 2010-12-13. Retrieved 2010-12-18.


