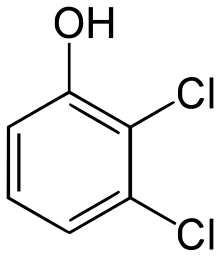
2,3-Dichlorophenol
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dichlorophenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 2043615 | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.546 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2020 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4Cl2O | |
| Molar mass | 163.00 g·mol−1 |
| Odor | Phenolic |
| Melting point | 56.8 °C (134.2 °F; 329.9 K)[2] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.44[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H311, H314, H411 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2,3-Dichlorophenol (2,3-DCP) is a chlorinated derivative of phenol with the molecular formula Cl2C6H3OH.
References[edit]
Cited sources[edit]
- Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 9781498754293.

