Wikipedia:Picture of the day/Archive
|
Featured picture tools: |
These featured pictures, as scheduled below, appeared as the picture of the day (POTD) on the English Wikipedia's Main Page in the last 30 days.
You can add an automatically updating POTD template to your user page using {{Pic of the day}} (version with blurb) or {{POTD}} (version without blurb). For instructions on how to make custom POTD layouts, see Wikipedia:Picture of the day.Purge server cache
April 19

|
Picea omorika, commonly known as the Pančić spruce or the Serbian spruce, is a species of coniferous tree endemic to the valley of the Drina in western Serbia, and eastern Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a total range of only about 60 hectares (150 acres) at altitudes of 800 to 1,600 metres (2,625 to 5,249 ft). The species was originally discovered near the Serbian village of Zaovine on Mount Tara in 1875, and named by the Serbian botanist Josif Pančić. It is a medium-sized evergreen tree that generally grows to a height of around 20 metres (66 ft), with a trunk diameter of up to 1 metre (3 ft). It has buff-brown shoots with dense hair coverage and needle-like leaves. Its cones are fusiform in shape and grow to a length of 4 to 7 centimetres (2 to 3 in). They are dark purple when young, maturing to dark brown, and have stiff scales. This young female P. omorika cone, with a length of 22 millimetres (0.87 in), was photographed near Keila, Estonia. Photograph credit: Ivar Leidus
Recently featured:
|
April 18
|
A basso porto (At the Lower Harbour) is an opera in three acts by the Italian composer Niccola Spinelli. The opera sets an Italian-language libretto by Eugene Checchi, based on Goffredo Cognetti's 1889 play O voto. It premiered to critical success at the Cologne Opera on April 18, 1894, sung in a German translation by Ludwig Hartmann and Otto Hess. This watercolour illustration depicts the set design by Riccardo Salvadori for act 1 of the opera's premiere. A basso porto is set in the slums of Naples, and Spinelli included mandolins and guitars in his orchestral score. Set design credit: Riccardo Salvadori
Recently featured:
|
April 17

|
The American white pelican (Pelecanus erythrorhynchos) is a large aquatic soaring bird from the order Pelecaniformes. It breeds in interior North America, moving south and to the coasts, as far as Costa Rica, in winter. Along with the trumpeter swan, it is one of the longest birds native to North America, with an overall length of about 50 to 70 inches (130 to 180 cm). The beak measures 11.3 to 15.2 inches (290 to 390 mm) in males and 10.3 to 14.2 inches (260 to 360 mm) in females, while its wingspan is around 95 to 120 inches (240 to 300 cm). The American white pelican does not dive for its food as some other pelican species do, instead catching its prey while swimming. Each bird eats more than 4 pounds (1.8 kg) of food a day, predominantly fish, which ranges from the size of minnows to 3.5-pound (1.6 kg) pickerels. This adult American white pelican in non-breeding plumage was photographed at Las Gallinas Wildlife Ponds in San Rafael, California. Photograph credit: Frank Schulenburg
Recently featured:
|
April 16

|
|
Jean Ignace Isidore Gérard (1803–1847) was a French illustrator and caricaturist who published under the pseudonym of Jean-Jacques Grandville or J. J. Grandville. He has been called "the first star of French caricature's great age", and Grandville's book illustrations described as featuring "elements of the symbolic, dreamlike, and incongruous, and they retain a sense of social commentary". The anthropomorphic vegetables and zoomorphic figures that populated his cartoons anticipated and influenced the work of generations of cartoonists and illustrators including John Tenniel, Gustave Doré, Félicien Rops, and Walt Disney. He has also been called a "proto-surrealist" and was greatly admired by André Breton and others in the Surrealist movement. This illustration by Grandville is plate 52 from a 1854 collection of hand-coloured lithographs titled Les métamorphoses du jour (The Metamorphoses of the Day), and depicts five anthropomorphic male dogs following a female dog, all dressed in human clothing. The print is captioned "Temps de canicule", meaning 'heatwave weather' but incorporating a pun in French; canicule literally translates to 'dog days of summer' and may also refer here to animals being 'in heat'. Illustration credit: Jean Ignace Isidore Gérard; restored by Adam Cuerden
Recently featured:
|
April 15

|
The Notre-Dame fire was a structural fire that broke out in the roof space of Notre-Dame de Paris, a medieval Catholic cathedral in Paris, France, on 15 April 2019. By the time the fire was extinguished, the cathedral's wooden spire (flèche) had collapsed, most of the wooden roof had been destroyed, and the cathedral's upper walls were severely damaged. Extensive damage to the interior was prevented by the vaulted stone ceiling, which largely contained the burning roof as it collapsed. Many works of art and religious relics were moved to safety, but others suffered smoke damage, and some of the exterior art was damaged or destroyed. The cathedral's altar, two pipe organs, and three 13th-century rose windows suffered little or no damage. Three emergency workers were injured, and the site and nearby areas of Paris were contaminated with toxic dust and lead. Investigators in 2020 believed the fire to have been "started by either a cigarette or a short circuit in the electrical system". French president Emmanuel Macron set a five-year deadline to restore the cathedral. This photograph shows the central section of Notre-Dame's spire engulfed in flames. Photograph credit: Guillaume Levrier
Recently featured:
|
April 14

|
Nassarius arcularia, commonly known as the casket nassa or the little box dog whelk, is a species of sea snail in the Nassa mud snail or dog whelk family, Nassariidae. It is found in tropical and subtropical coastal waters across the world, inhabiting muddy areas close to the shoreline. The shell, which is very common, has a thickness of up to 3 centimetres (1.2 inches) and varies in form – for example, in the elongation of the whorls and the longitudinal folds – as well as in color, with some specimens entirely white while others have brown bands. The young of this species have folds and striae that are much more prominent. This composite photograph shows five different views of a N. arcularia shell, with a length of 2.2 centimetres (0.87 inches), that was collected in Madagascar. Photograph credit: H. Zell
Recently featured:
|
April 13

|
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). In addition to lead, some deposits contain up to 0.5 percent silver, in the form of silver sulfide or as limited silver in solid solution; when present, this byproduct far surpasses the main lead ore in revenue. Galena has been used since antiquity, one of its oldest uses being the production of kohl, an eye cosmetic now regarded as toxic due to the risk of lead poisoning. In modern times, galena is primarily used to extract its constituent minerals. In addition to silver, it is the most important global source of lead, for uses such as in lead-acid batteries. This sample of galena, measuring 3.5 cm × 2.5 cm × 2.0 cm (1.38 in × 0.98 in × 0.79 in), contains a small amount of gold-colored pyrite and was extracted from the Huanzala Mine in the Peruvian region of Ancash. This photograph was focus-stacked from 156 separate images. Photograph credit: Ivar Leidus
Recently featured:
|
April 12

|
|
The orange chat (Epthianura aurifrons) is a species of bird in the honeyeater family, Meliphagidae, endemic to Australia. With a length of around 10 to 12 centimetres (3.9 to 4.7 inches) and average wingspan of 19 centimetres (7.5 inches), it is a small ground songbird with relatively long, broad and rounded wings and a short square-ended tail. The male's feathers are mostly a deep, warm, cadmium yellow with orange overtones, and this colour is strongest on the crown and breast. Females are mottled in grey-brown, with underparts a softer fawny yellow. Its diet consists mainly of small insects, spiders and other invertebrates that are on the ground or shrubs. Its call consists of a metallic twang tang and a softer tchek tchek sound. This orange chat perched on a twig was photographed near Lake Cargelligo in New South Wales, Australia. Photograph credit: John Harrison
Recently featured:
|
April 11

|
The Maison carrée (French for 'square house') is an ancient Roman temple in Nîmes, southern France. It is a mid-sized Augustan provincial temple of the imperial cult, and one of the best-preserved Roman temples to survive in the territory of the former Roman Empire. Built in the early 1st century AD, it was dedicated or rededicated to Gaius and Lucius Caesar, grandsons and adopted heirs of Augustus, who both died young. The Maison carrée is similar to a Tuscan-style Roman temple as described in the writings of Vitruvius, a contemporary Roman writer on architecture. It has undergone several restorations over the centuries and was inscribed on the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites in 2023. This photograph of the Maison carrée at evening was taken in 2019. Photograph credit: Krzysztof Golik
Recently featured:
|
April 10

|
The gatekeeper (Pyronia tithonus) is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae, found across Europe. It is typically orange with two large brown spots on its wings and a brown pattern on the edge of its wings, although a large number of aberrant forms are known. The eyespots on the forewings most likely reduce bird attacks, so it is often seen resting with its wings open. Colonies vary in size depending on the available habitat, and can range from a few dozen to several thousand butterflies. This gatekeeper was photographed in Botley in Oxfordshire, England. Photograph credit: Charles J. Sharp
Recently featured:
|
April 9

|
|
The Andasol solar power station is a 150-megawatt concentrated solar power station and Europe's first commercial plant to use parabolic troughs. Located near Guadix in Andalusia, Spain, the Andasol plant uses tanks of molten salt as thermal energy storage to continue generating electricity, irrespective of whether the sun is shining or not. It consists of three projects, completed in 2008, 2009 and 2011, and occupying a total area of about 200 hectares (490 acres). Because of its high altitude (1,100 m; 3,600 ft) and the semi-arid climate, the site has exceptionally high annual direct insolation. This aerial view of the Andasol plant was taken in 2021, with the snow-capped peaks of the Sierra Nevada in the background. Photograph credit: kallerna
Recently featured:
|
April 8

|
Nithya Menen (born 8 April 1988) is an Indian actress and singer who works primarily in Malayalam, Tamil and Telugu films. After appearing in roles in 1998 and 2006 as a child actress, her first lead role was in the Malayalam film Aakasha Gopuram, which was released in 2008. Her debut in leading roles in Telugu and Tamil films were Ala Modalaindi (2011) and Nootrenbadhu (2011). Her Hindi debut was Mission Mangal (2019). As of 2024, Menen has appeared in more than 50 films and has appeared in several lists of top actresses compiled by Rediff.com and Forbes India. This portrait photograph of Menen was taken in 2023. Photograph credit: Augustus Binu
Recently featured:
|
April 7

|
The bell miner (Manorina melanophrys), also known as the bellbird, is a colonial honeyeater species endemic to southeastern Australia. The name miner is derived from an old alternative spelling of myna, and is shared with other members of the genus Manorina. The birds feed almost exclusively on the dome-like coverings, referred to as "bell lerps", of certain psyllid bugs that feed on eucalyptus sap from the leaves. The psyllids make these bell lerps from their own honeydew secretions in order to protect themselves from predators and the environment. This bell miner was photographed on the Nepean River in Penrith, New South Wales. Photograph credit: John Harrison
Recently featured:
|
April 6

|
|
The Battle of Shiloh, also known as the Battle of Pittsburg Landing, was a major battle in the American Civil War fought on April 6–7, 1862. The fighting took place in southwestern Tennessee, which was part of the war's western theater. Two Union armies combined to defeat the Confederate Army of Mississippi. Major General Ulysses S. Grant was the Union commander, while General Albert Sidney Johnston was the Confederate commander until his battlefield death, when he was replaced by his second-in-command, General P. G. T. Beauregard. Though victorious, the Union army had more casualties than the Confederates, and with an overall total of almost 24,000 injuries and fatalities, it was one of the bloodiest battles in the entire war. This chromolithograph of the Battle of Shiloh was produced by American illustrator Thure de Thulstrup and printed by L. Prang & Co. in Boston in 1888. Illustration credit: Thure de Thulstrup; restored by Adam Cuerden |
April 5

|
Oligodon, commonly known as the kukri snakes, form a genus of colubrid snakes that was first described by Austrian zoologist Leopold Fitzinger in 1826. This genus is widespread throughout central and tropical Asia. This photograph shows a Hua Hin kukri snake (Oligodon huahin), in Kaeng Krachan National Park, Thailand. Photograph credit: Rushen
Recently featured:
|
April 4

|
Al-Wakwak is an island, or possibly more than one island, in medieval Arabic geographical and imaginative literature. Sources variously identify al-Wakwak as representing Japan, Madagascar, Sumatra or Java, with others describing it as an island in the China Sea ruled by a queen with an entirely female population. This painting in watercolor and gold on paper was created in Mughal India in the early 1600s, and depicts a plant that brings forth animal life in multiple forms, derived from a conflation of medieval Persian and Quranic sources, including descriptions of al-Wakwak as inhabited by half-plant and half-animal creatures. The work is now in the collection of the Cleveland Museum of Art in Ohio. Painting credit: unknown
Recently featured:
|
April 3
|
Sojourner is a robotic Mars rover that landed in Ares Vallis, a channel in the Chryse Planitia region, on July 4, 1997. Sojourner was operational on Mars for 92 sols (95 Earth days). It was the first wheeled vehicle to rove on a planet other than Earth and formed part of the Mars Pathfinder mission. This panoramic photograph is formed of various images of Sojourner taken by the Mars Pathfinder lander, composited into a 360-degree image referred to by NASA as the "presidential" panorama. Since the camera's position was consistent, it is possible to see these images of the rover in the context of the entire landscape.
Recently featured:
|
April 2

|
|
The European bee-eater (Merops apiaster) is a bird in the bee-eater family, Meropidae. It breeds in southern and central Europe, northern and southern Africa, and western Asia. Except for the resident southern African population, the species is strongly migratory, wintering in tropical Africa. This species, like other bee-eaters, is a richly coloured, slender bird. It has brown and yellow upper parts, whilst the wings are green and the beak is black. It can reach a length of 27–29 cm (10.6–11.4 in), including the two elongated central tail feathers. The most important prey item in its diet is Hymenoptera, mostly the European honey bee. Its impact on bee populations, however, is small. It eats less than 1% of the worker bees in areas where it lives. This group of three European bee-eaters, each with a dragonfly in its mouth, was photographed in Kondor Tanya, Kecskemét, Hungary. Photograph credit: Charles J. Sharp
Recently featured:
|
April 1

|
Nelly Martyl (1 April 1884 – 9 November 1953) was a French opera singer based in Paris who participated in several world premieres. After making her professional debut in 1907 in Gluck's Armide, she joined the Opéra-Comique, where she appeared as Micaela in Bizet's Carmen, Sophie in Massenet's Werther, Mimi in Puccini's La bohème and in the title role of Massenet's Manon, among others. During World War I and the 1918 flu epidemic, she worked as a nurse and received the Croix de Guerre for her service. After the war, she created a charitable medical foundation with automobile racer Magdeleine Goüin. This photograph of Martyl was taken by the French photographer Jean Reutlinger, probably between 1907 and 1912. Photograph credit: Jean Reutlinger; restored by Adam Cuerden
Recently featured:
|
March 31

|
The shy hamlet (Hypoplectrus guttavarius) is a small Western Atlantic species of fish in the family Serranidae. It is found predominantly around rocks and corals in Caribbean inshore areas at low depths, in temperatures of about 22 to 27 °C (72 to 80 °F). The shy hamlet has a yellow head and fins followed by a brown-black body, with bright blue stripes around the eye and on the snout. The species is carnivorous, feeding on crustaceans as well as other bony fish. This shy hamlet was photographed in an aquarium at Wilhelma, a zoological-botanical garden in Stuttgart, Germany. Photograph credit: H. Zell
Recently featured:
|
March 30

|
The City Palace of Jaipur, constructed between 1727 and 1732, is a royal residence located in Jaipur, Rajasthan, India. It was the ceremonial and administrative seat of the Kingdom of Amber, and home of its rulers, from the time of the state's foundation in 1727 by Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II until 30 March 1949. The palace continues to be a residence of the royal family of Jaipur and is a popular tourist attraction. This picture shows the Leheriya gate, one of four intricately designed gates in an inner courtyard of the palace. The gate is dedicated to Hindu god Ganesha (carved above the door) with the green colour representing the season of spring. Photograph credit: Jakub Hałun
Recently featured:
|
March 29

|
Head of Christ is a painting in oil on panel by the Italian Renaissance painter Antonio da Correggio, dated 1521. It depicts the head of Christ, wearing the crown of thorns. In the background there is a white cloth showing that the image represents the Veil of Veronica, but Christ's head is given volume through alternate use of light and dark shadows. The painting is in the J. Paul Getty Museum in Los Angeles. Correggio was known for creating some of the most sumptuous religious paintings of the period. The Getty Museum considers this artwork as one of the masterpieces of painting held by the museum. Painting credit: Antonio da Correggio
Recently featured:
|
March 28

|
|
Crepidotus is a genus of fungus in the family Crepidotaceae. Species of Crepidotus all have small, convex to fan-shaped sessile caps and grow on wood or plant debris. The species are cosmopolitan in distribution, and are well-documented from the Northern temperate to the South American regions. This Crepidotus variabilis cap growing on a branch was photographed in De Famberhorst, a nature reserve near Joure in Friesland, Netherlands. The photograph was focus-stacked from 42 separate images. Photograph credit: Dominicus Johannes Bergsma
Recently featured:
|
March 27
|
|
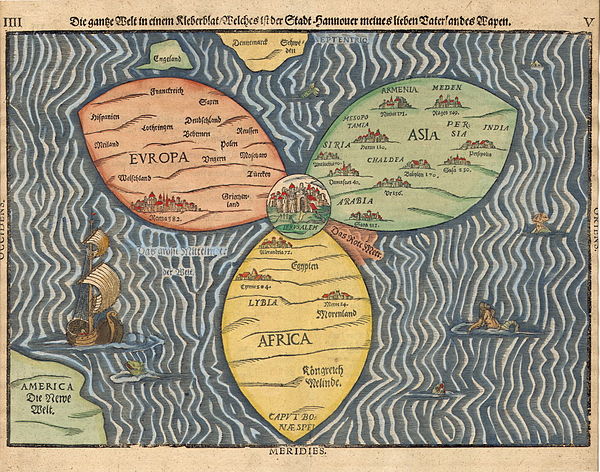
The Bünting cloverleaf map is a historic mappa mundi drawn by the German theologian and cartographer Heinrich Bünting. The map was published in his book Itinerarium Sacrae Scripturae in 1581. The map depicts the three continents of the Old World, Europe, Africa and Asia, as three leaves forming the shape of a clover, with Jerusalem at the centre. The three continents include captions for some of their countries and illustrations of cities. The clover is surrounded by the ocean, with its surface including illustrations of sea creatures, monsters, and a ship. England and Denmark are represented as two island-shapes above Europe's leaf, while the Americas are shown as a mostly unrevealed shape in the lower left corner, captioned Die Neue Welt (the New World). Map credit: Heinrich Bünting
Recently featured:
|
March 26

|
The red-browed finch (Neochmia temporalis) is a species of estrildid finch that inhabits the east coast of Australia. The species is distinguished by the bright red stripe above the eye, and bright red rump. The rest of the body is grey, with olive wing coverts and collar. Juveniles do not have red brow marks, and they lack olive colouration on the collar and wing coverts. The adults are 11 to 12 centimetres (4.3 to 4.7 inches) long. This red-browed finch was photographed in Penrith, New South Wales. Photograph credit: John Harrison
Recently featured:
|
March 25

|
Ulysses S. Grant (1822–1885) was the 18th president of the United States, in office from 1869 to 1877. He graduated from the U.S. Military Academy at West Point and retired after serving in the Mexican–American War. When the Civil War began in 1861, he rejoined the U.S. Army and won major victories at Shiloh and Vicksburg, and in the Chattanooga campaign. After promotion to Commanding General, Grant confronted Robert E. Lee in a series of bloody battles in Virginia in 1864, trapping Lee's army in the siege of Petersburg. Lee's surrender to Grant at Appomattox on April 9, 1865, ended the war. After the war, he implemented Congressional Reconstruction. Elected president in 1868, Grant led the Republicans in their effort to remove the vestiges of Confederate nationalism, protect African-American citizenship, and support economic prosperity nationwide. In foreign policy, Grant sought to increase American trade and influence, while remaining at peace with the world. His presidency has often come under criticism for tolerating corruption and, in his second term, leading the nation into an economic depression. After an unsuccessful attempt at nomination for a third term in 1880, he completed his memoirs, garnering critical acclaim and financial success. This line engraving of Grant was produced by the Bureau of Engraving and Printing (BEP) as part of a BEP presentation album of the first 26 presidents. Engraving credit: Bureau of Engraving and Printing; restored by Andrew SHiva
Recently featured:
|
March 24

|
PAGEOS (Passive Geodetic Earth Orbiting Satellite) was a balloon satellite which was launched by NASA in 1966. It was placed into a polar orbit (inclination 85–86°) with a height of approximately 4000 km, which became gradually lower during its nine years of operation. The satellite partly disintegrated in July 1975, which was followed by a second break-up that occurred in January 1976 resulting in the release of a large number of fragments. Most of these re-entered the Earth's atmosphere during the following decade. This photograph shows a test inflation of a PAGEOS satellite in a blimp hangar at Weeksville, North Carolina, in 1965. Photograph credit: NASA
Recently featured:
|
March 23

|
Frere Hall is a building in Karachi, Pakistan, built in 1865 to serve as the city's town hall during British colonial rule in the Indian subcontinent. Named in 1884 in honour of Henry Bartle Frere, a British administrator who had earlier served as Commissioner of Sind and Governor of Bombay, the building is now a library and a tourist attraction noted for its Venetian Gothic architecture, and is also used for exhibitions and events. Photographed credit: Alexander Savin
Recently featured:
|
March 22

|
Laocoön and His Sons is an ancient sculpture which was excavated in Rome, Italy, in 1506. It depicts the Trojan priest Laocoön and his sons Antiphantes and Thymbraeus being attacked by sea serpents. The figures in the statue are nearly life-sized, with the entire group measuring just over 2 metres (6 ft 7 in) in height. The statue is likely to be the same one that received praise from the Roman writer Pliny the Elder, who attributed the work (then housed in the palace of the emperor Titus) to three Greek sculptors from the island of Rhodes: Agesander, Athenodoros and Polydorus, but he did not mention the work's date or patron. Modern scholars are not certain of the work's origins; it might be an original work or a copy of an earlier bronze sculpture. After its discovery, Laocoön and His Sons was put on public display in the Vatican Museums, where it remains. Sculpture credit: attributed to Agesander, Athenodoros and Polydorus; photographed by Wilfredo Rodríguez
Recently featured:
|
March 21

|
Arabis hirsuta, also known as the hairy rock-cress, is a flowering plant of the genus Arabis in the family Brassicaceae. In previous North American works, this species has been broadly defined to include plants native to Europe, Asia, and the northern half of North America, but the name is now more often used to describe a narrower subgroup. The species grows on chalk slopes, dunes, hedgebanks, walls and rocks. Arabis hirsuta grows to a height of up to around 75 centimetres (30 inches) and is usually unbranched, with a long spike of flowers and stiff hairs. The lower leaves of the plant form a rosette, while the stalkless upper leaves clasp the stem. Flowering is from June to August. It has white petals, cylindrical fruits pressed close to the stem and reddish brown seeds. This A. hirsuta plant at the start of its flowering phase was photographed in Keila, Estonia. Photograph credit: Ivar Leidus
Recently featured:
|
Picture of the day archives and future dates

