User:Jrwst36/X-ray photoelectron diffraction
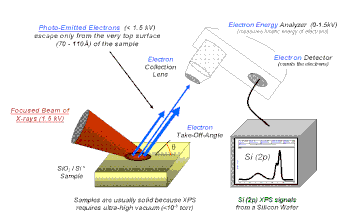
X-ray photoelectron diffraction (XPD) is a quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 1 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires ultra high vacuum (UHV) conditions.
XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its "as received" state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some of the surface contamination, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.
- XPS is also known as ESCA, an abbreviation for Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis.
- XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2) because the diameter of these orbitals is so small, reducing the catch probability to almost zero.
- Detection limits for most of the elements are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).
- XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion modified materials and many others.
XPS is used to measure:
- elemental composition of the surface (top 1–10 nm usually)
XPS can be performed using either a commercially built XPS system, a privately built XPS system or a synchrotron-based light source combined with a custom designed electron analyzer. Commercial XPS instruments in the year 2005 used either a highly focused 20 to 200 micrometer beam of monochromatic aluminium Kα X-rays or a broad 10–30 mm beam of non-monochromatic (polychromatic) magnesium X-rays. A few, special design, XPS instruments can analyze volatile liquids or gases, materials at low or high temperatures or materials at roughly 1 torr vacuum, but there are relatively few of these types of XPS systems.
Because the energy of an X-ray with particular wavelength is known, the electron binding energy of each of the emitted electrons can be determined by using an equation that is based on the work of Ernest Rutherford (1914):
where Ebinding is the binding energy (BE) of the electron, Ephoton is the energy of the X-ray photons being used, Ekinetic is the kinetic energy of the electron as measured by the instrument and φ is the work function of the spectrometer (not the material).
History
[edit]Physics
[edit]Components of an XPS system
[edit]The main components of a commercially made XPS system include:
- A source of X-rays
- An ultra-high vacuum (UHV) stainless steel chamber with UHV pumps
- An electron collection lens
- An electron energy analyzer
- Mu-metal magnetic field shielding
- An electron detector system
- A moderate vacuum sample introduction chamber
- Sample mounts
- A sample stage
- A set of stage manipulators
Uses and capabilities
[edit]XPS is routinely used to determine:
- What elements and the quantity of those elements that are present within the top 1-12 nm of the sample surface
See also
[edit]- Photoemission spectroscopy
- Ultra-violet photoelectron spectroscopy
- List of materials analysis methods
Related methods
[edit]- UPS, Ultra-violet photoelectron spectroscopy
- PES, Photoemission spectroscopy
- ZEKE, Zero Electron Kinetic Energy spectroscopy
- AES, Auger electron spectroscopy
- EDS, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, (EDX or EDXRF)
- PEEM, Photoelectron emission microscopy PEEM
References
[edit]Further reading
[edit]External links
[edit]Category:Atomic physics Category:Molecular physics Category:Spectroscopy Category:Surface chemistry Category:Scientific techniques

