Paper size: Difference between revisions
m →Tablet sizes: dab Paper ream |
→Expressing paper thickness and density: adding (paper weight) for U.S. based searchers |
||
| Line 581: | Line 581: | ||
Although the movement is toward the international standard metric paper sizes, on the way there from the traditional ones there has been at least one new size just a little larger than that used internationally. British architects and industrial designers once used a size called "Antiquarian" as listed above, but given in "New Metric Handbook," (Tutt & Adler 1981) as 813 by 1372 mm. This is a bit larger than the A0 size. So for a short time, a size called A0a was used in Britain, being 1000 mm by 1370 mm, to get that extra 100 mm on the longer side, write Tutt & Adler. |
Although the movement is toward the international standard metric paper sizes, on the way there from the traditional ones there has been at least one new size just a little larger than that used internationally. British architects and industrial designers once used a size called "Antiquarian" as listed above, but given in "New Metric Handbook," (Tutt & Adler 1981) as 813 by 1372 mm. This is a bit larger than the A0 size. So for a short time, a size called A0a was used in Britain, being 1000 mm by 1370 mm, to get that extra 100 mm on the longer side, write Tutt & Adler. |
||
==Expressing paper thickness and density== |
==Expressing paper thickness and density (paper weight)== |
||
===Grammage=== |
===Grammage=== |
||
Revision as of 21:02, 17 October 2006

There have been many standard sizes of paper at different times and in different countries, but today there are basically only two systems in place: the international standard (A4 and its siblings), and the North American sizes.
The international standard: ISO 216
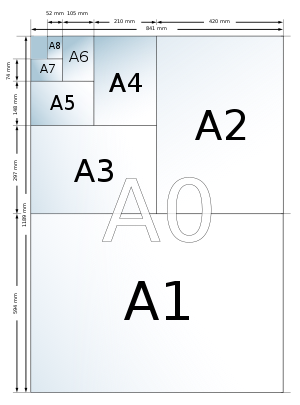
The international paper size standard, ISO 216, is based on the metric system, with the base format being a sheet of paper measuring 1 m² in area. This standard has been adopted by all countries in the world except the United States and Canada. In Mexico and the Philippines, despite the ISO standard having been officially adopted, the U.S. "Letter" format is still in common use.
The most widely known size in the ISO format is A4.
ISO paper sizes are all based on a single aspect ratio of the square root of two, or approximately 1:1.4142. The advantages of basing a paper size upon this ratio were already noted in 1768 by the German scientist Georg Lichtenberg (in a letter to Johann Beckmann). In the beginning of the twentieth century, Dr Walter Porstmann turned Lichtenberg's idea into a proper system of different paper sizes. Porstmann's system was introduced as a DIN standard (DIN 476) in Germany in 1922, replacing a vast variety of other paper formats. Even today the paper sizes are called "DIN A4" in everyday use in Germany.
The DIN 476 standard spread quickly to other countries, and before the outbreak of World War II it had been adopted by the following countries:
- Belgium (1924)
- Netherlands (1925)
- Norway (1926)
- Switzerland (1929)
- Sweden (1930)
- Soviet Union (1934)
- Hungary (1938)
- Italy (1939)
During the war it was adopted by Uruguay (1942), Argentina (1943) and Brazil (1943); and directly afterwards the standard continued to spread to other countries:
|
|
By 1975 so many countries were using the German system that it was established as an ISO standard, as well as the official United Nations document format. By 1977 A4 was the standard letter format in 88 of 148 countries, and today only the U.S. and Canada have not adopted the system.
The largest standard size, A0, has an area of 1 m². The long side of the sheet is calculated by taking the 4th root of 2, i.e. 1.189 metre and the short side is the inverse of that number, i.e. 0.841 metre. A1 is formed by cutting a piece of A0 in half, which retains the aspect ratio. This particular measurement system was chosen in order to allow folding of one standard size into another, which cannot be accomplished with traditional paper sizes.
Brochures are made by using material at the next size up i.e. material at A3 is folded to make A4 brochures. Similarly, material at A4 is folded to make A5 brochures.
It also allows scaling without loss of image from one size to another. Thus an A4 page can be enlarged to A3 and retain the exact proportions of the original document. Office photocopiers in countries that use ISO 216 paper often have one tray filled with A4 and another filled with A3. A simple method is usually provided (e.g. one button press) to enlarge A4 to A3 or reduce A3 to A4. Thus an A4 brochure when open is A3 and can be placed on the copier and either printed directly onto the A3 paper or reduced to A4.

There is also a much less common B series. The area of B series sheets is the geometric mean of successive A series sheets. So, B1 is between A0 and A1 in size, with an area of 0.71 m² (). As a result, B0 has one side 1-metre long, and other sizes in the B series have one side that is a half, quarter or eighth of a metre. While less common in office use, it is used for a variety of special situations. Many posters use B-series paper or a close approximation, such as 50 cm×70 cm; B5 is a relatively common choice for books. The B series is also used for envelopes and passports.
The C series is used only for envelopes and is defined in ISO 269. The area of C series sheets is the geometric mean of the areas of the A and B series sheets of the same number; for instance, the area of a C4 sheet is the geometric mean of the areas of an A4 sheet and a B4 sheet. This means that C4 is slightly larger than A4, and B4 slightly larger than C4. The practical usage of this is that a letter written on A4 paper fits inside a C4 envelope, and a C4 envelope fits inside a sturdier B4 envelope.
The scalability also means that less paper (and hence money) is wasted by printing companies.
| A Series Formats | B Series Formats | C Series Formats | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| size | in mm | in inches | in mm | in inches | in mm | in inches |
| 0 | 841 × 1189 | 33.1 × 46.8 | 1000 × 1414 | 39.4 × 55.7 | 917 × 1297 | 36.1 × 51.1 |
| 1 | 594 × 841 | 23.4 × 33.1 | 707 × 1000 | 27.8 × 39.4 | 648 × 917 | 25.5 × 36.1 |
| 2 | 420 × 594 | 16.5 × 23.4 | 500 × 707 | 19.7 × 27.8 | 458 × 648 | 18.0 × 25.5 |
| 3 | 297 × 420 | 11.7 × 16.5 | 353 × 500 | 13.9 × 19.7 | 324 × 458 | 12.8 × 18.0 |
| 4 | 210 × 297 | 8.3 × 11.7 | 250 × 353 | 9.8 × 13.9 | 229 × 324 | 9.0 × 12.8 |
| 5 | 148 × 210 | 5.8 × 8.3 | 176 × 250 | 6.9 × 9.8 | 162 × 229 | 6.4 × 9.0 |
| 6 | 105 × 148 | 4.1 × 5.8 | 125 × 176 | 4.9 × 6.9 | 114 × 162 | 4.5 × 6.4 |
| 7 | 74 × 105 | 2.9 × 4.1 | 88 × 125 | 3.5 × 4.9 | 81 × 114 | 3.2 × 4.5 |
| 8 | 52 × 74 | 2.0 × 2.9 | 62 × 88 | 2.4 × 3.5 | 57 × 81 | 2.2 × 3.2 |
| 9 | 37 × 52 | 1.5 × 2.0 | 44 × 62 | 1.7 × 2.4 | 40 × 57 | 1.6 × 2.2 |
| 10 | 26 × 37 | 1.0 × 1.5 | 31 × 44 | 1.2 × 1.7 | 28 × 40 | 1.1 × 1.6 |
The tolerances specified in the standard are
- ±1.5 mm for dimensions up to 150 mm,
- ±2 mm for lengths in the range 150 to 600 mm, and
- ±3 mm for any dimension above 600 mm.
German extensions
The German standard DIN 476 was published in 1922 and is the original specification of the ISO A and B sizes. However, it still differs in two details from its international successor:
DIN 476 provides an extension to formats larger than A0, denoted by a prefix factor. In particular, it lists the two formats 2A0, which is twice the area of A0, and 4A0, which is four times A0:
| 4A0 | 1682 × 2378 |
|---|---|
| 2A0 | 1189 × 1682 |
DIN 476 also specifies slightly tighter tolerances, namely ±1 mm (< 150 mm), ±1.5 mm (150–600 mm), and ±2 mm (>600 mm), respectively.
Swedish extensions
The Swedish standard SIS 014711 generalized the ISO system of A, B, and C formats by adding D, E, F, and G formats to it. Its D format sits between a B format and the next larger A format (just like C sits between A and the next larger B). The remaining formats fit in between all these formats, such that the sequence of formats A4, E4, C4, G4, B4, F4, D4, H4, A3 is a geometric progression, in which the dimensions grow by a factor 21/16 from one size to the next. However, the SIS 014711 standard does not define any size between a D format and the next larger A format (called H in the previous example). None of these additional formats beyond C have turned out to be particularly useful in practice and they have not caught on internationally.
Japanese B-series variant
The JIS defines two main series of paper sizes. The JIS A-series is identical to the ISO A-series, but with slightly different tolerances. The area of B-series paper is 1.5 times that of the corresponding A-paper, so the length ratio is approximately 1.22 times the length of the corresponding A-series paper. The aspect ratio of the paper is the same as for A-series paper. Both A- and B-series paper is widely available in Japan and most photocopiers are loaded with at least A4 and B4 paper.
There are also a number of traditional paper sizes, which are now used mostly only by printers. The most common of these old series are the Shiroku-ban and the Kiku paper sizes.
| B- | Shiroku ban 4x6/ |
Kiku | |
|---|---|---|---|
| -0 | 1030 x 1456 | ||
| -1 | 728 x 1030 | ||
| -2 | 515 x 728 | ||
| -3 | 364 x 515 | ||
| -4 | 257 x 364 | 264 x 379 | 227 x 306 |
| -5 | 182 x 257 | 189 x 262 | 151 x 227 |
| -6 | 128 x 182 | 189 x 262 | |
| -7 | 91 x 128 | 127 x 188 | |
| -8 | 64 x 91 | ||
| -9 | 45 x 64 | ||
| -10 | 32 x 45 | ||
| -11 | 22 x 32 | ||
| -12 | 16 x 22 |
North American paper sizes
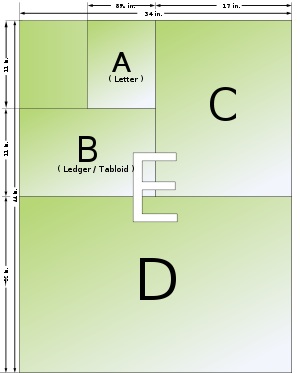
Loose sizes
Current standard sizes of U.S. paper are a subset of the traditional sizes referred to below. "Letter", "Legal", and "Ledger"/"Tabloid" are by far the most commonly used of these for everyday activities. The origin of the exact dimensions of "Letter" size paper (8.5" x 11", 216 mm × 279 mm) are lost in tradition and not well documented. The author of the American Forest and Paper Association website argues that the dimension originates from the days of manual paper making, and that the 11 inch length of the page is about a quarter of "the average maximum stretch of an experienced vatman's arms" [1]. However, this does not explain the width or aspect ratio.
There is an additional paper size, to which the name "government-letter" was given by the IEEE Printer Working Group: the 8-by-10½ inch paper that is used in America for children's writing. It was prescribed by Herbert Hoover when he was Secretary of Commerce to be used for U.S. government forms, apparently to enable discounts from the purchase of paper for schools. In later years, as photocopy machines proliferated, citizens wanted to make photocopies of the forms, but the machines did not generally have this size paper in their bins. Ronald Reagan therefore had the U.S. government switch to letter size. 8" × 10½" is still commonly used in spiral-bound notebooks and the like.
An alternative explanation in the past for the difference between "government size" (as government-letter size was referred to at the time) and letter size paper was that the slightly smaller sheet used less paper, and therefore saved the government money in both paper and filing space. However, when Reagan prescribed the change to letter size, it was commonly stated that U.S. paper manufacturers had standardized their production lines for letter size, and were meeting government orders by trimming ½" each from two sides of letter-size stock; thus the government was allegedly paying more for its smaller paper size before Reagan abolished it. The different paper size also reportedly restricted the government's ability to take advantage of modular office furniture designs that were becoming common in the 1980's, whose cabinets were designed for letter size paper.
U.S. paper sizes are currently standard in the United States and (partly) the Philippines, which uses U.S. "Letter," but the Philippine "Legal" size is 8½-by-13 inches. ISO ranges are available, but not widely used, in the Philippines.
In Canada, U.S. paper sizes are a de facto standard. The government, however, uses a combination of ISO paper sizes, and CAN 2-9.60M “Paper Sizes for Correspondence” specifies P1 through P6 paper sizes, which are the U.S. paper sizes rounded to the nearest half-centimeter [2]. Mexico has adopted the ISO standard, but U.S. "Letter" format is very common, as the market is dominated by U.S. suppliers who offer "Letter" at a much lower price than A4. Elsewhere in the world, paper and other stationery in U.S. sizes is not easily available. See switch costs, network effects and standardization for possible reasons for differing regional adoption rates of the ISO standard sizes.
ANSI paper sizes
In 1995, the American National Standards Institute adopted ANSI/ASME Y14.1 which defined a regular series of paper sizes based upon the de facto standard 8½" x 11" "letter" size which it assigned "ANSI A". This series also includes "ledger"/"tabloid" as "ANSI B". This series is somewhat similar to the ISO standard in that cutting a sheet in half shortwise would produce two sheets of the next smaller size. Unlike the ISO standard, however, the arbitrary aspect ratio forces this series to have two alternating aspect ratios. The ANSI series is show below.
With care, documents can be prepared so that the text and images fit on either ANSI or their equivalent ISO sheets at 1:1 reproduction scale.
| Name | Inches | mm | Ratio | AKA | ISO Similar Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANSI A | 11 × 8½ | 279.4 × 215.9 | 1.2941 | Letter | |
| ANSI B | 17 × 11 | 431.8 × 279.4 | 1.5455 | Ledger, Tabloid | |
| ANSI C | 22 × 17 | 538.8 × 431.8 | 1.2941 | ||
| ANSI D | 34 × 22 | 863.6 × 538.8 | 1.5455 | ||
| ANSI E | 44 × 34 | 1117.6 × 863.6 | 1.2941 |
Other, larger sizes continuing the alphabetic series illustrated above exist, but it should be noted that they are not part of the series per se, because they do not exhibit the same aspect ratios. For example, Engineering F size (40 x 28) also exists, but is rarely encountered, as are G, H, ... N size drawings. G size is 22.5 inches high, but variable width up to 90 inches in increments of 8.5 inches, i.e., roll format. H and larger letter sizes are also roll formats. Such sheets were at one time used for full-scale layouts of aircraft parts, wiring harnesses and the like, but today are generally not needed, due to widespread use of Computer-aided design (CAD) and Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM).
Architectural sizes
In addition to the ANSI system as listed above, there is a corresponding series of paper sizes used for architectural purposes. This series also shares the property that bisecting each size produces two of the size below. This series is likely preferred by architects due to the fact that the aspect ratios (4:3 & 3:2) are rational unlike their ANSI counterparts. The architectural series, usually abbreviated "Arch", is shown below:
| Name | Inches | mm | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arch A | 12 × 9 | 304.8 × 228.6 | 1.3333 |
| Arch B | 18 × 12 | 457.2 × 304.8 | 1.5 |
| Arch C | 24 × 18 | 609.6 × 457.2 | 1.3333 |
| Arch D | 36 × 24 | 914.4 × 609.6 | 1.5 |
| Arch E | 48 × 36 | 1219.2 × 914.4 | 1.3333 |
Other sizes
| Name | Inches | mm | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quarto | 10 × 8 | 254 × 203 | 1.25 |
| Foolscap | 13 × 8 | 330 × 203 | 1.625 |
| Executive, (or Monarch) | 10½ × 7¼ | 267 × 184 | 1.4483 |
| Government-Letter | 10½ × 8 | 267 × 203 | 1.3125 |
| Letter | 11 × 8½ | 279 × 216 | 1.2941 |
| Legal | 14 × 8½ | 356 × 216 | 1.6471 |
| Ledger, Tabloid | 17 × 11 | 432 × 279 | 1.5455 |
| Post | 19¼ × 15½ | 489 × 394 | 1.2419 |
| Crown | 20 × 15 | 508 × 381 | 1.3333 |
| Large Post | 21 × 16½ | 533 × 419 | 1.2727 |
| Demy | 22½ × 17½ | 572 × 445 | 1.2857 |
| Medium | 23 × 18 | 584 × 457 | 1.2778 |
| Royal | 25 × 20 | 635 × 508 | 1.25 |
| Elephant | 28 × 23 | 711 × 584 | 1.2174 |
| Double Demy | 35 × 23½ | 889 × 597 | 1.4894 |
| Quad Demy | 45 × 35 | 1143 × 889 | 1.2857 |
| Statement | 8½ × 5½ | 216 × 140 | 1.5455 |
| Index card | 5 × 3 | 127 x 76 | 1.667 |
| Index card | 6 × 4 | 152 x 102 | 1.5 |
| Index card | 8 × 5 | 203 x 127 | 1.6 |
| International business card | 3⅜ × 2⅛ | 85.60 × 53.98 | 1.586 |
| U.S. business card | 3½ × 2 | 89 × 51 | 1.75 |
Tablet sizes
The sizes listed above are for paper sold loosely in reams. There are a large number of sizes of tablets of paper, that is, sheets of paper kept from flying around by being bound at one edge, usually by a strip of plastic or hardened PVA adhesive. Often there is a pad of cardboard (or greyboard) at the bottom of the stack. Such a tablet serves as a portable writing surface, and the sheets have lines printed on them, usually in blue, to make writing in a line easier. An older means of binding is to have the sheets stapled to the cardboard along the top of the tablet; there is a line of perforated holes across every page just below the top edge from which any page may be torn off. Lastly, a pad of sheets each weakly stuck with adhesive to the sheet below, trade-marked as "Post-It" or "Stick-Em" and available in various sizes, serve as a sort of tablet.
The significance of taking separate note of these sizes is that their contents are just as likely to be photocopied and enlarged, of course onto loose paper, as are the more standardized international sizes of paper.
"Letter pads" are of course 8½ by 11 inches, but the term "Legal pad" is often used for pads of this size besides those of 8½ by 14 inches. There are "Steno pads" (used by stenographers) of 6 by 9 inches, and pads for pre-school children of twice and four times this size, but which have lines going the long way across the paper: 9 by 12 inches and 12 by 18 inches. For the latter use, there are also pads 10¾ by 13½ inches.
For varied commercial purposes, all sorts of sizes have been recently observed: 4 by 5½ inches; 5 by 8 inches; 5⅜ by 8¼ inches; 6 by 9½ inches; 7¼ by 9½ inches; and 7¾ by 9⅞ inches.
The only "metric" paper in the shops where this observation was taken are a few Chinese-made "composition books" for children which are 190 mm by 247 mm, a slight modification from the 7¾ by 9¾ inch ones. But the holes in the sheets of any of these tablets fit American-standard binders.
Of course, in countries where the ISO sizes are standard, most notebooks and tablets are sized to ISO specifications (for example, most newsagents in Australia stock A4 and A3 tablets).
Traditional inch-based paper sizes
Traditionally, a number of different sizes were defined for large sheets of paper, and paper sizes were defined by the sheet name and the number of times it had been folded. Thus a full sheet of "Royal" paper was 25 × 20 inches, and "Royal Octavo" was this size folded 3 times, so as to make eight sheets, and was thus 10 by 6¼ inches.
Imperial sizes were used in the United Kingdom and its territories. Some of the base sizes were as follows:
| Name | inches | mm | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emperor | 72 × 48 | 1829 × 1219 | 1.5 |
| Antiquarian | 53 × 31 | 1346 × 787 | 1.7097 |
| Grand Eagle | 42 × 28¾ | 1067 × 730 | 1.4609 |
| Double Elephant | 40 x 26¾ | 1016 x 678 | 1.4984 |
| Colombier | 34½ × 23½ | 876 × 597 | 1.4681 |
| Atlas* | 34 × 26 | 864 × 660 | 1.3077 |
| Double Demy | 35½ x 22½ | 902 x 572 | 1.5777 |
| Double Large Post | 33 x 21 | 838 × 533 | 1.5713 |
| Imperial* | 30 × 22 | 762 × 559 | 1.3636 |
| Double Post | 30½ x 19 | 762 x 483 | 1.6052 |
| Elephant* | 28 × 23 | 711 × 584 | 1.2174 |
| Princess | 28 × 21½ | 711 × 546 | 1.3023 |
| Cartridge | 26 × 21 | 660 × 533 | 1.2381 |
| Super Royal | 27 x 19 | 686 × 483 | 1.4203 |
| Royal* | 25 × 20 | 635 × 508 | 1.25 |
| Sheet and Half Post | 23½ × 19½ | 597 × 495 | 1.2051 |
| Medium* | 23 × 17½ | 584 × 470 | 1.2425 |
| Demy* | 22½ × 17½ | 572 × 445 | 1.2857 |
| Large Post | 21 × 16½ | 533 × 419 | 1.2727 |
| 20 × 15½ | 508 × 394 | 1.2903 | |
| Copy Draught | 20 × 16 | 508 × 406 | 1.25 |
| Crown* | 20 × 15 | 508 × 381 | 1.3333 |
| Post* | 19¼ × 15½ | 489 × 394 | 1.2419 |
| Pinched Post | 18½ × 14¾ | 470 × 375 | 1.2533 |
| Foolscap* | 17 × 13½ | 432 × 343 | 1.2593 |
| Small Foolscap | 16½ × 13¼ | 419 × 337 | 1.2453 |
| Brief | 16 × 13½ | 406 × 343 | 1.1852 |
| Pott | 15 × 12½ | 381 × 318 | 1.2 |
* The sizes marked with an asterisk are used in the US.
The common divisions and their abbreviations include:
| Name(s) | Abbr. | Folds | Leaves | Pages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Folio | fo/f | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Quarto | 4to | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| Sexto or Sixmo | 6to/6mo | 3 | 6 | 12 |
| Octavo | 8vo | 3 | 8 | 16 |
| Duodecimo or Twelvemo | 12mo | 4 | 12 | 24 |
| Sextodecimo or Sixteenmo | 16mo | 4 | 16 | 32 |
Foolscap Folio is often referred to simply as 'Folio' or 'Foolscap'. Similarly, 'Quarto' is more correctly 'Copy Draught Quarto'.
Many of these sizes were only used for making books (see bookbinding), and would never have been offered for ordinary stationery purposes.
Transitional paper sizes
PA series
| Name | mm² | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| PA0 | 840 × 1120 | 3:4 |
| PA1 | 560 × 840 | 2:3 |
| PA2 | 420 × 560 | 3:4 |
| PA3 | 280 × 420 | 2:3 |
| PA4 | 210 × 280 | 3:4 |
| PA5 | 140 × 210 | 2:3 |
| PA6 | 105 × 140 | 3:4 |
| PA7 | 70 × 105 | 2:3 |
| PA8 | 52 × 70 | ≈3:4 |
| PA9 | 35 × 52 | ≈2:3 |
| PA10 | 26 × 35 | ≈3:4 |
A transitional size called PA4 (210 mm × 280 mm, 8¼ in × 11 in) was proposed for inclusion into the ISO 216 standard in 1975. It has the height of Canadian P4 paper (215 mm × 280 mm, about 8½ in × 11 in) and the width of international A4 paper (210 mm × 297 mm). The table to the right shows how this format can be generalized into an entire format series.
The PA formats did not end up in ISO 216, because the committee felt that the set of standardized paper formats should be kept to the minimum necessary. However, PA4 remains of practical use today. In landscape orientation, it has the same 4:3 aspect ratio as the displays of traditional TV sets, most computers and data projectors. PA4 is therefore a good choice as the format of computer presentation slides. At the same time, PA4 is the largest format that fits on both A4 and U.S./Canadian "Letter" paper without resizing.
PA4 is used today by many international magazines, because it can be printed easily on equipment designed for either A4 or U.S. "Letter".
Antiquarian
Although the movement is toward the international standard metric paper sizes, on the way there from the traditional ones there has been at least one new size just a little larger than that used internationally. British architects and industrial designers once used a size called "Antiquarian" as listed above, but given in "New Metric Handbook," (Tutt & Adler 1981) as 813 by 1372 mm. This is a bit larger than the A0 size. So for a short time, a size called A0a was used in Britain, being 1000 mm by 1370 mm, to get that extra 100 mm on the longer side, write Tutt & Adler.
Expressing paper thickness and density (paper weight)
Grammage
Throughout the world, except in regions using US paper sizes, the product of thickness and density of paper is expressed in grams per square metre (g/m²). This quantity is commonly called grammage in both English and French (ISO 536), though printers in most English-speaking countries still refer to the "weight" of paper, i.e. 80 gsm.
Typical office paper has a grammage of 80 g/m², therefore a typical A4 sheet (1/16 m²) weighs 5 g.
The unofficial unit symbol "gsm" instead of the official "g/m²" is also occasionally encountered in English speaking countries.
While paper is measured by weight, card is measured by thickness in micrometres.
"Uncut" ream basis weight
In countries using U.S. paper sizes, paper density is often specified in pounds. The stated mass is that of a ream of 500 sheets. However, the ream of that mass is normally not the one sold to the customer. Instead, the specified number of pounds is the mass of a "basis ream" in which the sheets have some larger size. Often, this is a size used during the manufacturing process before the paper was cut to the dimensions in which it is sold. So, to compute the weight per area, one must know
- the weight of the basis ream, which is labeled in pounds;
- the number of sheets in that ream, which is usually 500;
- the dimensions of an "uncut" sheet in that ream.
These "uncut" basis sizes vary between paper types, are not normally labelled on the product, are not formally standardized, and therefore have to be guessed or inferred somehow from trading practice. Common examples are:
| 17 in × 22 in | 19 in × 24 in | 20 in × 26 in |
| 22 in × 28 in | 22.5 in × 28.5 in | 22 in × 34 in |
| 24 in × 36 in | 25 in × 38 in | 25.5 in × 30.5 in |
For conversion to grammage, in addition the ratio between avoirdupois pound and gram (1 lb ≈ 454 g) and between square inch and square metre (1 m² ≈ 1550 in²) are needed: 1 lb/in² ≈ 703700 g/m².
For example, a "20 pound ream of Letter paper" has a weight of only 5 pounds if the basis dimensions used are twice the cut dimensions. Since the cut dimensions are 8½ in × 11 in, the "uncut" basis dimensions are probably 17 in × 22 in. Therefore, paper weight per area of this type of paper is likely to be:
See also
- Photographic printing — standard photographic print sizes
- Punchhole — filing holes
- Envelope size
- Index card
- Book size
References
- International standard ISO 216, Writing paper and certain classes of printed matter — Trimmed sizes — A and B series. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, 1975.
- International standard ISO 217: Paper — Untrimmed sizes — Designation and tolerances for primary and supplementary ranges, and indication of machine direction. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, 1995.
- M. Kuhn: International standard paper sizes. Web page, Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge, 1996–2006.
- Max Helbig, Winfried Hennig: DIN-Format A4 – Ein Erfolgssystem in Gefahr. Beuth-Kommentare, Beuth Verlag, Berlin, 1998. ISBN 3-410-11878-0
- Arthur D. Dunn: Notes on the standardization of paper sizes. Ottawa, Canada, 54 pages, 1972.
- American Forest and Paper Association - FAQ: Why is the standard paper size in the U.S. 8 ½" x 11"?
External links
- Page listing conversion tables for paper weights
- Web page on traditional paper sizes used in books, with reference tables
- IEEE-ISTO 5101.1-2002 "The Printer Working Group Standard for Media Standardized Names" (PDF)
- Paper Sizes
- Japanese and international paper size
- Georg C. Lichtenberg (25 Oct. 1786) Letter to Johann Bergmann.


