2006 Italian general election: Difference between revisions
Rescuing 7 sources and tagging 1 as dead. #IABot (v1.6.1) |
|||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
Initial exit polls suggested a victory for Prodi, but the results narrowed as the count progressed. On 11 April 2006, Prodi declared victory;<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/4897994.stm Centre-left claims Italy victory], [[BBC News]]</ref> Berlusconi never conceded defeat explicitly but this is not required by the [[Italian law]]. |
Initial exit polls suggested a victory for Prodi, but the results narrowed as the count progressed. On 11 April 2006, Prodi declared victory;<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/4897994.stm Centre-left claims Italy victory], [[BBC News]]</ref> Berlusconi never conceded defeat explicitly but this is not required by the [[Italian law]]. |
||
[[Italian general election, 2006#Results|Preliminary results]] showed The Union leading the House of Freedoms in the [[Italian Chamber of Deputies|Chamber of Deputies]], with 340 seats to 277, thanks to obtaining a majority bonus (actual votes were distributed 49.81% to 49.74%). One more seat is allied with The Union ([[Aosta Valley]]) and 7 more seats in the foreign constituency. The House of Freedoms had secured a slight majority of Senate seats elected within Italy (155 seats to 154), but The Union won 4 of the 6 seats allocated to [[#Vote abroad|voters outside Italy]], giving them control of both chambers.<ref>http://www.cnn.com/2006/WORLD/europe/04/11/italy.elections/index.html</ref> |
[[Italian general election, 2006#Results|Preliminary results]] showed The Union leading the House of Freedoms in the [[Italian Chamber of Deputies|Chamber of Deputies]], with 340 seats to 277, thanks to obtaining a majority bonus (actual votes were distributed 49.81% to 49.74%). One more seat is allied with The Union ([[Aosta Valley]]) and 7 more seats in the foreign constituency. The House of Freedoms had secured a slight majority of Senate seats elected within Italy (155 seats to 154), but The Union won 4 of the 6 seats allocated to [[#Vote abroad|voters outside Italy]], giving them control of both chambers.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.cnn.com/2006/WORLD/europe/04/11/italy.elections/index.html |title=Archived copy |accessdate=2006-04-11 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20060412121023/http://www.cnn.com/2006/WORLD/europe/04/11/italy.elections/index.html |archivedate=2006-04-12 |df= }}</ref> |
||
On 19 April 2006, Italy's [[Court of Cassation (Italy)|Supreme Court of Cassation]] ruled that Prodi had indeed won the election, winning control of the Chamber of Deputies by only 24,755 votes out of more than 38 million votes cast, and winning 158 seats in the Senate to 156 for Berlusconi's coalition. Even so, Berlusconi refused to concede defeat, claiming unproven fraud. |
On 19 April 2006, Italy's [[Court of Cassation (Italy)|Supreme Court of Cassation]] ruled that Prodi had indeed won the election, winning control of the Chamber of Deputies by only 24,755 votes out of more than 38 million votes cast, and winning 158 seats in the Senate to 156 for Berlusconi's coalition. Even so, Berlusconi refused to concede defeat, claiming unproven fraud. |
||
| Line 372: | Line 372: | ||
An electoral survey published on 15 September 2005 by the national left newspaper ''[[La Repubblica]]''<ref>{{it icon}} [http://www.repubblica.it/2005/i/sezioni/politica/leggeletto/sondaggio/sondaggio.html {{lang|it|Dalla vittoria alla sconfitta la riforma "scippa" l'Unione}}], La Repubblica</ref> claimed that, with the initial proposal of electoral reform become law, the House of Freedoms would win the next elections 340-290, even if they won only 45% of votes and the opposition coalition The Union won 50%, because The Union also includes several small parties with less than 4% of national votes. This could have been avoided if the small opposition parties ran on a common ticket. Aim of this bill of reform was to reduce the number of parties, and particularly the moderate centre-left would have taken advantage in respect to the smaller radical left parties. |
An electoral survey published on 15 September 2005 by the national left newspaper ''[[La Repubblica]]''<ref>{{it icon}} [http://www.repubblica.it/2005/i/sezioni/politica/leggeletto/sondaggio/sondaggio.html {{lang|it|Dalla vittoria alla sconfitta la riforma "scippa" l'Unione}}], La Repubblica</ref> claimed that, with the initial proposal of electoral reform become law, the House of Freedoms would win the next elections 340-290, even if they won only 45% of votes and the opposition coalition The Union won 50%, because The Union also includes several small parties with less than 4% of national votes. This could have been avoided if the small opposition parties ran on a common ticket. Aim of this bill of reform was to reduce the number of parties, and particularly the moderate centre-left would have taken advantage in respect to the smaller radical left parties. |
||
The UDC, commenting on the proposal, asked for the abolition of the 4% cut-off clause, whereas the [[National Alliance (Italy)|National Alliance]] did not show any favour to this attempt of reform, with its leader [[Gianfranco Fini]] claiming to want first to vote for the constitutional reform, and then for the new voting system, on condition that the 4% cut-off were not repealed.<ref>[http://today.reuters.it/news/newsArticle.aspx?type=topNews&storyID=2005-09-14T175917Z_01_CON463255_RTRIDST_0_OITTP-FINI-LEGGE-ELETTORALE-DEVOLUTION.XML], [[Reuters]]</ref> |
The UDC, commenting on the proposal, asked for the abolition of the 4% cut-off clause, whereas the [[National Alliance (Italy)|National Alliance]] did not show any favour to this attempt of reform, with its leader [[Gianfranco Fini]] claiming to want first to vote for the constitutional reform, and then for the new voting system, on condition that the 4% cut-off were not repealed.<ref>[http://today.reuters.it/news/newsArticle.aspx?type=topNews&storyID=2005-09-14T175917Z_01_CON463255_RTRIDST_0_OITTP-FINI-LEGGE-ELETTORALE-DEVOLUTION.XML]{{dead link|date=November 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}, [[Reuters]]</ref> |
||
This proposal of law was strongly questioned by the opposition coalition, who defined it an "attempted coup". Opposition leader [[Romano Prodi]] said it was "totally unacceptable".<ref>{{it icon}} [http://www.repubblica.it/2005/i/sezioni/politica/leggeletto/leggeletto/leggeletto.html {{lang|it|Legge elettorale, accordo nella Cdl Unione insorge: "Blocchiamo le Camere"}}], La Repubblica</ref> Several newspapers politically oriented to the left nicknamed the electoral system proposal by the House of Freedoms as "{{lang|it|Truffarellum}}", after "{{lang|it|truffa}}" ([[Italian language|Italian]] for "[[fraud]]") and the "{{lang|la|Mattarellum}}", (from [[Sergio Mattarella]]), the most common name for the previous Italian electoral law (there is a recent custom to nickname new electoral systems by a somewhat Latinised version of the name of the lawmaker; another one is the system used in regional elections, the so-called "{{lang|la|Tatarellum}}" from Pinuccio Tatarella). |
This proposal of law was strongly questioned by the opposition coalition, who defined it an "attempted coup". Opposition leader [[Romano Prodi]] said it was "totally unacceptable".<ref>{{it icon}} [http://www.repubblica.it/2005/i/sezioni/politica/leggeletto/leggeletto/leggeletto.html {{lang|it|Legge elettorale, accordo nella Cdl Unione insorge: "Blocchiamo le Camere"}}], La Repubblica</ref> Several newspapers politically oriented to the left nicknamed the electoral system proposal by the House of Freedoms as "{{lang|it|Truffarellum}}", after "{{lang|it|truffa}}" ([[Italian language|Italian]] for "[[fraud]]") and the "{{lang|la|Mattarellum}}", (from [[Sergio Mattarella]]), the most common name for the previous Italian electoral law (there is a recent custom to nickname new electoral systems by a somewhat Latinised version of the name of the lawmaker; another one is the system used in regional elections, the so-called "{{lang|la|Tatarellum}}" from Pinuccio Tatarella). |
||
| Line 378: | Line 378: | ||
Notably, some smaller opposition parties, such as [[Communist Refoundation Party]] and [[Union of Democrats for Europe]] (UDEUR), supported a proportional electoral law; nevertheless, they declared they were against an electoral reform by this parliament, because the current law would be changed too close to the 2006 general election. |
Notably, some smaller opposition parties, such as [[Communist Refoundation Party]] and [[Union of Democrats for Europe]] (UDEUR), supported a proportional electoral law; nevertheless, they declared they were against an electoral reform by this parliament, because the current law would be changed too close to the 2006 general election. |
||
The Italian prime minister [[Silvio Berlusconi]] had previously been a strong supporter of the plurality-based electoral law; in 1995, talking about his coalition, he even defined the plurality principle as "our religion".<ref>{{it icon}} [http://www.dsmilano.it/html/Pressroom/2005/04/rep5_0429_unione-nessun-blitz.htm {{lang|it|Nessun blitz prima delle elezioni}}], [[DS Milano]]</ref> |
The Italian prime minister [[Silvio Berlusconi]] had previously been a strong supporter of the plurality-based electoral law; in 1995, talking about his coalition, he even defined the plurality principle as "our religion".<ref>{{it icon}} [http://www.dsmilano.it/html/Pressroom/2005/04/rep5_0429_unione-nessun-blitz.htm {{lang|it|Nessun blitz prima delle elezioni}}] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110723022653/http://www.dsmilano.it/html/Pressroom/2005/04/rep5_0429_unione-nessun-blitz.htm |date=2011-07-23 }}, [[DS Milano]]</ref> |
||
A modified version of the first proposal, this time with a 2% threshold for entering Parliament and without vote of preference for candidates, but still without the support of the opposition, was presented to the Chamber of Deputies. The voting count started on 11 October 2005; the lower house of Italian parliament then approved the electoral reform on 14 October.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/4340434.stm Italy deputies back voting reform], BBC News</ref> |
A modified version of the first proposal, this time with a 2% threshold for entering Parliament and without vote of preference for candidates, but still without the support of the opposition, was presented to the Chamber of Deputies. The voting count started on 11 October 2005; the lower house of Italian parliament then approved the electoral reform on 14 October.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/4340434.stm Italy deputies back voting reform], BBC News</ref> |
||
| Line 757: | Line 757: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
<small>Source: Interior Ministry of Italy, [http://www.elezionipolitiche.interno.it/politiche/camera060409/C0000000.htm Votes], [http://www.elezionipolitiche.interno.it/politiche/camera060409/j0000000.htm Seats]</small> |
<small>Source: Interior Ministry of Italy, [https://web.archive.org/web/20060510234739/http://www.elezionipolitiche.interno.it/politiche/camera060409/C0000000.htm Votes], [https://web.archive.org/web/20060510235130/http://www.elezionipolitiche.interno.it/politiche/camera060409/j0000000.htm Seats]</small> |
||
===Aosta Valley=== |
===Aosta Valley=== |
||
| Line 1,224: | Line 1,224: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
<small>Source: Interior Ministry of Italy, [http://www.elezionipolitiche.interno.it/politiche/camera060409/C0000000.htm Votes], [http://www.elezionipolitiche.interno.it/politiche/camera060409/j0000000.htm Seats]</small> |
<small>Source: Interior Ministry of Italy, [https://web.archive.org/web/20060510234739/http://www.elezionipolitiche.interno.it/politiche/camera060409/C0000000.htm Votes], [https://web.archive.org/web/20060510235130/http://www.elezionipolitiche.interno.it/politiche/camera060409/j0000000.htm Seats]</small> |
||
====Notes==== |
====Notes==== |
||
| Line 1,638: | Line 1,638: | ||
* {{it icon}} [http://brunik.altervista.org/ {{lang|it|''Il Termometro Politico''}} (The Political Thermometer)] |
* {{it icon}} [http://brunik.altervista.org/ {{lang|it|''Il Termometro Politico''}} (The Political Thermometer)] |
||
* {{en icon}} [http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/4812794.stm Q&A: Italian election] |
* {{en icon}} [http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/4812794.stm Q&A: Italian election] |
||
* {{it icon}} [http://politiche.interno.it/ Election results from the Interior Ministry] |
* {{it icon}} [https://web.archive.org/web/20061209222831/http://politiche.interno.it/ Election results from the Interior Ministry] |
||
* {{it icon}} [http://elezionistorico.interno.it/ Election results from the Interior Ministry (Archives of all Elections)] |
* {{it icon}} [http://elezionistorico.interno.it/ Election results from the Interior Ministry (Archives of all Elections)] |
||
Revision as of 00:39, 18 November 2017
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 630 seats in the Italian Chamber of Deputies 315 seats in the Italian Senate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 83.6%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
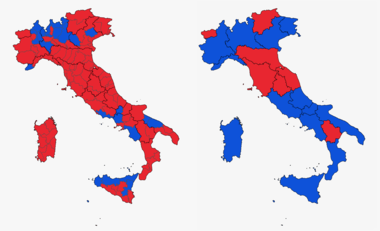 Election results maps for the Chamber of Deputies (on the left) and for the Senate (on the right). Red denotes provinces and regions with a Union plurality, Blue denotes those with a House of Freedom plurality. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2006 Italian general election for the two Chambers of the Italian Parliament was held on 9 and 10 April 2006. Romano Prodi, leader of the centre-left coalition The Union, narrowly defeated the incumbent Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi, leader of the centre-right coalition House of Freedoms.
Initial exit polls suggested a victory for Prodi, but the results narrowed as the count progressed. On 11 April 2006, Prodi declared victory;[2] Berlusconi never conceded defeat explicitly but this is not required by the Italian law.
Preliminary results showed The Union leading the House of Freedoms in the Chamber of Deputies, with 340 seats to 277, thanks to obtaining a majority bonus (actual votes were distributed 49.81% to 49.74%). One more seat is allied with The Union (Aosta Valley) and 7 more seats in the foreign constituency. The House of Freedoms had secured a slight majority of Senate seats elected within Italy (155 seats to 154), but The Union won 4 of the 6 seats allocated to voters outside Italy, giving them control of both chambers.[3]
On 19 April 2006, Italy's Supreme Court of Cassation ruled that Prodi had indeed won the election, winning control of the Chamber of Deputies by only 24,755 votes out of more than 38 million votes cast, and winning 158 seats in the Senate to 156 for Berlusconi's coalition. Even so, Berlusconi refused to concede defeat, claiming unproven fraud.
Recent developments, including publishing of a controversial documentary film about alleged frauds in the ballot counting during the election, brought in December 2006 the Electoral Committee of the Italian Chamber of Deputies to request for a recount of all ballot papers, starting from a 10% sample.[citation needed]
The electoral campaign
During the election campaign, a political battle began between Romano Prodi, who led the centre-left coalition The Union and had been President of the European Commission from 1999 to 2004 and Prime Minister of Italy from 1996 to 1998. On the other hand, Silvio Berlusconi led the centre-right House of Freedoms; Berlusconi had been the incumbent Prime Minister since the 2001 general election, and had previously served as Prime Minister also in 1994 and 1995.
The House of Freedoms
The House of Freedoms was the coalition supporting the incumbent government led by Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi, and mainly included the same parties as in the previous general election. This is the coalition of parties created before the election: Template:Italian general election, 2006-House of Freedoms
The New Italian Socialist Party (NPSI), a small social-democratic party composed of former members of the late Italian Socialist Party and led by former 1980s and 1990s minister Gianni De Michelis, which was part of the Berlusconi III Cabinet as a minister without portfolio, suffered a split on its last national congress (21 to 23 October 23, 2005), with a left-wing faction, led by Bobo Craxi, son of the late Bettino Craxi, who decided to immediately leave the House of Freedoms and unilaterally elected Craxi himself as new party leader. The NPSI contested the election with a joint list with the Christian Democracy for the Autonomies.
As for the candidate who led the coalition into the general election, Berlusconi experienced an actual loss of support from Union of Christian and Centre Democrats (UDC), who asked for a return of the electoral law to a proportional system (which would most likely favour them) and a primary election to formally decide the alliance's candidate for Prime Minister. When the party list representation system was restored (albeit a form very different from the UDC proposal) and Marco Follini, critic of several reforms imposed by Berlusconi on the whole coalition, resigned from the UDC secretaryship, the possibility of a change of leadership inside the House of Freedoms was significantly reduced. On 27 October 2005, Lorenzo Cesa was appointed as new UDC secretary, becoming the successor of Follini himself. The coalition announced a "three-forwards" system, meaning that the Prime Ministerial candidate will be the political leader, among Casini, Fini and Berlusconi, whose party will win most votes. Since Berlusconi's party was known to be by far the largest one, it was understood that Berlusconi was the actual candidate.
One event which caused heavy criticism from the opposition was the support, sought and obtained by Berlusconi, of a number of fascist movements and parties, notably the Social Alternative of Alessandra Mussolini, granddaughter of the former dictator of Italy, and Luca Romagnoli, a holocaust denier.[citation needed] Supporters of Berlusconi responded to this pointing to the presence in The Union of two communist parties, which had among their candidates anarchist activist Francesco Caruso and a transgender, Vladimir Luxuria.[citation needed]
The Union
The Olive Tree coalition, expression of the Italian centre-left, was expanded as The Union, and led for the election by former Prime Minister and former President of the European Commission Romano Prodi, who had already beaten Berlusconi in the 1996 general election. Prodi's candidacy was confirmed by a national primary election, held on 16 October 2005.
The former coalition was enlarged in order to cover the whole ensemble of Italian centre-left to left-wing factions. The parties in the alliance are: Template:Italian general election, 2006-The Union
The Rose in the Fist was officially founded on 25 September 2005, when the Italian Radicals, a libertarian-influenced party, officially declared an alliance with the Italian Democratic Socialists (SDI) in the form of a confederation, with explicit references to the politics of Tony Blair, José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero and Loris Fortuna, an Italian politician in the 1970s who became famous for his laicist proposals, and is considered the father of the law on divorce. This confederation immediately caused a stir for not having signed the political platform of The Union, being the only centre-left party not to do that; the Rose in the Fist, represented by Emma Bonino in the final platform meeting, in fact protested about insufficient mentions of social issues such as legalisation of civil unions. The Socialists, led by Bobo Craxi, who were the breakaway left wing of the New Italian Socialist Party which emerged the House of Freedoms, was supposed to join the Rose in the Fist confederation, but instead reorganised itself in a single party, which however failed to get over the 2% of national votes. However, Bobo Craxi was able to enter in the Lower House, as he was one of the leading candidates for The Olive Tree in Lombardy.
The Union is also supported by a number of minor parties and movements, although of those only the Pensioners' Party has any elected representation (1 Member of European Parliament).
Main leaders
| Coalition | Portrait | Name | Most recent position | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bgcolor="Template:The Union (Italy)/meta/color" | | The Union | 
|
Romano Prodi | Prime Minister of Italy (1996–1998) Leader of The Olive Tree (2004–incumbent) |
| bgcolor="Template:House of Freedoms/meta/color" | | House of Freedoms | 
|
Silvio Berlusconi | Prime Minister of Italy (2001–incumbent) President of Forza Italia (1994–incumbent) |
Debates
For some time, Silvio Berlusconi had challenged Romano Prodi to a debate on national television. Prodi, however, said he would accept only if certain rules had been set. Possibly because he thought he was behind in the polls, Berlusconi saw the debate as a chance to turn the tables, and accused Prodi of fleeing from him. It is notable that, in the 2001 elections, it was Berlusconi who refused to meet the centre-left candidate, Francesco Rutelli.
Two televised debates were set by the Parliamentary Committee of Inspection on RAI, which had the goal of ensuring equal treatment for the two political sides. However, Prodi contested the deliberation of this Committee, which allowed Berlusconi to also hold a final televised speech after the debates as Prime Minister. Prodi refused to participate in any debate until this final speech had been cancelled. The issue was resolved on 3 March, when Berlusconi finally agreed to cancel the final speech.
The debates lasted about 90 minutes each, did not include commercials, and had a preset time for each answer and each reply, and the obligation to film only the speaking person at any given time. The candidates were also forbidden to bring any kind of notes with them, even though they could write some down during the debate, and no audience was allowed to participate. This set of rules was very unusual in Italian political talk shows, where politicians usually interrupt each other, talk simultaneously and for as long as they can hold the word. Questions to candidates are posted by two journalists from the Italian press: the moderator himself was not allowed to ask any questions, but only to present the debate and guarantee respect of the rules. At the end of the debates, the candidates are allowed to make a final statement of 3 minutes.
The first televised debate, held on 14 March, was broadcast live on Rai Uno, and moderated by Clemente Mimun, Director of TG1. It featured questions from journalists Roberto Napoletano of Il Messaggero and Marcello Sorgi of La Stampa. It was watched by over 16 million people, a record for a political TV show. During his final speech, Berlusconi, who often overran his intervention times, attacked the rules of the debate, in his opinion too strict, whereas Prodi praised them, pointing out the fact that they are used in US debates this way, as well. Some observers commented that Berlusconi had been disappointing in this debate, scribbling nervously while he was talking and at a point confusing Iran and Iraq; while all politicians claimed their candidate had won the debate, it was generally agreed that Berlusconi had not dealt a strong blow to Prodi.
The second debate,[4] moderated by Bruno Vespa, an Italian journalist and anchorman, was held on April 3 and broadcast live on Rai Uno, featuring questions from Napoletano and Sorgi (same journalists of the first debate). It was dominated by the economic proposals and was more intense, with much stronger tones between Prodi and Berlusconi. In this debate, Berlusconi had the possibility of making the final 3-minute statement: in this time, he delivered his "surprise blow" proposing the abolition of ICI, a local tax on real estate whose money belongs to local city councils.
Later on, it turned out that Berlusconi's proposal was not completely agreed upon in the rest of the House of Freedoms, and Prodi, immediately after the debate, noted "about ICI, I want to know what the centre-right mayors think about".
Platforms
The Union
After a long discussion, the centre-left coalition released its official platform on 10 February 2006,[5] and presented it to the public the next day. However, the Rose in the Fist refused to sign it in, because it did not explicitly include some issues, such as civil unions and LGBT rights. The platform has been criticised by the House of Freedoms because of its 281-page length.
A reduced, more readable, version of the official political platform [6] was released by the coalition, in order to answer the critics from the centre-right coalition.
The main points of the centre-left platform were:
- More safety, by moving police resources from immigration and escort issues to the control of the territory;
- Controlled immigration and promotion of legal ways to immigrate in Italy;
- A quicker and more reliable judicial system;
- Full condemnation and fight of dodging and regularisation of concealed labour;
- More integration with the European Union;
- Recognition of rights for civil, unmarried couples;
- Immediate withdrawal of the Italian troops in Iraq;
- Numerical restraint and regulation of the typologies of flexible labour;
- Reduction of taxes on work by 5% (often referred to as the fiscal wedge), to be financed by increased policing activity against tax dodgers;
- Increase in taxes on temporary work positions to encourage permanent employment.
House of Freedoms
The platform of the House of Freedoms was released on 25 February. It was 22 pages long,[7] and it was defined as the continuance of the first five years of centre-right government. It is different by the contract with Italians (just five basic points) which characterised the 2001 general election. It was criticised as "vague" and "propaganda".
The main points of the centre-right platform were:
- Increase of fiscal autonomy for Regions ([federalismo fiscale] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help), fiscal federalism);
- Realisation of the so-called [grandi opere] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) (big works), notably the Strait of Messina Bridge;
- Support for smaller and family companies, and the Made in Italy export goods business;
- Tax reduction;
- Consolidation of relationships with the USA and reaffirmation of the commitment to the European Union;
- Defence of the values of family as based on marriage;
- Rise of legal penalties for criminal offences;
- Keeping up with the current politics for creating jobs, especially for the young Italians and the women;
- Restrictions on immigration
Opinion polling
According to the opinion polls released, mainly commissioned for national newspapers, magazines and TV stations, The Union was clearly leading the race to the general election. The three surveys which show a majority of votes for the House of Freedoms were all commissioned by Berlusconi's party Forza Italia. Notably, the surveys of Penn, Schoen & Berland, a U.S. research firm, were commissioned by Berlusconi because he claimed the national surveys to be politically biased.
According to the Italian [par condicio] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) law, it is forbidden to publish any opinion polling in the 15 days which precede the election (25 March, in this case).
The final result (49.8% Union vs 49.7% House of Freedoms) was about 3% different from almost all polls (including all the exit polls) reducing the expected 5% gap between the coalition to a difference of about 0.1%. On Italian TV some tried to explain this discrepancy claiming that some House of Freedoms voters were ashamed to admit that they planned to vote for them. Others claimed that the last week of electoral campaign, dominated by Berlusconi's proposal of cutting ICI and by the media's insistence on the alleged new taxes advocated by The Union, persuaded a large number of Italians, usually uninterested to politics, to cast a vote for the House of Freedoms.
| Polling Firm | Date | The Union [L'Unione] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) |
House of Freedoms [Casa delle Libertà] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPR marketing (exit poll) | 10 April 2006 | 50-53 | 46-49 |
| Nexus (exit poll) | 10 April 2006 | 50-54 | 47-49 |
| Piepoli Institute (in house poll) | 10 April 2006 | 52 | 47 |
| IPR Marketing | 22 March 2006 | 52 | 47 |
| TNS Abacus | 20 March | 51.5 | 48 |
| GfK Eurisko | 20 March | 52 | 46.7 |
| Ekma Ricerche | 20 March | 53.5 | 46 |
| SWG | 17 March | 52.8 | 46.4 |
| IPR Marketing | 16 March | 52 | 47.7 |
| GfK Eurisko | 15 March | 51 | 46.5 |
| TNS Abacus | 13 March | 51.5 | 48 |
| Ekma Ricerche | 13 March | 53 | 46.3 |
| IPR Marketing | 12 March | 52 | 47.7 |
| SWG | 10 March | 52.6 | 46 |
| Penn, Schoen & Berland | 9 March | 48.3 | 48.8 |
| Euromedia Research | 9 March | 49.3 | 50 |
| TNS Abacus | 9 March | 51 | 47.5 |
| Lorien Consulting | 7 March | 51.1 | 48.1 |
| IPR Marketing | 7 March | 52.2 | 47.5 |
| Ekma Ricerche | 6 March | 52 | 47.5 |
| SWG | 3 March | 52 | 47 |
| IPR Marketing | 1 March | 52.2 | 47.3 |
| TNS Abacus | 1 March | 51.5 | 47 |
| Ekma Ricerche | 27 February | 51.8 | 47.2 |
| SWG | 23 February | 51.8 | 47.2 |
| TNS Abacus | 22 February | 51.5 | 47 |
| IPR Marketing | 21 February | 52.1 | 47.4 |
| Ekma Ricerche | 20 February | 51.2 | 47 |
| SWG | 17 February | 51 | 47.8 |
| IPR Marketing | 16 February | 52 | 47.5 |
| Penn, Schoen & Berland | 16 February | 48.2 | 48.4 |
| TNS Abacus | 15 February | 51 | 47 |
| Ekma Ricerche | 13 February | 51.5 | 47.5 |
| SWG | 10 February | 51.6 | 47.3 |
| TNS Abacus | 8 February | 51 | 46.5 |
| IPR Marketing | 7 February | 52 | 47 |
| Ekma Ricerche | 6 February | 52.5 | 46.5 |
| SWG | 4 February | 51.2 | 46.6 |
| TNS Abacus | 1 February | 51 | 46 |
| Euromedia Research | 1 February | 50.9 | 47.9 |
| IPR Marketing | 31 January | 52.2 | 47.2 |
| Lorien Consulting | 30 January | 51.5 | 45.9 |
| SWG | 28 January | 51.4 | 46.2 |
| TNS Abacus | 25 January | 51 | 45.5 |
| IPR Marketing | 25 January | 52.5 | 47 |
| Lorien Consulting | 23 January | 51.3 | 46 |
| SWG | 22 January | 51.7 | 45.7 |
| TNS Abacus | 18 January | 50.5 | 46 |
| Euromedia Research | 18 January | 51.7 | 48.3 |
| IPR Marketing | 18 January | 52 | 46 |
| Lorien Consulting | 16 January | 51.4 | 45.7 |
| SWG | 16 January | 51.4 | 46 |
| IPR Marketing | 11 January | 52 | 46 |
| TNS Abacus | 11 January | 51 | 46 |
| SWG | 5 January | 49.7 | 47.9 |
| IPR Marketing | 11 December 2005 | 52.8 | 44.9 |
| IPR Marketing | 7 November | 52.5 | 44.5 |
| IPR Marketing | 25 October | 52 | 45 |
Political issues
The election date

In July 2005, President Carlo Azeglio Ciampi asked current PM Silvio Berlusconi about the opportunity for an early election for the first half of April 2006, in order to prevent a big political deadlock (the mandate of President Ciampi himself would be over in May 2006 and a newly elected government was not likely be in office within three weeks). Berlusconi however refused the deal, claiming he would stay in office until the due date of his term.[8][9]
But, on 18 October, Berlusconi announced that the election would be held on 9 April 2006, eventually following the suggestions from President Ciampi. Berlusconi also announced that the next administrative elections (which include the mayoral elections of Rome, Milan and Naples) will be held in May, the day after Romano Prodi had asked to vote for all elections the same day, in April.[10][11] Berlusconi stated this was due to his fear that good government by centre-left mayors could favour the centre-left in the general election. Critics say holding all elections in the same day could save millions of euros in public expenditure.
The [par condicio] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) law
One of the main topics that was relevant for this general election was the [par condicio] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) law. Its name, in Latin, means equal treatment; a special law which guarantees all the main majority and opposition political forces to have equal media treatment, in terms of times and spaces, and, furthermore, denies political commercials for TV and radio outside some dedicated transmissions.
Berlusconi had declared several times that he wants the [par condicio] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) law to be either repealed or at least changed in a much lighter way.[12][13][14] Critics and opponents said that Berlusconi's willingness to have the law abolished were dictated by his almost complete control of 6 channels (his family holding company controls Mediaset, which broadcasts three national private channels, and controls indirectly, as Head of Government, the three RAI public broadcasting channels).
In his latter government years, Berlusconi attempted to accelerate his desires; however UDC, who is part of the Berlusconi government, declared several times its opposition to either abolish or change the [par condicio] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) law, with secretary Lorenzo Cesa, after his election as party leader, who pointed out his refusal of any change of the law.[15]
The law however did not prevent Berlusconi from using his TV channels of Mediaset, and even SMS via cellphones,[16] to manage to get more votes. During the election day Berlusconi's channels aired a lot of messages to remind people who were watching his TV channels to use their vote together with spots saying "Mediaset gives you everything without asking for anything in return". While these spots didn't break the par condicio law, it was broken by some of the journalists (especially Emilio Fede, well known for his political ideas) of the Berlusconi's channels and in March and April 2006, the Autorità per le Garanzie nelle Comunicazioni fined twice his privately owned channels for violation of the par condicio law, the biggest fine to date (300,000 €).[17]
Tax breaks
Before winning the 2001 general election and becoming Prime Minister of Italy, Berlusconi signed in a TV show a Contract with Italians, where he promised, if elected, to fulfil at least four of the five points included in it. One of the main points regarded a tax break for income levels, whereas The Olive Tree policy was essentially to maintain a progressive taxation system.
The generalised tax break was somewhat enacted in 2005, and included in the last Financial Measure. The opposition blamed Berlusconi for doing the tax break in one of the worst economic periods for the country, with no coverage for the resulting debt, and accused Berlusconi's allies of accepting the tax break in return for better power positions; during the negotiations for the Financial Measure, the National Alliance leader, and, at that date, vice-premier, Gianfranco Fini, was moved to the Ministry for Foreign Affairs, and UDC leader Marco Follini, who had no ministerial role before that date, was chosen to replace Fini.
In the electoral campaign, Berlusconi and the whole centre-right coalition almost daily criticised the left, alleging that Prodi would increase taxes if elected, pointing out the centre-left proposal to have a 5% cut of the tax wedge.
Taxes became the main topic for the end of the electoral campaign, with Berlusconi citing Prodi would reintroduce the inheritance tax, abrogated in 2001, and increase the tax system on treasury bills (BOT, CCT) and would tax stockmarket trading. Prodi pointed out the fact that he would reintroduce the inheritance tax only for the very rich people, and would not increase the taxes on treasury bills.
Foreign reputation

A good friend of George W. Bush and Vladimir Putin, Berlusconi supported the American invasion of Iraq, and, during the Italian EU presidency, suggested to Chairman of the PES Group in the European Parliament Martin Schulz, during a talk, a role of kapo (concentration-camp inmate appointed as supervisor) for a hypothetical movie, claiming he would be "perfect" for the role. When Berlusconi entered the Strasburg Parliament he was welcomed with posters in various languages addressing him as "Godfather of Europe", explicitly referring to Francis Ford Coppola's cinematic series about the mafia, without respecting his high institutional role as EU Council president. Afterwards Mr Berlusconi exploded at the insisting questions of MP Schulz. This diplomatic incident cooled down the Italy-Germany foreign relations for a period. Eventually a phone call between the Prime Minister and German Chancellor Gerhard Schröder put an end to the dispute.
In 2001 Berlusconi declared Western civilisation to be "superior to Islam", which he was very much criticised for.[18]
But in particular the international English-speaking press, such as Financial Times and Newsweek, criticized Berlusconi's work. Several times, before and after his election as prime minister, the weekly worldwide magazine The Economist accused Berlusconi of being essentially "unfit to lead Italy".[19][20][21]
New voting rights for Italians living abroad
For the first time in Italian history, Italian citizens living abroad were able to vote by postal ballot (without having to physically return to Italy to cast their vote) for 12 deputies and 6 senators who will represent them in the Italian Parliament, an unusual system that was supported by Silvio Berlusconi and promoted by Mirko Tremaglia. These parliamentary seats are organised into four constituencies (Europe, North & Central America, Latin America, and Africa/Asia/Oceania). Candidates must live in their respective constituencies.
Forty-two percent of eligible voters abroad participated in the elections. Prodi's The Union managed to secure 4 of the 6 Senate seats, while Berlusconi's Forza Italia and an Independent candidate each gained 1 of the remaining 2 seats, aiding Prodi in gaining a majority in the Italian Senate. In the House of Deputies, 7 seats went to The Union, 4 to Berlusconi's coalition, and one to an Independent candidate. In North America, candidates from Toronto and Chicago were elected to the House of Deputies while the candidate from New York City was elected to the Senate.
Berlusconi claimed, in challenging the election results, that there were irregularities in the vote abroad. The result of the vote may have been influenced by the fact that numerous right-wing parties put forward candidates in the constituencies abroad, while there were few centre-left candidates, thereby splitting the centre-right vote. This tactical error may be explained through the novelty of the vote abroad.
Voting rights for Italians living abroad prior to 2006
Italian citizens living outside of Italy have always had the De Jure right to vote in all referendums and elections being held in Italy (provided they had registered their residence abroad with their relevant consulate). However until late 2001, any citizen wishing to vote, was required to physically return to the city or town in Italy where he or she was registered on the electoral roll. The only exception to this rule was for the Italian elections to the european parliament in which voters could cast their ballot at their nearest consulate but only if they had their residence in one of the other 14 European Union nations.
Until 2001 the Italian state offered citizens living abroad a free return train journey to their home town in Italy in order to vote, however the portion of the train journey that was free of charge was only on Italian soil. Any costs incurred in getting from their place of residence abroad to the Italian border had to be covered by the citizen wanting to vote, therefore a free return train journey was hardly an incentive for the large Italian communities living as far away as in the United States, Argentina or Australia. For this reason very few Italians abroad made use of this right to vote, unless they lived in cities and towns that bordered to Italy such as in Germany, Switzerland, France and Austria. Various Italian minorities living abroad (notably in the United States) protested frequently at this lack of political representation especially if they paid taxes on property owned in Italy.
After numerous years of petitioning and fierce debate, the Italian government, in late 2001, finally passed a law allowing Italian citizens living abroad to vote in elections in Italy by postal ballot. The change was the result of a thirty-year struggle to recognise the rights and special interests of Italians who have migrated abroad but retained their Italian identity.
Italians wishing to excise this right must first register their residence abroad with their relevant consulate.
Constitutional reform
During the last few months of 2004, the House of Freedoms coalition proposed a large reform of the current Italian Constitution, which was formulated in 1948.[22] It proposes several changes to the current political system: it reduces the number of MPs from about 950 to 750, it gives more power to the prime minister (no longer called president of the council), there will be no possibility to express a vote of no confidence against the prime minister without indicating his successor (similar to Germany's constructive vote of no confidence); it puts an end to the necessity of a law being approved by both Chambers, attributing a clear competence to each of them; it gives more power to the regions, with several references to devolution, the main programme point of the Lega Nord, still guaranteeing, according to the new version of article 127, the national interest, which had been cancelled by the previous reform of the left.

The Italian Constitution prescribes that both chambers must accept every modification to the constitution twice within three months, and, if it passes with less than two thirds of the votes at the second scrutiny, a national referendum on the modification can be held (the reform will make it always possible to call such a referendum). Since the centre-left opposition opposed to the new constitutional reform, describing it as "dangerous", "separatist", and "antidemocratic",[23] the first procedural step, that is, the approval by the Chamber of Deputies, was done successfully in October 2004, but with less than ⅔ of the lower-house votes, making possible the confirmative referendum.[24] The second favourable polling, in Senate, was done in March 2005, whereas the third one occurred on October 20. During the third polling, former UDC leader Marco Follini announced he would abstain from the final vote, not support anymore the constitutional reform, followed by his party fellow Bruno Tabacci.[25][26]
On November 17, the Senate approved the constitutional reform in its final instance; Northern League leader Umberto Bossi attended the discussion and the voting, returning to the Parliament, even if just as spectator, after his illness. During the vote, Domenico Fisichella announced his opposition to the reform, and his immediate resignation from the party, going against the party line about the issue. Italian MPs quite easily change party and even coalition: in the legislature between 1996 and 2001 15% of MPs did so.[27]
The House of Freedoms' proposal of constitutional reform has been done in a unilateral way - no agreement with the opposition, whereas the current Italian Constitution was written after World War II by all the national political forces (except the fascists), ranging from Liberals, to Christian Democrats, to Socialists, to Communists and others. According to the House of Freedom, this policy was adopted in order to correct the constitutional reform approved by the former centre-left majority in 2001 (Constitutional law 3/2001) with the same modus - no agreement with the opposition. However, the new reform deeply modifies constitutional system of Italy, while the 2001 reform just partially modified a section of the Constitution.
The national referendum, requested by the centre-left opposition and a number of associations and regions - even by the centre-right ruled Lombardy, has been kept on 25–26 June 2006 and it has been concluded with the refusal of the constitutional reform by 61.32% of voting.
The 2005 regional elections
On 3 and 4 April 2005, regional elections were held in 13 Italian regions (the election in Basilicata was put off for two weeks because of irregularities). The final result actually reversed the political scenario of Italy, with the opposition centre-left coalition The Union winning in 11 regions, while the governing centre-right coalition House of Freedoms maintaining only two of the eight regions they were ruling before the election. These results have brought some right-wing members, including vice-premier Marco Follini, to ask for early national election.
The left-wing primary election

On 16 October 2005, a primary election was held to officially declare the one and only candidate for the centre-left coalition The Union.[28] Over four million voters have participated to the election.
Major candidate Romano Prodi, who has been one of the main supporters of the primary election, gained a clear win, obtaining about 75% of the votes and defeating Communist Refoundation Party leader Fausto Bertinotti, Green Alfonso Pecoraro Scanio, former magistrate Antonio Di Pietro, Catholic centrist Clemente Mastella, independent candidate Ivan Scalfarotto and far-left candidate Simona Panzino. The election was also opened to non-Italian official residents, even if they will not be eligible to vote for the general election.
Economic issues
Italy was the only European country in which there is an almost-zero rate of growth in economy, and one of the highest debts in the whole EU, which brought Berlusconi to ask successfully to have the Treaty of Maastricht parameters relaxed. This led to several critics of the Berlusconi's policy on economy, strictly linked to the work of the Italian Ministry of Economy of Giulio Tremonti, which was forced to resign in 2004 after heavy protests from parties of his own coalition, especially the National Alliance, and returned to his previous cabinet position one year later, following the resignation of Domenico Siniscalco; Tremonti's work for trying to fill the cash deficit was often based on amnesties for infringement of tax and building regulations. Prodi and the centre-left often criticised that facet of the Italian centre-right.
Job security
The regulation of temporary employment was first introduced as "pacchetto Treu" during the 1996–2001 centre-left government. It was then changed by Minister of Labour Roberto Maroni in 2003, introducing a high number of temporary labour forms and made temporary labour cheaper than permanent.
The centre-left heavily criticised the current law, claiming it has damaged the future of the younger people. More recently, Prodi defined the current labour law as "much worse than French CPE".
The centre-left has proposed to put temporary and permanent job costs on the same level, contain the number of temporary labour forms, and regulate internships.
The electoral system
Since 1994 and 2001 general elections, Italy had a mixed electoral system, with 75% of the seats assigned through a plurality voting system, and 25% through a proportional one.
The Italian Chamber of Deputies has 630 seats, the Senate 315 (exactly half).
Approval of a new voting system
A white paper for a proportional-only electoral system was presented to the Chamber of Deputies on 13 September 2005, only seven months before the 2006 general election. This reform, strongly backed by the centrist Union of Christian and Centre Democrats (UDC), proposed a 4% threshold before a party gained any seats, and a majority bonus of (at least) 340 seats for the winning coalition, the total votes for each coalition being the sum of the votes of those coalition parties which had won at least 4% of the national votes. The new proposal was approved by parliament.[29]
An electoral survey published on 15 September 2005 by the national left newspaper La Repubblica[30] claimed that, with the initial proposal of electoral reform become law, the House of Freedoms would win the next elections 340-290, even if they won only 45% of votes and the opposition coalition The Union won 50%, because The Union also includes several small parties with less than 4% of national votes. This could have been avoided if the small opposition parties ran on a common ticket. Aim of this bill of reform was to reduce the number of parties, and particularly the moderate centre-left would have taken advantage in respect to the smaller radical left parties.
The UDC, commenting on the proposal, asked for the abolition of the 4% cut-off clause, whereas the National Alliance did not show any favour to this attempt of reform, with its leader Gianfranco Fini claiming to want first to vote for the constitutional reform, and then for the new voting system, on condition that the 4% cut-off were not repealed.[31]
This proposal of law was strongly questioned by the opposition coalition, who defined it an "attempted coup". Opposition leader Romano Prodi said it was "totally unacceptable".[32] Several newspapers politically oriented to the left nicknamed the electoral system proposal by the House of Freedoms as "Truffarellum", after "truffa" (Italian for "fraud") and the "Mattarellum", (from Sergio Mattarella), the most common name for the previous Italian electoral law (there is a recent custom to nickname new electoral systems by a somewhat Latinised version of the name of the lawmaker; another one is the system used in regional elections, the so-called "Tatarellum" from Pinuccio Tatarella).
Notably, some smaller opposition parties, such as Communist Refoundation Party and Union of Democrats for Europe (UDEUR), supported a proportional electoral law; nevertheless, they declared they were against an electoral reform by this parliament, because the current law would be changed too close to the 2006 general election.
The Italian prime minister Silvio Berlusconi had previously been a strong supporter of the plurality-based electoral law; in 1995, talking about his coalition, he even defined the plurality principle as "our religion".[33]
A modified version of the first proposal, this time with a 2% threshold for entering Parliament and without vote of preference for candidates, but still without the support of the opposition, was presented to the Chamber of Deputies. The voting count started on 11 October 2005; the lower house of Italian parliament then approved the electoral reform on 14 October.[34] The new electoral was then eventually approved on December 16, 2005, and countersigned by President Ciampi on 23 December 2005.[35]
Roberto Calderoli, the main author of this electoral reform, defined this law "a rascality" (using the mildly vulgar term "porcata").
Ironically, the new electoral law allowed Mr Prodi to count on a large majority in the Chamber and to obtain majority also in the Senate, where The House of Freedoms actually had more votes (49.88% vs. 49.18% for The Union).
Results for the Chamber of Deputies
Overall results
 | ||||||||||||||
| Coalition | Party | Italy (19 regions) | Aosta Valley | Italians abroad | Total seats |
+/– | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | ||||||
| rowspan="10" bgcolor="Template:The Union (Italy)/meta/color"| | The Union | bgcolor="Template:The Olive Tree (Italy)/meta/color" | | The Olive Tree (DS–DL) | 11,930,983 | 31.27 | 220 | — | — | 0 | 421,414 | 43.39 | 6 | 226 | +7 |
| bgcolor="Template:Communist Refoundation Party/meta/color" | | Communist Refoundation Party (PRC) | 2,229,464 | 5.84 | 41 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 41 | +30 | ||
| Rose in the Fist (RNP) | 990,694 | 2.60 | 18 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 18 | +9 | |||
| bgcolor="Template:Italy of Values/meta/color" | | Italy of Values (IdV) | 877,052 | 2.30 | 16 | — | — | 0 | 27,432 | 2.82 | 1 | 17 | +17 | ||
| bgcolor="Template:Party of Italian Communists/meta/color" | | Party of Italian Communists (PdCI) | 884,127 | 2.32 | 16 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 16 | +6 | ||
| bgcolor="Template:Federation of the Greens/meta/color" | | Federation of the Greens (FdV) | 784,803 | 2.06 | 15 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 15 | +7 | ||
| bgcolor="Template:Union of Democrats for Europe/meta/color" | | Union of Democrats for Europe (UDEUR) | 534,088 | 1.40 | 10 | — | — | 0 | 9,721 | 1.00 | 0 | 10 | – | ||
| South Tyrolean People's Party (SVP) | 182,704 | 0.48 | 4 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 4 | +1 | |||
| bgcolor="Template:Autonomy Liberty Democracy/meta/color" | | Autonomy Liberty Democracy (ALD) | — | — | 0 | 34,168 | 43.44 | 1 | — | — | 0 | 1 | New | ||
| Total seats | 340 | 1 | 7 | 348 | – | |||||||||
| rowspan="7" bgcolor="Template:House of Freedoms/meta/color"| | House of Freedoms | bgcolor="Template:Forza Italia/meta/color" | | Forza Italia (FI) | 9,048,976 | 23.72 | 137 | 13,374 | 17.00 | 0 | 202,536 | 20.86 | 3 | 140 | −54 |
| bgcolor="Template:National Alliance (Italy)/meta/color" | | National Alliance (AN) | 4,707,126 | 12.34 | 71 | — | — | 0 | 72 | −27 | |||||
| For Italy in the World with Tremaglia | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 72,105 | 7.42 | 1 | |||||
| bgcolor="Template:Union of Christian and Centre Democrats/meta/color" | | Union of Christian and Centre Democrats (UDC) | 2,580,190 | 6.76 | 39 | — | — | 0 | 66,456 | 6.75 | 0 | 39 | −1 | ||
| bgcolor="Template:Lega Nord/meta/color" | | Northern League – MpA (LN–MpA) | 1,747,730 | 4.58 | 26 | 1,566 | 1.99 | 0 | 20,205 | 2.08 | 0 | 26 | −4 | ||
| Christian Democracy – Socialist Party (DC–PS) | 285,474 | 0.75 | 4 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 4 | – | |||
| Total seats | 277 | 0 | 4 | 281 | – | |||||||||
| Italian Associations in South America (AISA) | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 99,817 | 10.28 | 1 | 1 | New | |||
| Total | 630 | – | ||||||||||||
Italy (19 regions out of 20)
Results by region (19 regions out of 20)
| Region | The Union | House of Freedoms |
|---|---|---|
| style="background:Template:Italy. Common Good/meta/color;"| | style="background:Template:Centre-right coalition (Italy)/meta/color;"| | |
| Abruzzo | 52.82 | 47.05 |
| Apulia | 48.29 | 51.54 |
| Basilicata | 60.08 | 39.49 |
| Calabria | 56.71 | 42.84 |
| Naples | 52.40 | 47.28 |
| Campania | 49.28 | 50.36 |
| Emilia-Romagna | 59.92 | 40.08 |
| Friuli-Venezia Giulia | 44.84 | 54.51 |
| Rome | 52.29 | 47.56 |
| Lazio | 44.04 | 55.96 |
| Liguria | 53.63 | 46.37 |
| Milan | 46.34 | 53.66 |
| Lombardy 2 | 38.91 | 61.09 |
| Lombardy 3 | 46.22 | 53.78 |
| Marche | 55.22 | 44.78 |
| Molise | 50.95 | 49.05 |
| Turin | 55.43 | 44.57 |
| Piedmont | 44.12 | 55.88 |
| Sardinia | 52.49 | 45.35 |
| Sicily 1 | 43.51 | 56.05 |
| Sicily 2 | 40.50 | 59.50 |
| Trentino-Alto Adige | 62.00 | 35.32 |
| Tuscany | 61.75 | 38.25 |
| Umbria | 57.53 | 42.47 |
| Veneto 1 | 38.90 | 58.76 |
| Veneto 2 | 42.20 | 53.92 |
Source: Interior Ministry of Italy, Votes, Seats
Aosta Valley
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomy Liberty Democracy | 34,168 | 43.44 | 1 | |
| Aosta Valley (UV-SA-FA) | 24,119 | 30.66 | 0 | |
| bgcolor="Template:Forza Italia/meta/color" | | Forza Italia–National Alliance | 13,374 | 17.00 | 0 |
| bgcolor="Template:Union of Christian and Centre Democrats/meta/color" | | Union of Christian and Centre Democrats | 2,282 | 2.90 | 0 |
| Social Alternative | 1,587 | 2.02 | 0 | |
| bgcolor="Template:Lega Nord/meta/color" | | Northern League | 1,566 | 1.99 | 0 |
| bgcolor="Template:Pensioners' Party (Italy)/meta/color" | | Pensioners' Party | 1,135 | 1.44 | 0 |
| Tricolour Flame | 430 | 0.55 | 0 | |
| Total | 78,661 | 100.00 | 1 | |
Italians abroad
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bgcolor="Template:The Union (Italy)/meta/color"| | The Union | 421,414 | 43.39 | 6 |
| bgcolor="Template:Forza Italia/meta/color" | | Forza Italia | 202,536 | 20.86 | 3 |
| Italian Associations in South America | 99,817 | 10.28 | 1 | |
| For Italy in the World with Tremaglia | 72,105 | 7.42 | 1 | |
| bgcolor="Template:Union of Christian and Centre Democrats/meta/color"| | Union of Christian and Centre Democrats | 66,456 | 6.75 | 0 |
| bgcolor="Template:Italy of Values/meta/color"| | Italy of Values | 27,432 | 2.82 | 1 |
| bgcolor="Template:Lega Nord/meta/color"| | Northern League–Movement for Autonomy | 20,205 | 2.08 | 0 |
| South American Union Italian Emigrants | 14,205 | 1.46 | 0 | |
| Party of Italians in the World | 11,250 | 1.16 | 0 | |
| The Other Sicily | 10,867 | 1.12 | 0 | |
| Union of Democrats for Europe | 9,721 | 1.00 | 0 | |
| Social Alternative | 7,030 | 0.72 | 0 | |
| Love Italy | 3,732 | 0.38 | 0 | |
| Independent Alternative for Italians Abroad | 3,474 | 0.36 | 0 | |
| Tricolour Flame | 1,197 | 0.12 | 0 | |
| Total | 971,152 | 100.00 | 12 | |
Results for the Senate of the Republic
Overall results
 | |||||||||||||||||
| Coalition | Party | Italy (18 regions) | Aosta Valley | Trentino-Alto Adige | Italians abroad | Total seats |
+/– | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | ||||||
| rowspan="11" bgcolor="Template:The Union (Italy)/meta/color"| | The Union | bgcolor="Template:Democrats of the Left/meta/color" | | Democrats of the Left (DS) | 5,977,347 | 17.50 | 62 | — | — | 0 | 343,279 | 59.83 | 5 | 393,357 | 44.14 | 4 | 65 | +1 |
| bgcolor="Template:The Union (Italy)/meta/color" | | The Olive Tree | 59,498 | 0.17 | 1 | — | — | 0 | ||||||||||
| bgcolor="Template:The Daisy/meta/color" | | The Daisy (DL) | 3,664,903 | 10.73 | 39 | — | — | 0 | 43 | ±0 | ||||||||
| bgcolor="Template:Communist Refoundation Party/meta/color" | | Communist Refoundation Party (PRC) | 2,518,361 | 7.37 | 27 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 27 | +23 | |||||
| bgcolor="Template:Party of Italian Communists/meta/color" | | Together with the Union (FdV–PdCI–CU) | 1,423,003 | 4.17 | 11 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 11 | +1 | |||||
| bgcolor="Template:Italy of Values/meta/color" | | Italy of Values (IdV) | 986,191 | 8.89 | 4 | — | — | 0 | 26,486 | 2.97 | 0 | 4 | +3 | |||||
| bgcolor="Template:Union of Democrats for Europe/meta/color" | | Union of Democrats for Europe (UDEUR) | 477,226 | 1.40 | 3 | — | — | 0 | 13,507 | 1.52 | 0 | 3 | – | |||||
| bgcolor="Template:South Tyrolean People's Party/meta/color" | | South Tyrolean People's Party (SVP) | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 3 | ±0 | |||||
| Consumers' List – DC | 72,199 | 0.21 | 1 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 1 | New | ||||||
| bgcolor="Template:Autonomy Liberty Democracy/meta/color" | | Autonomy Liberty Democracy (ALD) | — | — | 0 | 32,554 | 44.17 | 1 | — | — | 0 | 1 | New | |||||
| Total seats | 148 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 158 | – | |||||||||||
| rowspan="5" bgcolor="Template:House of Freedoms/meta/color"| | House of Freedoms | bgcolor="Template:Forza Italia/meta/color" | | Forza Italia (FI) | 8,202,890 | 24.01 | 78 | 11,505 | 15.61 | 0 | 175,139 | 30.53 | 2 | 186,386 | 20.92 | 1 | 80 | −8 |
| bgcolor="Template:National Alliance (Italy)/meta/color" | | National Alliance (AN) | 4,235,208 | 12.40 | 41 | — | — | 0 | 41 | +4 | ||||||||
| bgcolor="Template:Union of Christian and Centre Democrats/meta/color" | | Union of Christian and Centre Democrats (UDC) | 2,309,442 | 6.76 | 21 | 2,264 | 3.07 | 0 | 57,278 | 6.43 | 0 | 21 | −8 | |||||
| bgcolor="Template:Lega Nord/meta/color" | | Northern League – MpA (LN–MpA) | 1,530,667 | 4.48 | 13 | 1,574 | 2.14 | 0 | 18,544 | 2.08 | 0 | 14 | −3 | |||||
| Total seats | 153 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 156 | – | |||||||||||
| Italian Associations in South America (AISA) | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | — | — | 0 | 85,745 | 9.62 | 1 | 1 | New | |||
| Total | 315 | – | |||||||||||||||
Italy (18 regions out of 20)
Source: Interior Ministry of Italy, Votes, Seats
Notes
Note: 7 Senators a vita (for life): Francesco Cossiga (Former Italian President), Oscar Luigi Scalfaro (Former Italian President), Giulio Andreotti (Former Italian Prime Minister), Rita Levi Montalcini (Nobel Prize winner for Medicine 1986), Emilio Colombo (Former Italian Prime Minister), Giorgio Napolitano (Former President of Italian Chamber of Deputies and Minister of the Interior), Sergio Pininfarina.
Aosta Valley
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomy Liberty Democracy | 32,554 | 44.17 | 1 | |
| Aosta Valley (UV-SA-FA) | 23,574 | 31.98 | 0 | |
| bgcolor="Template:Forza Italia/meta/color" | | Forza Italia–National Alliance | 11,505 | 15.61 | 0 |
| bgcolor="Template:Union of Christian and Centre Democrats/meta/color" | | Union of Christian and Centre Democrats | 2,264 | 3.07 | 0 |
| bgcolor="Template:Lega Nord/meta/color" | | Northern League | 1,574 | 2.14 | 0 |
| bgcolor="Template:Pensioners' Party (Italy)/meta/color" | | Pensioners' Party | 1,046 | 1.42 | 0 |
| Social Alternative | 775 | 1.05 | 0 | |
| Tricolour Flame | 416 | 0.56 | 0 | |
| Total | 73,708 | 100.00 | 1 | |
Trentino-Alto Adige/South Tyrol
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bgcolor="Template:Democratic Party (Italy)/meta/color"| | South Tyrolean People's Party–The Union | 198,156 | 34.54 | 3 |
| bgcolor="Template:House of Freedoms/meta/color" | | House of Freedoms | 175,139 | 30.53 | 2 |
| South Tyrolean People's Party | 117,495 | 20.48 | 2 | |
| bgcolor="Template:The Union (Italy)/meta/color"| | The Union | 27,628 | 4.81 | 0 |
| Die Freiheitlichen | 16,765 | 2.92 | 0 | |
| bgcolor="Template:Pensioners' Party (Italy)/meta/color"| | Pensioners' Party | 16,381 | 2.86 | 0 |
| Tricolour Flame | 14,819 | 2.58 | 0 | |
| Autonomist People's Union | 7,327 | 1.28 | 0 | |
| Total | 573,710 | 100.00 | 7 | |
Italians abroad
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bgcolor="Template:The Union (Italy)/meta/color"| | The Union | 393,357 | 44.14 | 4 |
| bgcolor="Template:Forza Italia/meta/color" | | Forza Italia | 186,386 | 20.92 | 1 |
| Italian Associations in South America | 85,745 | 9.62 | 1 | |
| For Italy in the World with Tremaglia | 65,055 | 7.30 | 0 | |
| bgcolor="Template:Union of Christian and Centre Democrats/meta/color"| | Union of Christian and Centre Democrats | 57,278 | 6.43 | 0 |
| bgcolor="Template:Italy of Values/meta/color"| | Italy of Values | 26,486 | 2.97 | 0 |
| bgcolor="Template:Lega Nord/meta/color"| | Northern League–Movement for Autonomy | 18,544 | 2.08 | 0 |
| Union of Democrats for Europe | 13,507 | 1.52 | 0 | |
| South American Union Italian Emigrants | 12,552 | 1.41 | 0 | |
| Party of Italians in the World | 10,888 | 1.22 | 0 | |
| The Other Sicily–For the South | 9,497 | 1.07 | 0 | |
| Tricolour Flame | 8,575 | 0.96 | 0 | |
| Independent Alternative for Italians Abroad | 3,191 | 0.36 | 0 | |
| Total | 891,061 | 100.00 | 6 | |
Results by region
| Region | Coalitions | Majority bonus winner |
Senators | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| style="width:80px; background-color:Template:The Union (Italy)/meta/color;"| | style="width:80px; background-color:Template:House of Freedoms/meta/color;"| | style="width:80px; background-color:Template:Other/meta/color;"| | |||

|

|
Others | |||
Lombardy |
20 | 27 | CdL | 47 | |
Campania |
17 | 13 | Union | 30 | |
Lazio |
12 | 15 | CdL | 27 | |
Sicily |
11 | 15 | CdL | 26 | |
Veneto |
10 | 14 | CdL | 24 | |
Piedmont |
9 | 13 | CdL | 22 | |
Emilia-Romagna |
12 | 9 | Union | 21 | |
Apulia |
9 | 12 | CdL | 21 | |
Tuscany |
11 | 7 | Union | 18 | |
Calabria |
6 | 4 | Union | 10 | |
Sardinia |
5 | 4 | Union | 9 | |
Liguria |
5 | 3 | Union | 8 | |
Marche |
5 | 3 | Union | 8 | |
Abruzzo |
4 | 3 | Union | 7 | |
Friuli-Venezia Giulia |
3 | 4 | CdL | 7 | |
Trentino-South Tyrol |
3 | 2 | 2 (SVP) | N/A | 7 |
Umbria |
4 | 3 | Union | 7 | |
Basilicata |
4 | 3 | Union | 7 | |
Molise |
1 | 1 | N/A | 2 | |
Aosta Valley |
1 (ALD) | N/A | 1 | ||
| Italians abroad | 4 | 1 | 1 (AISA) | N/A | 6 |
| Total | 148 | 153 | 4 | 305 | |
Vote count controversy
Although The Union led initial exit polls and was quickly expected to win the election, the gap with House of Freedoms narrowed as the votes were tabulated. The initial Interior Ministry results showed that Prodi had won the Chamber of Deputies by 25,204 votes, and Prodi declared victory on 11 April. Berlusconi, however, refused to concede, claiming discrepancies in the vote counting process, with 43,028 Chamber ballots and 39,822 Senate ballots to be re-checked by the Interior Ministry. Berlusconi also claimed problems with the vote from abroad, which was critical in giving L'Unione a majority in the Senate. Five ballot boxes were also found on the streets in Rome after the election.[36] On 14 April, however, the Interior Ministry announced that there had been a mistake in the report of the number of ballots to be rechecked. Only 2,131 Chamber ballots and 3,135 Senate ballots merited re-examination (reducing the total number of disputed ballots from the over 80,000 initially reported to just over 5,000). The result of this check added equally a few hundred votes to each coalition.
Analysts also believed that the vote from abroad was so overwhelmingly in favour of The Union that the election would be highly unlikely to be overturned in Berlusconi's favour.[37]
The last ruling of the supreme court ("Corte di Cassazione") on 19 April 2006 stated that Romano Prodi won the election by 24,755 votes.
On 23 November 2006, the Rome Attorney's office announced to have started an inquiry following the release of "Uccidete la democrazia" (Kill the democracy), a documentary movie about a supposed attempt by the centre-right government to manipulate the electoral results by switching a large number of blank ballot papers, which notably fell down from 4.2% to 1.1% of all valid papers (over one million less), to votes for the Forza Italia party.[38]
See also
- Elections in Italy
- History of Italy as a Republic
- Politics of Italy
- European Parliament Election, 2004 (Italy)
- Elections in 2006
- 2006 Italian Chamber of Deputies election, North and Central American division
- 2006 Italian Senate election, North and Central American division
References
- ^ http://english.peopledaily.com.cn/200604/11/eng20060411_257391.html
- ^ Centre-left claims Italy victory, BBC News
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2006-04-12. Retrieved 2006-04-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Fraser, Christian (2006-04-03). "Europe | Insults fly in Italy poll debate". BBC News. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ^ [1] Archived March 11, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ http://www.incontriamoci.romanoprodi.it/materiali/sintesi_programma.pdf
- ^ [2] Archived March 5, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Template:It icon Ciampi: "Meglio votare in anticipo" Casini: "Una scelta di buonsenso", La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Berlusconi al Quirinale da Ciampi "Sulle elezioni è stato frainteso", La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Prodi: "Si voti il 9 aprile per Politiche e amministrative", Centro Movimenti
- ^ Template:It icon Berlusconi a Prodi: «No all'election day», Corriere della Sera
- ^ Template:It icon Berlusconi parla ai giovani di FI "La par condicio legge bavaglio", La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Berlusconi accelera sulla par condicio Ma Casini dice: "Non sono d'accordo", La Repubblica
- ^ "Ign - Il portale d'informazione del Gruppo". Adnkronos. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ^ Template:It icon Udc, Cesa nuovo segretario "No a modifiche della par condicio", La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Sms, è polemica sul silenzio violato, chiesto l'intervento del garante, La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Par condicio, multa a Rete 4 e Italia Uno, Il Corriere della Sera
- ^ Berlusconi: West Superior to Islam, Radio Netherlands
- ^ Fit to run Italy?, The Economist
- ^ Italy and the EU, The Economist
- ^ A capo's annual report, The Economist/Ivo Forni
- ^ Template:It icon Come cambia la Costituzione, La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Rutelli: "Riforme, pagina nera", Fassino: "Pronti al referendum", La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Riforme, la Camera approva esultano i leader del Polo, La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It iconDal Senato ok alla Riforma tra le proteste dell'Unione, La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon La Camera approva la Devolution Berlusconi: "Ottima riforma", La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Devolution, dal Senato sì definitivo L'Unione: "Un danno per il Paese", La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Unione, accordo per le primarie Prodi: "Grande prova di democrazia", La Repubblica
- ^ Pole Agrees to Go Back to Proportional Vote, Corriere della Sera
- ^ Template:It icon Dalla vittoria alla sconfitta la riforma "scippa" l'Unione, La Repubblica
- ^ [3][permanent dead link], Reuters
- ^ Template:It icon Legge elettorale, accordo nella Cdl Unione insorge: "Blocchiamo le Camere", La Repubblica
- ^ Template:It icon Nessun blitz prima delle elezioni Archived 2011-07-23 at the Wayback Machine, DS Milano
- ^ Italy deputies back voting reform, BBC News
- ^ Template:It icon Ciampi ha firmato la legge elettorale, Corriere della Sera
- ^ Italy in limbo over vote counting, BBC News
- ^ Italian poll result set to stand, BBC News
- ^ "Brogli alle elezioni politiche, indaga la procura di Roma". Repubblica.it. 2006-11-23. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
External links
- Template:It icon Political & Electoral Surveys
- Template:It icon [Il Termometro Politico Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) (The Political Thermometer)]
- Template:En icon Q&A: Italian election
- Template:It icon Election results from the Interior Ministry
- Template:It icon Election results from the Interior Ministry (Archives of all Elections)


