Isogonal conjugate: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
As isogonal conjugation is a function, it makes sense to speak of the isogonal conjugate of sets of points, such as lines and circles. For example, the isogonal conjugate of a line is a [[circumconic and inconic|circumconic]]; specifically, an ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola according as the line intersects the [[circumcircle]] in 0, 1, or 2 points. The isogonal conjugate of the circumcircle is the line at infinity. Several well-known cubics (e.g., Thompson cubic, Darboux cubic, [[Neuberg cubic]]) are self-isogonal-conjugate, in the sense that if ''X'' is on the cubic, then ''X''<sup> −1</sup> is also on the cubic. |
As isogonal conjugation is a function, it makes sense to speak of the isogonal conjugate of sets of points, such as lines and circles. For example, the isogonal conjugate of a line is a [[circumconic and inconic|circumconic]]; specifically, an ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola according as the line intersects the [[circumcircle]] in 0, 1, or 2 points. The isogonal conjugate of the circumcircle is the line at infinity. Several well-known cubics (e.g., Thompson cubic, Darboux cubic, [[Neuberg cubic]]) are self-isogonal-conjugate, in the sense that if ''X'' is on the cubic, then ''X''<sup> −1</sup> is also on the cubic. |
||
==Another construction for the isogonal conjugate of a point== |
|||
For a given point P in the plane of triangle ABC, let the reflections of P in the sidelines BC, CA, AB be P<sub>a</sub>, P<sub>b</sub>, P<sub>b</sub>. Then the center of the circle P<sub>a</sub>P<sub>b</sub>P<sub>c</sub> is the isogonal conjugate pf P.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Steve Phelps |title=Constructing Isogonal Conjugates |url=https://www.geogebra.org/m/sRVERPyd |website=GeoGebra |publisher=GeoGebra Team |access-date=17 January 2022}}</ref> |
|||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 07:18, 17 January 2022

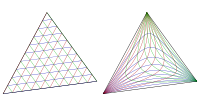
In geometry, the isogonal conjugate of a point P with respect to a triangle ABC is constructed by reflecting the lines PA, PB, and PC about the angle bisectors of A, B, and C respectively. These three reflected lines concur at the isogonal conjugate of P. (This definition applies only to points not on a sideline of triangle ABC.) This is a direct result of the trigonometric form of Ceva's theorem.
The isogonal conjugate of a point P is sometimes denoted by P*. The isogonal conjugate of P* is P.
The isogonal conjugate of the incentre I is itself. The isogonal conjugate of the orthocentre H is the circumcentre O. The isogonal conjugate of the centroid G is (by definition) the symmedian point K. The isogonal conjugates of the Fermat points are the isodynamic points and vice versa. The Brocard points are isogonal conjugates of each other.
In trilinear coordinates, if X = x : y : z is a point not on a sideline of triangle ABC, then its isogonal conjugate is 1/x : 1/y : 1/z. For this reason, the isogonal conjugate of X is sometimes denoted by X −1. The set S of triangle centers under trilinear product, defined by
- (p : q : r) * (u : v : w) = pu : qv : rw,
is a commutative group, and the inverse of each X in S is X −1.
As isogonal conjugation is a function, it makes sense to speak of the isogonal conjugate of sets of points, such as lines and circles. For example, the isogonal conjugate of a line is a circumconic; specifically, an ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola according as the line intersects the circumcircle in 0, 1, or 2 points. The isogonal conjugate of the circumcircle is the line at infinity. Several well-known cubics (e.g., Thompson cubic, Darboux cubic, Neuberg cubic) are self-isogonal-conjugate, in the sense that if X is on the cubic, then X −1 is also on the cubic.
Another construction for the isogonal conjugate of a point
For a given point P in the plane of triangle ABC, let the reflections of P in the sidelines BC, CA, AB be Pa, Pb, Pb. Then the center of the circle PaPbPc is the isogonal conjugate pf P.[1]
See also
External links
- Interactive Java Applet illustrating isogonal conjugate and its properties
- MathWorld
- Pedal Triangle and Isogonal Conjugacy
- ^ Steve Phelps. "Constructing Isogonal Conjugates". GeoGebra. GeoGebra Team. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
