Portal:Fungi
The Fungi Portal
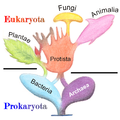
A fungus is any member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. The Fungi are classified as a kingdom that is separate from plants and animals. The discipline of biology devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology or fungal biology, which is historically regarded as a branch of botany, even though genetic studies have shown that fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants. Fungi reproduce via spores and grow as hyphae, mycelia, and futher specialized structures. Fungal spores are often produced on specialized structures or in fruiting bodies, such as the head of a mushroom. Abundant worldwide, most fungi are mostly invisible to the naked eye because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic lifestyles in soil, on dead matter, and as symbionts of plants, animals, or other fungi. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling and exchange. They have long been used as a direct source of food, such as mushrooms and truffles, as a leavening agent for bread, and in fermentation of various food products, such as wine, beer, and soy sauce.
Since the 1940s, fungi have been used for the production of antibiotics, and, more recently, various enzymes produced by fungi are used industrially and in detergents. Fungi are also used as biological agents to control weeds and pests. Many species produce bioactive compounds called mycotoxins, such as alkaloids and polyketides, that are toxic to animals including humans. The fruiting structures of a few species are consumed recreationally or in traditional ceremonies as a source of psychotropic compounds. Fungi can break down manufactured materials and buildings, and become significant pathogens of humans and other animals. Losses of crops due to fungal diseases or food spoilage can have a large impact on human food supplies and local economies. Despite their importance on human affairs, little is known of the true biodiversity of Kingdom Fungi, which has been estimated at around 1.5 million species, with about 5% of these having been formally classified.
| More about fungi... |
Selected article
Amanita ocreata resemble several edible species commonly consumed by humans, increasing the risk of accidental poisoning. Mature fruiting bodies can be confused with the edible A. velosa, A. lanei or Volvariella speciosa, while immature specimens may be difficult to distinguish from edible Agaricus mushrooms or puffballs. Similar in toxicity to the death cap (A. phalloides) and destroying angels of Europe (A. virosa) and eastern North America (A. bisporigera), it is a potentially deadly fungus responsible for a number of poisonings in California. Its principal toxic constituent, α-amanitin, damages the liver and kidneys, often fatally, and has no known antidote. The initial symptoms are gastrointestinal and include colicky abdominal pain, diarrhea and vomiting. These subside temporarily after 2–3 days, though ongoing damage to internal organs during this time is common; symptoms of jaundice, diarrhea, delirium, seizures, and coma may follow with death from liver failure 6–16 days post ingestion.
Selected species
Mycena galopus is found in North America and Europe. The saprobic fungus is an important leaf litter decomposer, and able to utilize all the major constituents of plant litter. It is especially adept at attacking cellulose and lignin, the latter of which is the second most abundant renewable organic compound in the biosphere. The mushroom latex contains chemicals called benzoxepines, which are thought to play a role in a wound-activated chemical defense mechanism against yeasts and parasitic fungi.
Things to do
If you want to help Wikipedia to improve its coverage of fungi, here are some things you can do...
- Assess some fungi articles.
- Join Wikipedia:WikiProject Fungi or ask on the talk page.
- Join the lichen task force.
- Review, improve, expand or clean some of the newly created fungi-related articles.
- Expand some high priority fungus stubs.
- Expand or sort other fungi-related stubs.
- Add images to articles in the list of unillustrated fungi articles, or add more articles to the list.
- Write fungi-related articles from scratch. For ideas of needed articles, see the redlinks on-
- Review the fungi articles flagged as needing attention.
WikiProjects
WikiProjects related to fungi:
Selected picture

Did you know?
- ... that the German lichenologist and taxonomist Ferdinand Christian Gustav Arnold had a personal herbarium of 150,000 specimens?
- ... that Verpa bohemica is a saprobic species of fungi distinguished from other species by its enormous spores?
- ... that the cap of the thimble fungus, Verpa conica, resembles a thimble?
- ... that the hallucinogenic mushroom Psilocybe naematoliformis was first discovered in a tropical rain forest in the Uxpanapa Region of Veracruz, in southeastern Mexico?
- ... that phylogenetic relationships between the mushroom Bovista nigrescens and species of Lycoperdaceae were established based on ITS and LSU sequence data from north European taxa?
General images -
Related portals
Topics
- Main topics lists: Outline of fungi and Outline of lichens
- Fungi: Bracket fungus, carnivorous fungus, coprophilous fungi, entomopathogenic fungus, evolution of fungi, lichen, mushroom, mycology (lichenology, mycotoxicology, paleomycology), mycorrhiza, pathogenic fungi, puffball, wood-decay fungus
- Fungal orders: Chytridiomycota, Blastocladiomycota, Neocallimastigomycota, Zygomycota, Glomeromycota. Dikarya: Ascomycota, Basidiomycota
- Fungi lists: Species: Agaricus species, Amanita species, Boletus species, Cortinarius species, Cyathus species, Hygrocybe species, Hygrophorus species, Inocybe species, Lactarius species, Mycosphaerella species, Panaeolus species, Psilocybe species, Russula species, Scleroderma species Other lists: Mycology journals, psilocybin mushrooms
- Uses: Edible mushroom, mushroom poisoning, psilocybin mushrooms, mushroom hunting, fungiculture, fermentation, baker's yeast, mycoremediation, lichenometry, mushroom dye



















![Image 15Pennate diatom from an Arctic meltpond, infected with two chytrid-like [zoo-]sporangium fungal pathogens (in false-colour red). Scale bar = 10 µm. (from Marine fungi)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b5/Pennate_diatom_infected_with_two_chytrid-like_fungal_pathogens.png/120px-Pennate_diatom_infected_with_two_chytrid-like_fungal_pathogens.png)