October 1967 lunar eclipse
| Total Lunar Eclipse October 18, 1967 | |
|---|---|
| (No photo) | |
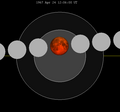
 The moon passes west to east (right to left) across the Earth's umbral shadow, shown in hourly intervals. | |
| Series | 126 (43 of 72) |
| Gamma | -0.3653 |
| Magnitude | 1.1426 |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Totality | 59:45 |
| Partial | 3:38:52 |
| Penumbral | 6:07:07 |
| Contacts UTC | |
| P1 | 7:12:15 |
| U1 | 8:26:21 |
| U2 | 9:45:54 |
| Greatest | 10:15:48 |
| U3 | 10:45:42 |
| U4 | 12:05:15 |
| P4 | 13:19:21 |
A total lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday, October 18, 1967, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1967, the first being on April 24, 1967.[1]
Visibility[edit]
It was completely visible over Asia, Australia, Pacific Ocean, North America, South America, and Arctic, seen rising over Asia and Australia and setting over North America and South America.
Related lunar eclipses[edit]
Lunar year series[edit]
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 1966–1969 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
| 111 | 1966 May 4
|
Penumbral
|
1.05536 | 116 | 1966 Oct 29
|
Penumbral
|
−1.05999 | |
| 121 | 1967 Apr 24
|
Total
|
0.29722 | 126 | 1967 Oct 18
|
Total
|
−0.36529 | |
| 131 | 1968 Apr 13
|
Total
|
−0.41732 | 136 | 1968 Oct 6
|
Total
|
0.36054 | |
| 141 | 1969 Apr 2
|
Penumbral
|
−1.17648 | 146 | 1969 Sep 25
|
Penumbral
|
1.06558 | |
| Last set | 1965 Jun 14 | Last set | 1965 Dec 8 | |||||
| Next set | 1970 Feb 21 | Next set | 1969 Aug 27 | |||||
Saros series[edit]
It is part of saros series 126.
Lunar saros series 126, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 70 lunar eclipse events including 14 total lunar eclipses. Solar Saros 133 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.
First penumbral lunar eclipse: 18 July 1228
First partial lunar eclipse: 24 March 1625
First total lunar eclipse: 19 June 1769
First central lunar eclipse: 11 July 1805
Greatest eclipse of the lunar saros 126: 13 August 1859, lasting 106 minutes.
Last central lunar eclipse: 26 September 1931
Last total lunar eclipse: 9 November 2003
Last partial lunar eclipse: 5 June 2346
Last penumbral lunar eclipse: 19 August 2472
1901-2100
Metonic series[edit]
This eclipse is the third of four Metonic cycle lunar eclipses on the same date, April 23–24, each separated by 19 years:
The Metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the Earth's shadow will in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date | Type | Saros | Date | Type | |
| 111 | 1948 Apr 23 | Partial | 116 | 1948 Oct 18 | Penumbral | |

|

| |||||
| 121 | 1967 Apr 24 | Total | 126 | 1967 Oct 18 | Total | |
|

| |||||
| 131 | 1986 Apr 24 | Total | 136 | 1986 Oct 17 | Total | |

|

| |||||
| 141 | 2005 Apr 24 | Penumbral | 146 | 2005 Oct 17 | Partial | |

|

| |||||
Tritos series[edit]
The tritos series repeats 31 days short of 11 years at alternating nodes. Sequential events have incremental Saros cycle indices.
This series produces 23 total eclipses between June 22, 1880 and August 9, 2120.
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type chart |
Saros | Date Viewing |
Type chart | |
| 120 | 1902 Apr 22
|
Total
|
121 | 1913 Mar 22
|
Total
| |
| 122 | 1924 Feb 20
|
Total
|
123 | 1935 Jan 19
|
Total
| |
| 124 | 1945 Dec 19
|
Total
|
125 | 1956 Nov 18
|
Total
| |
| 126 | 1967 Oct 18
|
Total
|
127 | 1978 Sep 16
|
Total
| |
| 128 | 1989 Aug 17
|
Total
|
129 | 2000 Jul 16
|
Total
| |
| 130 | 2011 Jun 15
|
Total
|
131 | 2022 May 16
|
Total
| |
| 132 | 2033 Apr 14
|
Total
|
133 | 2044 Mar 13
|
Total
| |
| 134 | 2055 Feb 11
|
Total
|
135 | 2066 Jan 11
|
Total
| |
| 136 | 2076 Dec 10
|
Total
|
137 | 2087 Nov 10
|
Total
| |
| 138 | 2098 Oct 10
|
Total
| ||||
Half-Saros cycle[edit]
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 133.
| October 12, 1958 | October 23, 1976 |
|---|---|

|

|
Tzolkinex[edit]
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of September 5, 1960
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of November 29, 1974
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ Hermit Eclipse: Saros cycle 126
- ^ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links[edit]
- 1967 Oct 18 chart Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC




