Metanephrine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
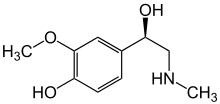
| IUPAC name
4-(1-hydroxy-2-methylamino-ethyl)-2-methoxy-phenol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Metanephrine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H15NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 197.231 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Metanephrine, also known as metadrenaline, is a metabolite of epinephrine (also known as adrenaline) created by action of catechol-O-methyl transferase on epinephrine. An article in the Journal of the American Medical Association, 2002, indicated that the measurement of plasma free levels of the metanephrines group of molecules (including metanephrine and normetanephrine) is the best tool in the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma, an adrenal medullary neoplasm.[1]
References[edit]
- ^ Lenders J, Pacak K, Walther M, Linehan W, Mannelli M, Friberg P, Keiser H, Goldstein D, Eisenhofer G (2002). "Biochemical diagnosis of pheochromocytoma: which test is best?". JAMA. 287 (11): 1427–34. doi:10.1001/jama.287.11.1427. PMID 11903030. Free full text with registration

