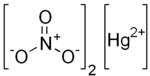
Mercury(II) nitrate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Mercury dinitrate
Mercury(II) nitrate | |
| Other names
Mercuric nitrate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.126 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1625 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Hg(NO3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 324.60 g/mol (anhydrous) |
| Appearance | colorless crystals or white powder |
| Odor | sharp |
| Density | 4.3 g/cm3 (monohydrate) |
| Melting point | 79 °C (174 °F; 352 K) (monohydrate) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in nitric acid, acetone, ammonia insoluble in ethanol |
| −74.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H272, H300, H310, H330, H373, H410 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Nonflammable |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0980 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Mercury(II) sulfate Mercury(II) chloride |
Other cations
|
Zinc nitrate Cadmium nitrate |
Related compounds
|
Mercury(I) nitrate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Mercury(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the formula Hg(NO3)2.xH2O. These colorless or white soluble crystalline salts are occasionally used as a reagent. It is made by treating mercury with hot concentrated nitric acid. Neither anhydrous nor monohydrate has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography.[1] The anhydrous material is more widely used.
Uses[edit]
Mercuric nitrate has been used in mercuration of ketones.[2] Mercuric nitrate was formerly used in carroting felt for hats.
Health information[edit]
Mercury compounds are highly toxic. The use of this compound by hatters and the subsequent mercury poisoning of said hatters is a common theory of where the phrase "mad as a hatter" came from.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Nolte, M.; Pantenburg, I.; Meyer, G. (9 December 2005). "The Monohydrate of Basic Mercuric Nitrate, [Hg(OH)](NO3)(H2O)". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie (in German). 632 (1). Wiley Publishing: 111–113. doi:10.1002/zaac.200500344. ISSN 0044-2313. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- ^ Morton, Avery A.; Penner, Hellmut P. (1951). "Mercuration of Ketones and Some Other Compounds with Mercuric Nitrate". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 73 (7): 3300–3304. doi:10.1021/ja01151a091.
External links[edit]
- ATSDR - Toxic Substances Portal - Mercury (11/14/2013)
- ATSDR - Public Health Statement: Mercury (11/14/2013)
- ATSDR - ALERT! Patterns of Metallic Mercury Exposure, 6/26/97 (link not traceable 11/14/2013)
- ATSDR - Medical Management Guidelines for Mercury (11/14/2013)
- ATSDR - Toxicological Profile: Mercury (11/14/2013)
- Safety data (MSDS)[permanent dead link] (link not traceable 11/14/2013)
- Mercuric Nitrate (ICSC)
- Mercury
- Mercury Information Packages
- How to Make Good Mercury Electrical Connections, Popular Science monthly, February 1919, Unnumbered page, Scanned by Google Books: https://books.google.com/books?id=7igDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PT14

