Iodobenzamide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
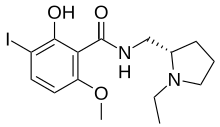
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-{[(2S)-1-Ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methyl}-2-hydroxy-3-iodo-6-methoxybenzamide | |
| Other names
IBZM; Iolopride
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H21IN2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 404.248 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| V09AB02 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Iodobenzamide (IBZM or iolopride) is a pharmaceutical drug used for diagnostic purposes. It is a dopamine antagonist and it can be used by nuclear medicine physicians as a radioactive tracer for SPECT where the radioactive isotope is iodine-123 or iodine-125.[1][2] The main purpose of a brain study with IBZM is the differentiation of Parkinson's disease from other neurodegenerative diseases such as Lewy Body dementia and multiple system atrophy.
References[edit]
- ^ Kung, H. F.; Guo, Y. Z.; Billings, J.; Xu, X.; Mach, R. H.; Blau, M.; Ackerhalt, R. E. (1988). "Preparation and biodistribution of [125I]IBZM: a potential CNS D-2 dopamine receptor imaging agent". Nuclear Medicine and Biology. 15 (2): 195–201. doi:10.1016/0883-2897(88)90088-8. PMID 2966782.
- ^ Kung, Hank, F.; Alavi; Chang; Kung; Keyes; Velchik; Billings; Pan; Noto (1990). "In vivo SPECT imaging of CNS D-2 dopamine receptors: initial studies with iodine-123-IBZM in humans". Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 31 (5): 573–579. PMID 2140408.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
